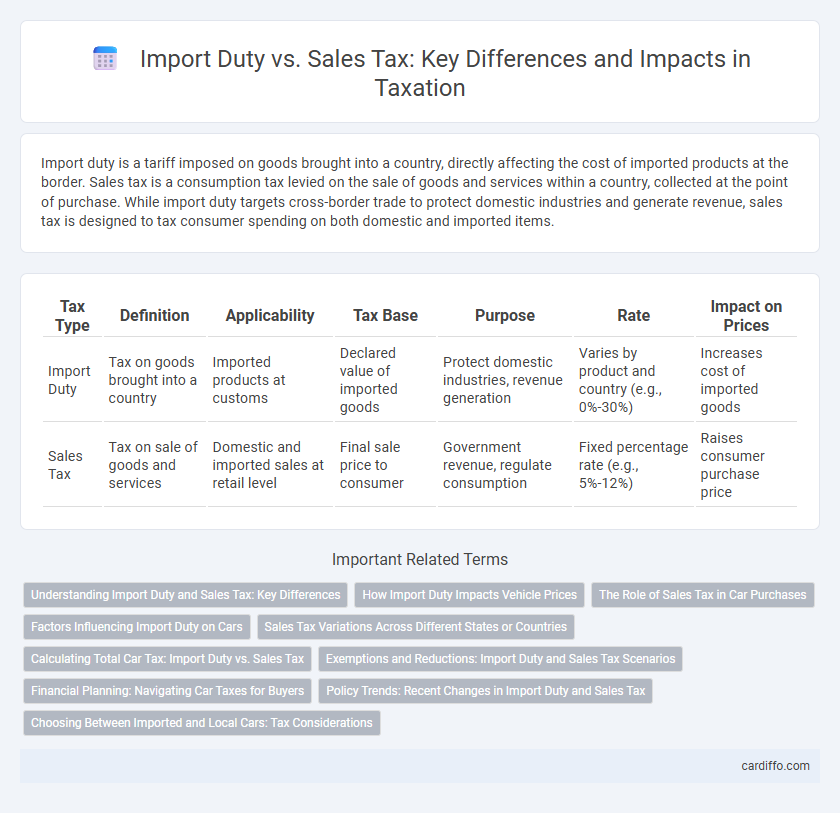
Import duty is a tariff imposed on goods brought into a country, directly affecting the cost of imported products at the border. Sales tax is a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and services within a country, collected at the point of purchase. While import duty targets cross-border trade to protect domestic industries and generate revenue, sales tax is designed to tax consumer spending on both domestic and imported items.
Table of Comparison
| Tax Type | Definition | Applicability | Tax Base | Purpose | Rate | Impact on Prices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Import Duty | Tax on goods brought into a country | Imported products at customs | Declared value of imported goods | Protect domestic industries, revenue generation | Varies by product and country (e.g., 0%-30%) | Increases cost of imported goods |
| Sales Tax | Tax on sale of goods and services | Domestic and imported sales at retail level | Final sale price to consumer | Government revenue, regulate consumption | Fixed percentage rate (e.g., 5%-12%) | Raises consumer purchase price |
Understanding Import Duty and Sales Tax: Key Differences
Import duty is a government-imposed tax on goods brought into a country, calculated based on the product's value, origin, and type, affecting international trade costs. Sales tax applies to the sale of goods and services within a country, collected at the point of purchase, influencing consumer prices domestically. Understanding the distinction helps businesses and consumers navigate compliance and financial planning across import transactions and local sales.
How Import Duty Impacts Vehicle Prices
Import duty significantly raises the cost of vehicles by adding a percentage-based tax on the value of imported cars, often making foreign models more expensive than domestically produced ones. This tax can vary widely depending on the country and type of vehicle, directly influencing consumer prices and overall market demand. Unlike sales tax, which is applied at the point of sale, import duty is imposed during the importation process, increasing the base price before retail markup.
The Role of Sales Tax in Car Purchases
Sales tax on car purchases directly affects the total cost to consumers, calculated as a percentage of the vehicle's sale price and remitted to state or local governments. Unlike import duty, which targets vehicles entering a country and aims to protect domestic industries, sales tax applies broadly to all vehicle sales regardless of origin, influencing consumer behavior and state revenue. Understanding the distinction between import duty and sales tax is crucial for buyers to accurately assess the total taxation impact on their car purchase.
Factors Influencing Import Duty on Cars
Import duty on cars is primarily influenced by the country of origin, vehicle type, engine size, and declared value, as each factor determines the applicable tariff rates set by customs authorities. Trade agreements and local regulatory policies further impact duty calculations, often leading to reduced rates for vehicles from partner nations or specific environmental standards compliance. Unlike sales tax, which is a percentage of the sale price applied at the point of sale, import duty is assessed at the border and can significantly affect the total cost of imported cars.
Sales Tax Variations Across Different States or Countries
Sales tax rates and regulations differ significantly across states and countries, reflecting diverse economic policies and consumption patterns. Some states impose higher sales taxes on luxury goods while others exempt essentials like food and medicine from sales tax, creating varied consumer cost structures. Internationally, value-added tax (VAT) systems often replace sales tax, involving multi-stage taxation that affects import tariffs and overall pricing strategies differently.
Calculating Total Car Tax: Import Duty vs. Sales Tax
Calculating total car tax involves understanding the distinctions between import duty and sales tax, where import duty is a tariff imposed on vehicles shipped across international borders, often based on the car's value, engine size, or weight. Sales tax applies nationally or locally on the transaction value when purchasing the vehicle, calculated as a percentage of the sale price and varying by jurisdiction. Accurate total tax estimation requires combining both import duty rates, which can range from 5% to 30%, with applicable sales tax percentages, ensuring compliance with regional tax regulations.
Exemptions and Reductions: Import Duty and Sales Tax Scenarios
Exemptions and reductions in import duty often apply to raw materials, essential goods, and diplomatic shipments, lowering costs for businesses engaged in international trade. Sales tax exemptions typically target necessities such as food, medicine, and education-related products to reduce the tax burden on consumers. Understanding the specific criteria for both import duty and sales tax exemptions enhances compliance and maximizes cost savings for importers and end-users.
Financial Planning: Navigating Car Taxes for Buyers
Import duty and sales tax both significantly impact the total cost when purchasing a car, requiring careful financial planning to avoid unexpected expenses. Import duty is typically calculated as a percentage of the vehicle's declared value and varies by country, often higher for luxury or non-domestically produced cars. Sales tax applies to the final sale price and can differ by state or region, making it essential for buyers to factor in both taxes to accurately estimate the overall purchase cost and budget accordingly.
Policy Trends: Recent Changes in Import Duty and Sales Tax
Recent policy trends in import duty and sales tax reveal a shift toward simplifying trade and boosting domestic industries by reducing import tariffs on essential goods while recalibrating sales tax rates to maintain revenue neutrality. Governments increasingly implement targeted import duty exemptions and preferential rates to facilitate raw material access for manufacturers and promote export competitiveness. Concurrent adjustments in sales tax frameworks, such as expanding the tax base and integrating digital payment reporting, aim to enhance compliance and streamline tax administration in line with evolving economic activities.
Choosing Between Imported and Local Cars: Tax Considerations
Import duty on imported cars often exceeds sales tax on locally manufactured vehicles, significantly impacting the total purchase cost. Buyers should assess import duty rates, typically ranging from 10% to 50% depending on the country, versus local sales tax percentages, which usually fall between 5% and 15%. Considering these tax differences can guide consumers in making cost-effective decisions when choosing between imported and local cars.
import duty vs sales tax Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com