Registration tax is a one-time fee imposed on the legal registration of assets like vehicles or property, reflecting their ownership transfer. Excise tax is a recurring levy on specific goods such as fuel, tobacco, and alcohol, aimed at regulating consumption and generating government revenue. Both taxes serve distinct purposes, with registration tax tied to ownership documentation and excise tax focused on production or sale.
Table of Comparison
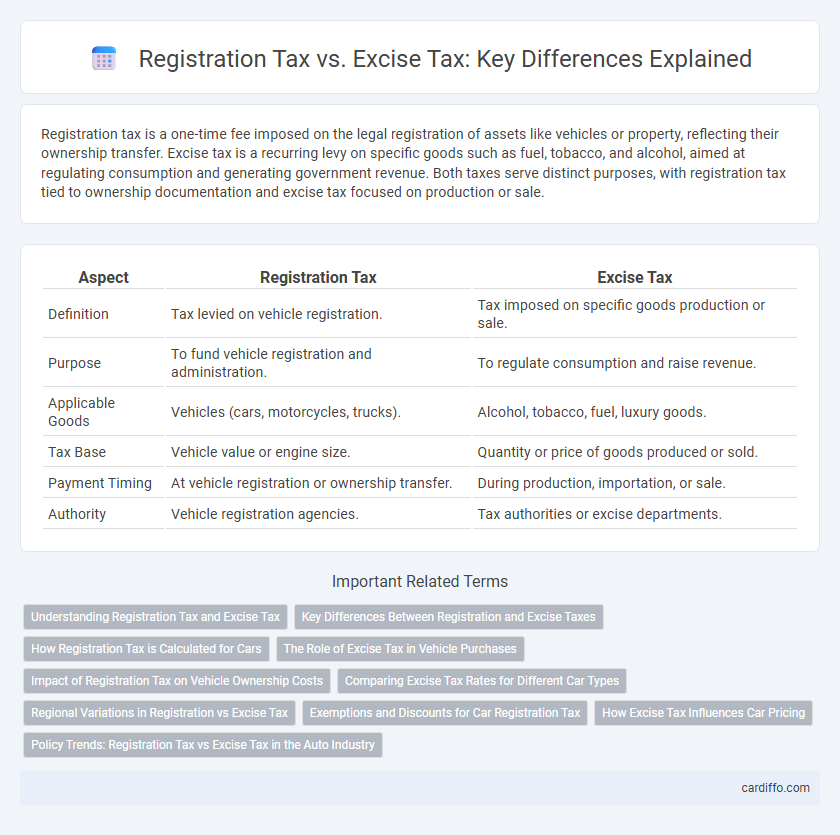
| Aspect | Registration Tax | Excise Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax levied on vehicle registration. | Tax imposed on specific goods production or sale. |
| Purpose | To fund vehicle registration and administration. | To regulate consumption and raise revenue. |
| Applicable Goods | Vehicles (cars, motorcycles, trucks). | Alcohol, tobacco, fuel, luxury goods. |
| Tax Base | Vehicle value or engine size. | Quantity or price of goods produced or sold. |
| Payment Timing | At vehicle registration or ownership transfer. | During production, importation, or sale. |
| Authority | Vehicle registration agencies. | Tax authorities or excise departments. |
Understanding Registration Tax and Excise Tax
Registration tax is a one-time fee imposed on the transfer or registration of ownership of assets such as vehicles or real estate, typically calculated based on the asset's value or type. Excise tax is an indirect tax levied on specific goods like alcohol, tobacco, and fuel, aimed at regulating consumption and generating government revenue. Both taxes serve distinct regulatory and fiscal purposes, with registration tax tied to ownership documentation and excise tax linked to product manufacturing or sale.
Key Differences Between Registration and Excise Taxes
Registration tax is a one-time levy imposed on the registration of assets such as vehicles or property, primarily aimed at transferring ownership rights. Excise tax is an indirect tax applied on the manufacture, sale, or consumption of specific goods like alcohol, tobacco, or fuel to discourage usage and generate government revenue. While registration tax is a fixed amount based on asset value or type, excise tax varies with quantity or price of goods and serves regulatory and fiscal purposes.
How Registration Tax is Calculated for Cars
Registration tax for cars is typically calculated based on several key factors including the vehicle's purchase price, engine size, CO2 emissions, and age. Many jurisdictions apply a percentage rate to the car's value or use a tiered system linked to emissions levels to determine the exact amount. Some regions also impose fixed fees or variable rates that increase with engine displacement or vehicle weight.
The Role of Excise Tax in Vehicle Purchases
Excise tax on vehicle purchases functions as a targeted levy imposed by governments to regulate consumption and generate revenue, typically calculated based on engine size, fuel type, or vehicle value. This tax influences consumer behavior by discouraging the purchase of high-emission or luxury vehicles, thereby promoting environmental sustainability and public health. Unlike registration tax, which is a recurring fee linked to vehicle ownership, excise tax is a one-time cost at the point of sale, directly impacting the initial affordability of vehicles.
Impact of Registration Tax on Vehicle Ownership Costs
Registration tax significantly increases the upfront cost of vehicle ownership, often calculated as a percentage of the vehicle's value, which can discourage new vehicle purchases. This tax directly influences the total cost of acquiring a vehicle by adding to the initial financial burden, unlike excise tax, which may be imposed periodically. Understanding the registration tax's role is crucial for budgeting vehicle expenses and evaluating the overall economic impact on consumers.
Comparing Excise Tax Rates for Different Car Types
Excise tax rates vary significantly depending on the type of vehicle, with luxury cars often subject to higher rates compared to standard passenger vehicles due to their perceived higher environmental impact and value. Hybrid and electric vehicles frequently benefit from reduced or exempt excise taxes as governments encourage eco-friendly transportation. Registration tax is typically a fixed annual fee based on vehicle weight or engine size, whereas excise tax rates fluctuate by vehicle classification, engine capacity, and emissions standards.
Regional Variations in Registration vs Excise Tax
Regional variations in registration tax reflect differences in state-level vehicle ownership fees, with some states imposing flat rates while others apply progressive scales based on vehicle value or weight. Excise tax rates vary significantly between jurisdictions, often influenced by local government policies targeting specific goods like alcohol, tobacco, or luxury items, resulting in wide disparities. Understanding these regional disparities is crucial for businesses and consumers to accurately estimate total tax liability on purchases and registrations within distinct territories.
Exemptions and Discounts for Car Registration Tax
Car registration tax exemptions often apply to electric vehicles, hybrids, and vehicles used for agricultural or humanitarian purposes, reducing the financial burden for these specific categories. Discounts on registration tax may be available for seniors, veterans, or low-income individuals, promoting equitable access to vehicle ownership. Excise tax exemptions are generally more limited, focusing primarily on specific fuel types or import conditions rather than broad vehicle categories.
How Excise Tax Influences Car Pricing
Excise tax on vehicles directly increases the manufacturing cost, leading manufacturers to adjust the retail price upward to maintain profit margins. Registration tax is a one-time fee paid by the owner to register the vehicle, whereas excise tax is embedded in the price of the car, affecting overall affordability. Higher excise taxes often discourage purchases of certain models, influencing market demand and pricing strategies within the automotive industry.
Policy Trends: Registration Tax vs Excise Tax in the Auto Industry
Current policy trends in the auto industry reveal a shift from registration tax reliance towards stricter excise tax structures to incentivize environmentally friendly vehicles and control emissions. Governments are increasingly adjusting excise tax rates based on vehicle CO2 emissions, promoting electric and hybrid models over traditional combustion engines. This shift reflects a broader regulatory focus on sustainability and emission reduction targets within automotive taxation frameworks.
Registration Tax vs Excise Tax Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com