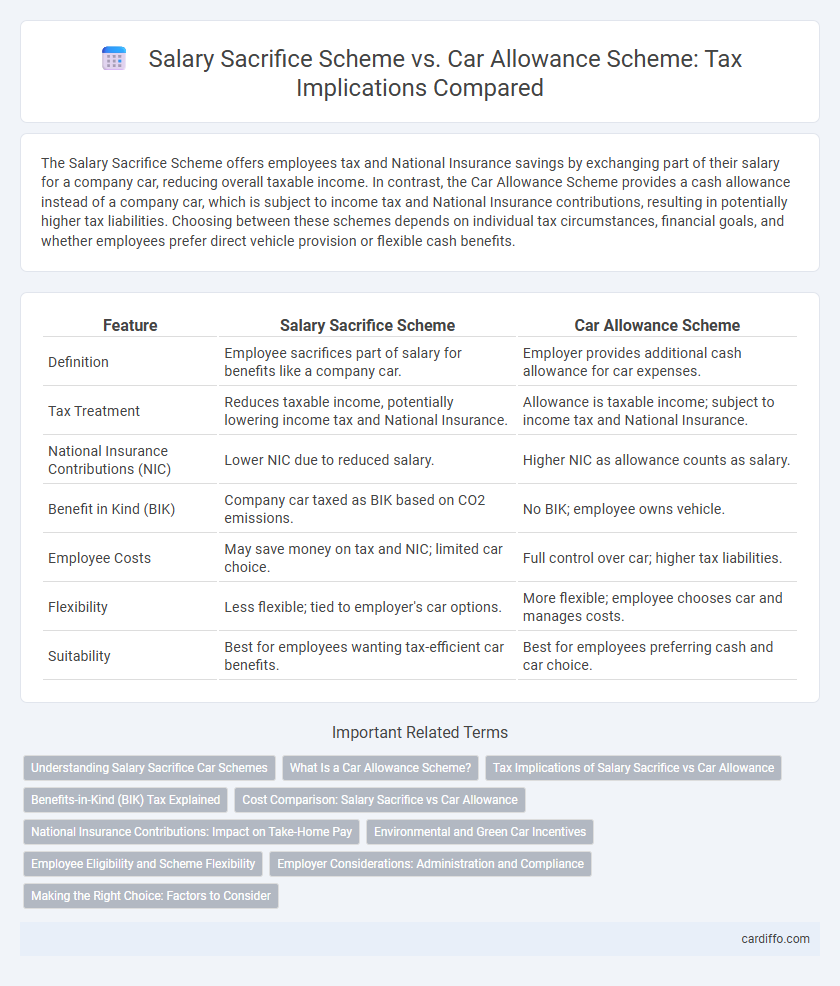
The Salary Sacrifice Scheme offers employees tax and National Insurance savings by exchanging part of their salary for a company car, reducing overall taxable income. In contrast, the Car Allowance Scheme provides a cash allowance instead of a company car, which is subject to income tax and National Insurance contributions, resulting in potentially higher tax liabilities. Choosing between these schemes depends on individual tax circumstances, financial goals, and whether employees prefer direct vehicle provision or flexible cash benefits.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Salary Sacrifice Scheme | Car Allowance Scheme |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee sacrifices part of salary for benefits like a company car. | Employer provides additional cash allowance for car expenses. |
| Tax Treatment | Reduces taxable income, potentially lowering income tax and National Insurance. | Allowance is taxable income; subject to income tax and National Insurance. |
| National Insurance Contributions (NIC) | Lower NIC due to reduced salary. | Higher NIC as allowance counts as salary. |
| Benefit in Kind (BIK) | Company car taxed as BIK based on CO2 emissions. | No BIK; employee owns vehicle. |
| Employee Costs | May save money on tax and NIC; limited car choice. | Full control over car; higher tax liabilities. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; tied to employer's car options. | More flexible; employee chooses car and manages costs. |
| Suitability | Best for employees wanting tax-efficient car benefits. | Best for employees preferring cash and car choice. |
Understanding Salary Sacrifice Car Schemes
Salary Sacrifice Car Schemes offer employees the opportunity to reduce their taxable income by exchanging part of their salary for a company-provided vehicle, often leading to significant tax savings. These schemes typically include lease payments, maintenance, and insurance costs bundled into the deduction, making budgeting predictable for employees while benefiting employers through National Insurance savings. Understanding the specific tax implications and potential impact on pensions and employee benefits is crucial when comparing Salary Sacrifice with Car Allowance Schemes.
What Is a Car Allowance Scheme?
A Car Allowance Scheme provides employees with a fixed cash payment added to their salary to cover vehicle expenses, offering flexibility without requiring company-owned cars. Unlike Salary Sacrifice Schemes, car allowances are taxable as regular income and do not reduce National Insurance contributions for employers or employees. This scheme simplifies administration for employers but may result in higher tax liabilities compared to salary sacrifice options designed to optimize tax efficiency.
Tax Implications of Salary Sacrifice vs Car Allowance
Salary Sacrifice Schemes reduce taxable income by allowing employees to exchange part of their salary for non-cash benefits, resulting in lower income tax and National Insurance contributions. Car Allowance Schemes increase taxable income since the allowance is added to gross salary, attracting tax and National Insurance at the employee's marginal rate. Employers and employees must carefully assess tax savings potential, considering personal tax brackets and benefit-in-kind rules.
Benefits-in-Kind (BIK) Tax Explained
Salary Sacrifice Schemes reduce taxable income by allowing employees to exchange part of their salary for non-cash benefits, lowering their Income Tax and National Insurance contributions on Benefits-in-Kind (BIK). Car Allowance Schemes provide a cash allowance instead of a company car, but employees bear the full tax burden on the allowance and BIK if they choose to buy a car personally. Understanding BIK tax rates is crucial as Salary Sacrifice often offers more significant tax savings through reduced BIK liabilities compared to Car Allowance alternatives.
Cost Comparison: Salary Sacrifice vs Car Allowance
Salary Sacrifice Schemes typically reduce taxable income by allowing employees to exchange part of their salary for non-cash benefits, resulting in lower income tax and National Insurance contributions. Car Allowance Schemes add a fixed amount to the employee's gross salary, increasing taxable income and associated tax liabilities, which can lead to higher overall costs. Evaluating net take-home pay under both schemes reveals Salary Sacrifice often offers greater cost savings due to reduced tax burdens and potential employer National Insurance savings.
National Insurance Contributions: Impact on Take-Home Pay
Salary Sacrifice Schemes reduce National Insurance Contributions (NICs) by lowering the employee's taxable salary, resulting in higher take-home pay compared to traditional Car Allowance Schemes where NICs apply to the full salary including allowances. Employees in Salary Sacrifice arrangements benefit from decreased employer and employee NICs due to contributions made before tax calculation. Car Allowance recipients face higher overall NICs, reducing net income since the allowance is subject to standard tax and NIC rates.
Environmental and Green Car Incentives
Salary Sacrifice Schemes often provide greater environmental benefits by enabling employees to lease low-emission or electric vehicles at reduced tax rates, leveraging government green car incentives. Car Allowance Schemes typically offer less tax efficiency and fewer opportunities to access specific electric vehicle subsidies or reduced company car tax rates. Employers and employees can maximize tax savings and contribute to sustainability goals more effectively through Salary Sacrifice Schemes aligned with environmental incentives.
Employee Eligibility and Scheme Flexibility
Employees eligible for the Salary Sacrifice Scheme typically include full-time and part-time staff who can reduce their gross salary in exchange for non-cash benefits, often subject to employer approval and specific plan rules. The Car Allowance Scheme generally applies to employees receiving a fixed sum added to their salary, offering greater flexibility in vehicle choice and ownership but with higher taxable income implications. Salary Sacrifice Schemes provide less flexibility once agreed but can deliver significant tax and National Insurance savings, while Car Allowance Schemes allow employees to manage their own vehicle expenses, impacting overall tax liabilities differently.
Employer Considerations: Administration and Compliance
Employers managing Salary Sacrifice Schemes must ensure strict compliance with tax regulations and maintain accurate payroll adjustments to reflect the reduced salary while providing fringe benefits. Car Allowance Schemes require clear documentation of additional taxable income and adherence to reporting standards, increasing administrative workloads. Choosing between these schemes depends on the employer's capacity to handle complexity in tax reporting and compliance obligations efficiently.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a Salary Sacrifice Scheme and a Car Allowance Scheme hinges on individual tax implications, overall compensation structure, and personal financial goals. Salary Sacrifice Schemes can offer tax and National Insurance savings by reducing taxable income, while Car Allowance Schemes provide more flexibility but may increase taxable earnings. Evaluating lifestyle, vehicle preferences, and long-term tax efficiency ensures the optimal decision aligned with both employer benefits and personal circumstances.
Salary Sacrifice Scheme vs Car Allowance Scheme Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com