Fleet taxation offers businesses streamlined tax management by consolidating multiple vehicles under a single tax account, reducing administrative burden and often qualifying for bulk discounts. Individual car taxation requires separate filings for each vehicle, leading to higher paperwork and potentially increased costs per vehicle. Choosing fleet taxation optimizes tax efficiency and simplifies compliance for companies operating multiple vehicles.
Table of Comparison
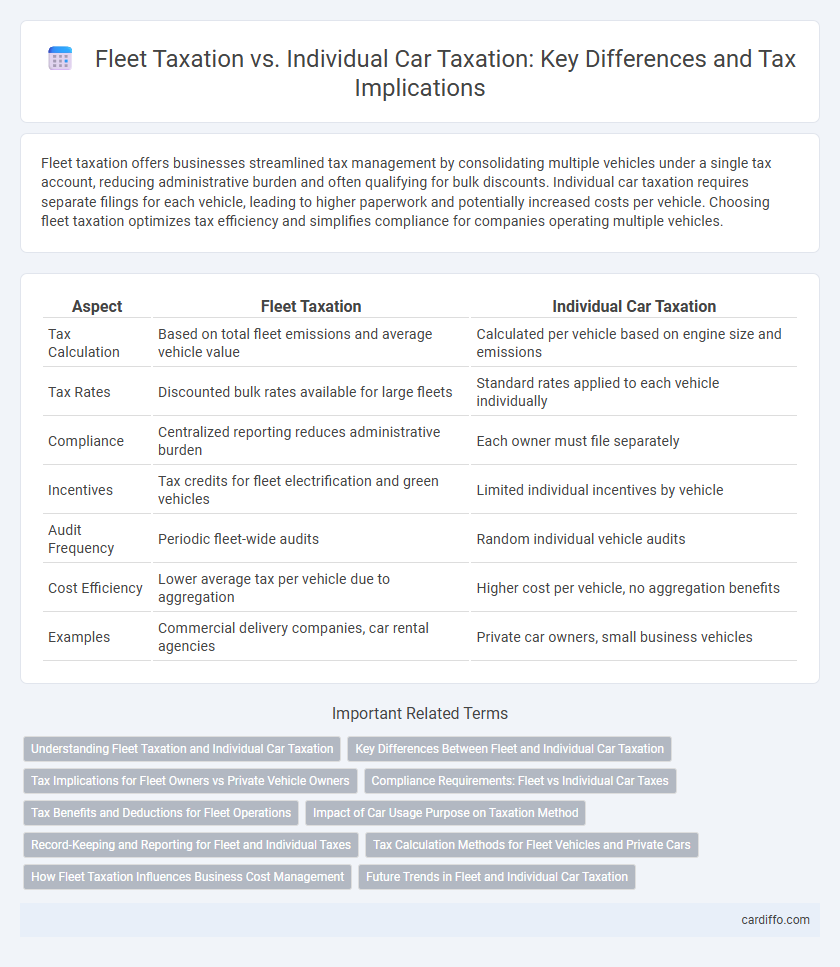
| Aspect | Fleet Taxation | Individual Car Taxation |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Calculation | Based on total fleet emissions and average vehicle value | Calculated per vehicle based on engine size and emissions |
| Tax Rates | Discounted bulk rates available for large fleets | Standard rates applied to each vehicle individually |
| Compliance | Centralized reporting reduces administrative burden | Each owner must file separately |
| Incentives | Tax credits for fleet electrification and green vehicles | Limited individual incentives by vehicle |
| Audit Frequency | Periodic fleet-wide audits | Random individual vehicle audits |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower average tax per vehicle due to aggregation | Higher cost per vehicle, no aggregation benefits |
| Examples | Commercial delivery companies, car rental agencies | Private car owners, small business vehicles |
Understanding Fleet Taxation and Individual Car Taxation
Fleet taxation consolidates tax liabilities for multiple vehicles owned by a single entity, offering streamlined compliance and potential cost savings through aggregated assessments. Individual car taxation requires separate tax calculations, payments, and record-keeping for each vehicle, often leading to higher administrative overhead. Understanding the distinctions between fleet and individual car taxation enables businesses and private owners to optimize tax strategies based on vehicle utilization and ownership scale.
Key Differences Between Fleet and Individual Car Taxation
Fleet taxation consolidates multiple vehicles under a single tax regime, often resulting in bulk discounts and simplified administration, whereas individual car taxation requires separate assessments for each vehicle, leading to varied rates based on individual usage and emissions. Fleet tax systems typically offer streamlined reporting and payment processes, reducing compliance burdens for businesses managing large vehicle groups, while individual car owners face personalized tax calculations linked to specific vehicle attributes and regional regulations. Key differences include the scale of taxation, eligibility for deductions, and administrative efficiency, with fleet taxation favoring commercial operators and individual taxation catering to private owners.
Tax Implications for Fleet Owners vs Private Vehicle Owners
Fleet taxation often involves lower per-vehicle tax rates and eligibility for bulk deductions, reducing the overall tax liability for businesses managing multiple vehicles. Individual car taxation typically imposes higher rates without bulk discounts, resulting in greater out-of-pocket expenses for private owners. Tax implications for fleet owners also include potential eligibility for fuel tax credits and depreciation allowances that are not available to individual vehicle taxpayers.
Compliance Requirements: Fleet vs Individual Car Taxes
Fleet taxation requires businesses to maintain detailed records for multiple vehicles, including usage logs, maintenance records, and consolidated tax filings, ensuring compliance with corporate tax regulations. Individual car taxation mandates personal record-keeping of vehicle usage, insurance, and periodic renewal documents, typically involving simpler filing processes. Both systems enforce vehicle-specific tax rates, but fleet taxation demands higher administrative oversight to meet regulatory compliance standards.
Tax Benefits and Deductions for Fleet Operations
Fleet taxation offers significant tax benefits and deductions compared to individual car taxation by allowing businesses to consolidate expenses such as fuel, maintenance, and depreciation under a single deductible category. Companies can leverage bulk purchase discounts and streamlined reporting, maximizing deductible costs and reducing overall taxable income more effectively than individual car owners. Enhanced deductions for fleet operations, including tax credits for eco-friendly vehicles and consolidated leasing costs, provide additional financial advantages not typically available to individual taxpayers.
Impact of Car Usage Purpose on Taxation Method
Fleet taxation often offers businesses tax deductions and incentives based on aggregate vehicle use, whereas individual car taxation typically depends on personal vehicle registration and usage patterns. The purpose of car usage significantly influences the taxation method; commercial vehicles used extensively for business may qualify for lower tax rates or exemptions under fleet taxation rules. Personal vehicles used mainly for private commuting are subject to standard individual tax rates, emphasizing how usage intent directly impacts fiscal obligations.
Record-Keeping and Reporting for Fleet and Individual Taxes
Fleet taxation requires detailed, centralized record-keeping of multiple vehicles, including mileage, fuel consumption, and maintenance logs, to ensure accurate tax reporting and compliance. Individual car taxation involves maintaining separate records for each vehicle, typically simpler but necessitating precise documentation for mileage and expenses to claim deductions or credits. Both systems demand diligent record management, yet fleet taxation systems often utilize specialized software for streamlined reporting to tax authorities.
Tax Calculation Methods for Fleet Vehicles and Private Cars
Fleet tax calculation typically involves aggregating vehicle data such as weight, fuel type, and emissions for the entire fleet, enabling bulk rate discounts or tiered tax brackets based on total fleet emissions or mileage. Individual car taxation calculates tax based on each vehicle's specific attributes, including engine size, CO2 emissions, and registration date, often resulting in varied rates per vehicle. Fleet taxation methods prioritize efficiency and overall emissions, while individual car taxation targets personalized environmental impact and vehicle usage.
How Fleet Taxation Influences Business Cost Management
Fleet taxation offers businesses significant cost management advantages by allowing aggregated tax assessments based on the total number or emissions of multiple vehicles, leading to potential bulk discounts and streamlined administrative processes. This contrasts with individual car taxation, where each vehicle incurs separate tax liabilities, increasing paperwork and reducing opportunities for optimized tax planning. Companies leveraging fleet taxation can better forecast expenses, improve cash flow management, and allocate resources more efficiently across their transportation assets.
Future Trends in Fleet and Individual Car Taxation
Future trends in fleet and individual car taxation emphasize increased adoption of dynamic tax models reflecting vehicle emissions, usage patterns, and electrification rates, encouraging sustainable transportation choices. Government policies are trending towards integrating telematics data and real-time monitoring to tailor tax rates more precisely for commercial fleets and private vehicles. Advances in regulatory frameworks aim to harmonize fleet taxation with evolving environmental standards while maintaining equitable tax burdens on individual car owners.
Fleet Taxation vs Individual Car Taxation Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com