State car tax varies widely depending on local regulations and is often based on vehicle value, age, or weight, directly impacting annual registration fees. Federal car tax generally pertains to import duties, emissions compliance fees, or specific federal surcharges, influencing the initial purchase price or eligibility criteria. Understanding the differences between state and federal car taxes helps vehicle owners anticipate total costs and ensure compliance with all tax obligations.
Table of Comparison
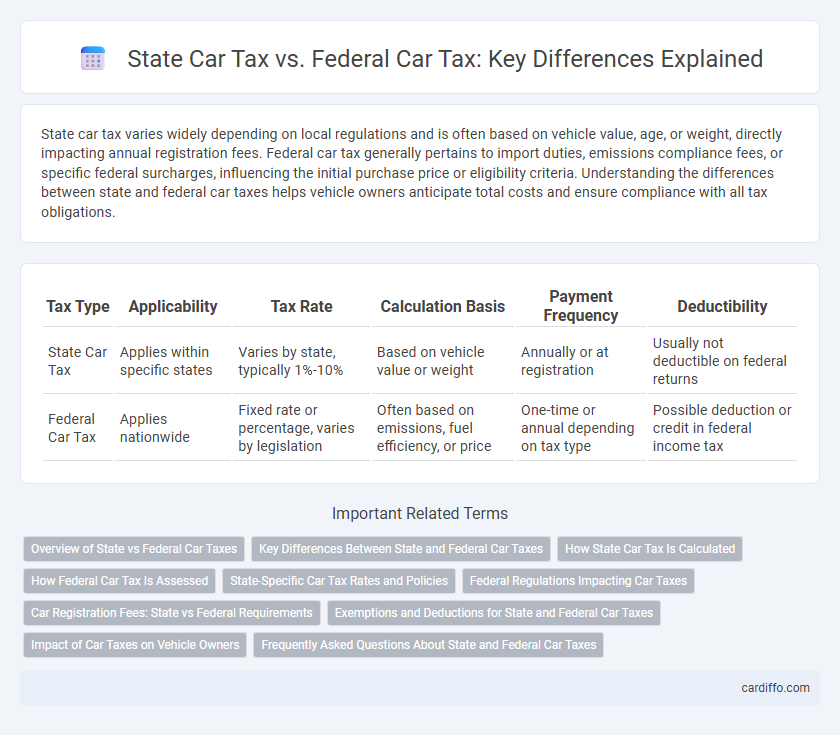
| Tax Type | Applicability | Tax Rate | Calculation Basis | Payment Frequency | Deductibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State Car Tax | Applies within specific states | Varies by state, typically 1%-10% | Based on vehicle value or weight | Annually or at registration | Usually not deductible on federal returns |
| Federal Car Tax | Applies nationwide | Fixed rate or percentage, varies by legislation | Often based on emissions, fuel efficiency, or price | One-time or annual depending on tax type | Possible deduction or credit in federal income tax |
Overview of State vs Federal Car Taxes
State car tax varies significantly by location, often including registration fees, personal property taxes, and sales taxes based on the vehicle's value. Federal car tax primarily involves fuel taxes and emissions-related fees, impacting nationwide vehicle operations and environmental compliance. Understanding the differentiation helps taxpayers optimize expenses and ensure adherence to both state-specific requirements and federal mandates.
Key Differences Between State and Federal Car Taxes
State car tax varies widely by location, often based on factors like vehicle value, age, and local regulations, while federal car tax is typically a fixed rate or percentage applied uniformly across the country. State taxes fund local infrastructure and public services, whereas federal taxes contribute to nationwide programs, including transportation and environmental initiatives. Understanding the key differences in tax rates, exemption criteria, and applicable fees is crucial for accurate vehicle cost planning and compliance.
How State Car Tax Is Calculated
State car tax is typically calculated based on the vehicle's purchase price, age, and the state's specific tax rate, which can vary widely across jurisdictions. Some states use a flat percentage of the vehicle's value, while others apply a progressive scale or consider factors like weight and fuel efficiency. Unlike federal car tax, which often focuses on emissions and safety standards fees, state car tax primarily aims to generate revenue for transportation infrastructure and public services.
How Federal Car Tax Is Assessed
Federal car tax is primarily assessed through the Gas Guzzler Tax, which targets vehicles with low fuel efficiency, imposing higher fees on models that consume excessive fuel. This tax is calculated based on the vehicle's combined city and highway mileage ratings, targeting passenger cars rather than trucks or SUVs. Unlike state car taxes, which vary by location and often depend on vehicle value or weight, federal car tax focuses on environmental impact and fuel economy standards set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
State-Specific Car Tax Rates and Policies
State car tax rates vary significantly, with some states imposing higher registration fees and personal property taxes based on the vehicle's value, age, or weight. Unlike the federal government, which does not levy a direct car tax, states set specific policies that influence annual costs, including sales tax on vehicle purchases and excise taxes. Understanding these state-specific regulations is crucial for accurate vehicle ownership cost estimation and compliance.
Federal Regulations Impacting Car Taxes
Federal regulations significantly influence car taxes through standardized emissions and safety requirements that determine vehicle classification and taxable value. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) enforces specific tax credits and deductions related to hybrid and electric vehicles, directly affecting taxable amounts at the federal level. These regulations create a uniform baseline that states build upon, resulting in variations in state car tax rates and structures influenced by federal guidelines.
Car Registration Fees: State vs Federal Requirements
Car registration fees vary significantly between state and federal levels, with states primarily imposing taxes based on vehicle value, weight, or age to fund local infrastructure and services. Federal car tax requirements are minimal and generally limited to specific environmental or import duties rather than routine registration fees. Understanding the distinct purposes and calculations of state versus federal car taxes is critical for accurate vehicle cost planning and compliance.
Exemptions and Deductions for State and Federal Car Taxes
State car tax often includes exemptions and deductions based on vehicle type, usage, or age, such as exemptions for electric vehicles or classic cars, while federal car tax primarily focuses on deductions related to business use or depreciation under IRS guidelines. Many states offer specific tax credits or incentives for fuel-efficient or zero-emission vehicles, reducing the overall taxable value at the state level. Federal deductions allow taxpayers to claim expenses like vehicle depreciation or mileage when used for business purposes, distinct from state-imposed registration or property vehicle taxes.
Impact of Car Taxes on Vehicle Owners
State car taxes vary widely, often based on vehicle value, age, or weight, directly affecting annual ownership costs for vehicle owners. Federal car taxes, such as the gas guzzler tax or import tariffs, influence vehicle prices and manufacturer incentives, indirectly impacting consumers' purchasing decisions. Understanding the combined effect of state and federal car taxes is essential for accurate cost forecasting and budgeting for vehicle owners.
Frequently Asked Questions About State and Federal Car Taxes
State car tax rates vary significantly depending on the state, usually calculated as a percentage of the vehicle's purchase price or assessed value. Federal car tax primarily applies to imported vehicles, including tariffs and excise taxes set by U.S. Customs and Border Protection, with rates depending on vehicle type and origin country. Common FAQs address the differences in tax obligations, how to calculate each tax, and which authorities collect them during vehicle registration or importation processes.
State Car Tax vs Federal Car Tax Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com