Depreciation deduction allows businesses to allocate the cost of a pet-related asset over its useful life, reducing taxable income gradually each year. Capital allowance enables the immediate or accelerated write-off of certain qualifying expenses, often providing faster tax relief on pet care equipment or facilities. Understanding the distinction helps optimize tax benefits by aligning asset treatment with financial strategies in pet-related enterprises.
Table of Comparison
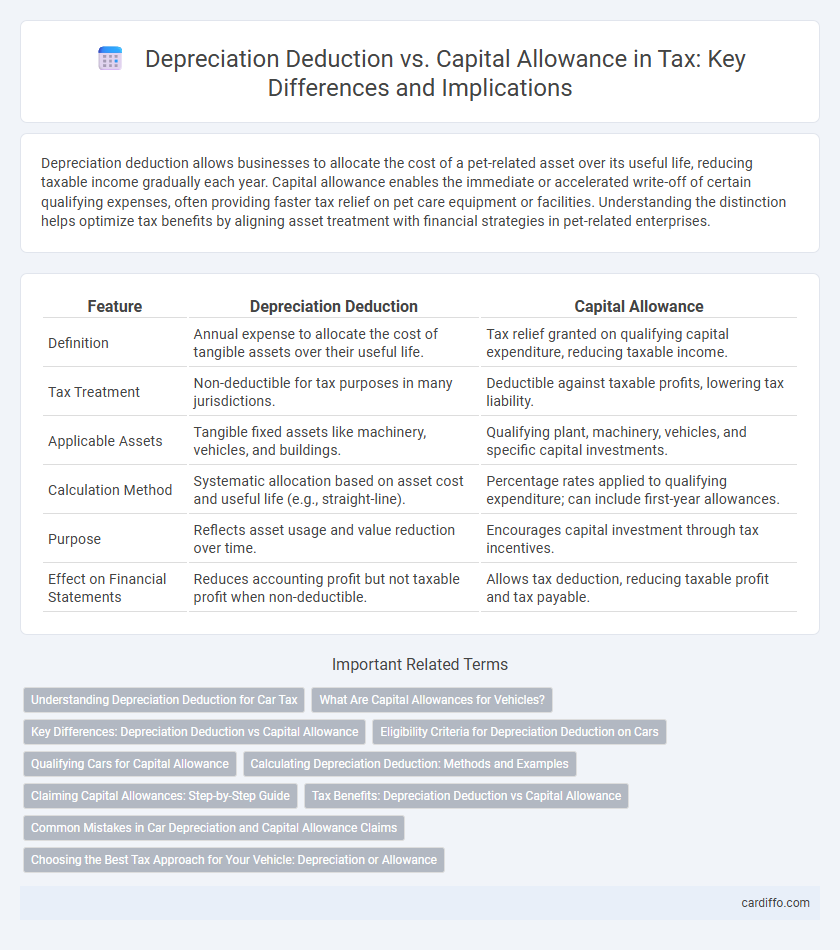
| Feature | Depreciation Deduction | Capital Allowance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Annual expense to allocate the cost of tangible assets over their useful life. | Tax relief granted on qualifying capital expenditure, reducing taxable income. |
| Tax Treatment | Non-deductible for tax purposes in many jurisdictions. | Deductible against taxable profits, lowering tax liability. |
| Applicable Assets | Tangible fixed assets like machinery, vehicles, and buildings. | Qualifying plant, machinery, vehicles, and specific capital investments. |
| Calculation Method | Systematic allocation based on asset cost and useful life (e.g., straight-line). | Percentage rates applied to qualifying expenditure; can include first-year allowances. |
| Purpose | Reflects asset usage and value reduction over time. | Encourages capital investment through tax incentives. |
| Effect on Financial Statements | Reduces accounting profit but not taxable profit when non-deductible. | Allows tax deduction, reducing taxable profit and tax payable. |
Understanding Depreciation Deduction for Car Tax
Depreciation deduction for car tax allows businesses to allocate the cost of a vehicle over its useful life, reducing taxable income each year based on the car's wear and tear. Unlike capital allowances, which provide specific tax relief on qualifying capital expenditures in a lump sum or phased amount, depreciation deduction systematically spreads the expense to match the car's usage period. Accurate records of the car's purchase price, usage, and depreciation method are essential to maximize tax benefits under IRS rules.
What Are Capital Allowances for Vehicles?
Capital allowances for vehicles enable businesses to deduct the cost of qualifying company cars, vans, or trucks from their taxable profits, reflecting the asset's depreciation. These allowances include the Annual Investment Allowance (AIA), first-year allowances, and Writing Down Allowances (WDAs), with specific rates based on vehicle CO2 emissions and type. Unlike standard depreciation, capital allowances provide HMRC-approved tax relief, allowing businesses to recover the cost of vehicles more efficiently over time.
Key Differences: Depreciation Deduction vs Capital Allowance
Depreciation deduction refers to the accounting method of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life but is not recognized for tax purposes, whereas capital allowance is a tax deduction granted based on government-approved rates for the wear and tear of qualifying fixed assets. Key differences include that depreciation affects financial statements without reducing taxable income directly, while capital allowances provide specific tax relief, reducing an entity's taxable profit. Additionally, capital allowances follow statutory schedules and rates set by tax authorities, unlike depreciation, which is based on accounting policies and estimates.
Eligibility Criteria for Depreciation Deduction on Cars
Eligibility for depreciation deduction on cars requires ownership and use of the vehicle in a business operation, with the car not classified as a luxury vehicle exceeding specific cost thresholds set by tax authorities. The vehicle must be used primarily for business purposes, typically over 50% of total usage, to qualify for these deductions. Personal use proportions reduce the deductible amount, and documentation such as mileage logs is essential to substantiate eligibility and calculate the depreciation expense accurately.
Qualifying Cars for Capital Allowance
Qualifying cars for capital allowance must meet specific criteria, such as CO2 emissions limits and vehicle type, to be eligible for tax relief on the purchase price. Unlike depreciation deduction, which is an accounting expense reflecting asset wear and tear, capital allowances provide tax relief based on statutory rules, allowing businesses to deduct a percentage of the car's cost annually from taxable profits. Cars with lower emissions typically qualify for enhanced capital allowance rates, optimizing tax efficiency for environmentally friendly vehicles.
Calculating Depreciation Deduction: Methods and Examples
Calculating depreciation deduction involves systematically allocating the cost of tangible assets over their useful lives using methods like straight-line, declining balance, and units of production. For example, under the straight-line method, a $10,000 asset with a 5-year useful life yields an annual depreciation expense of $2,000. Capital allowances, contrastingly, are tax reliefs that allow businesses to write off capital expenditure, often governed by tax authorities' specific rates and rules rather than accounting depreciation methods.
Claiming Capital Allowances: Step-by-Step Guide
Claiming capital allowances involves identifying qualifying assets, calculating the expenditure eligible for allowances, and applying the relevant rates as per tax regulations. The process begins by categorizing expenditures into pools such as the main pool or special rate pool, followed by computing writing-down allowances based on prescribed percentages. Accurate record-keeping of asset purchases and disposals is essential to optimize tax relief through capital allowances efficiently.
Tax Benefits: Depreciation Deduction vs Capital Allowance
Depreciation deduction allows businesses to gradually expense the cost of tangible assets over their useful lives, reducing taxable income and improving cash flow. Capital allowance provides tax relief by permitting a deduction for the cost of certain qualifying fixed assets, often accelerating tax benefits compared to standard depreciation. Understanding the eligibility criteria and applicable rates for both methods maximizes tax savings and supports strategic financial planning.
Common Mistakes in Car Depreciation and Capital Allowance Claims
Common mistakes in car depreciation and capital allowance claims include incorrectly categorizing vehicles, leading to inaccurate capital allowance rates and tax deductions. Many taxpayers fail to maintain detailed mileage logs, resulting in disallowed depreciation expenses and lost tax benefits. Overlooking the differences between writing down allowances and first-year allowances can also cause errors in claim amounts, reducing overall tax efficiency.
Choosing the Best Tax Approach for Your Vehicle: Depreciation or Allowance
Choosing between depreciation deduction and capital allowance for your vehicle depends on your business's tax strategy and cash flow needs. Depreciation deduction spreads the vehicle cost over its useful life, reducing taxable income gradually, while capital allowance often allows for accelerated write-offs, offering immediate tax relief. Evaluating your vehicle's expected usage, purchase price, and current tax regulations ensures optimal tax benefit and compliance.
Depreciation deduction vs capital allowance Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com