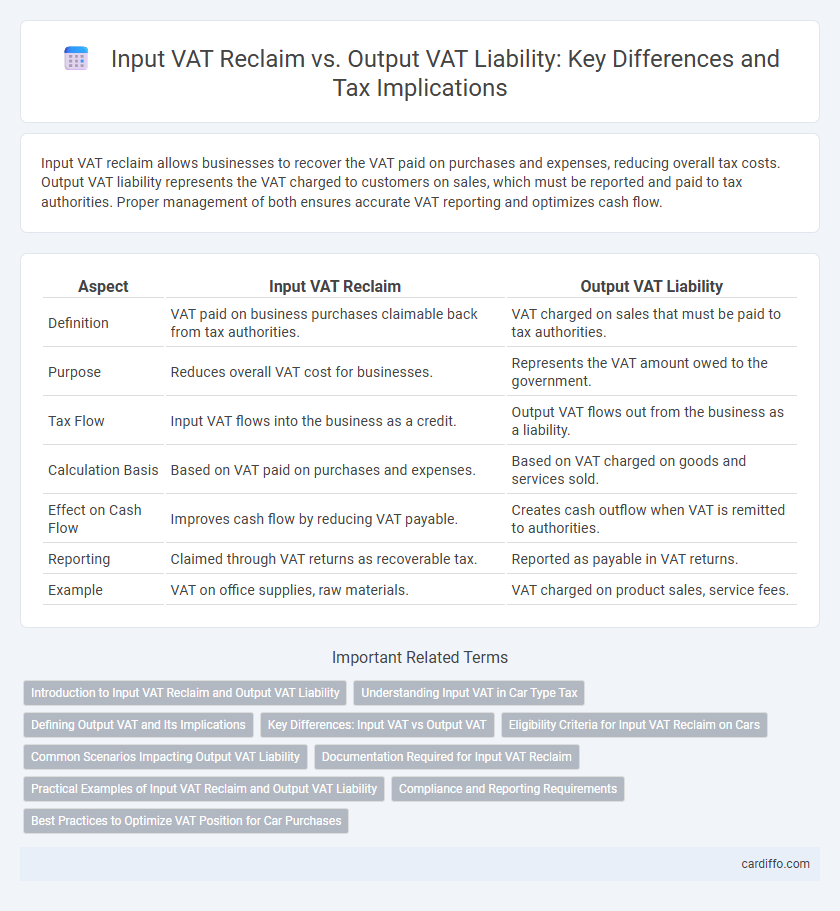
Input VAT reclaim allows businesses to recover the VAT paid on purchases and expenses, reducing overall tax costs. Output VAT liability represents the VAT charged to customers on sales, which must be reported and paid to tax authorities. Proper management of both ensures accurate VAT reporting and optimizes cash flow.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Input VAT Reclaim | Output VAT Liability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | VAT paid on business purchases claimable back from tax authorities. | VAT charged on sales that must be paid to tax authorities. |
| Purpose | Reduces overall VAT cost for businesses. | Represents the VAT amount owed to the government. |
| Tax Flow | Input VAT flows into the business as a credit. | Output VAT flows out from the business as a liability. |
| Calculation Basis | Based on VAT paid on purchases and expenses. | Based on VAT charged on goods and services sold. |
| Effect on Cash Flow | Improves cash flow by reducing VAT payable. | Creates cash outflow when VAT is remitted to authorities. |
| Reporting | Claimed through VAT returns as recoverable tax. | Reported as payable in VAT returns. |
| Example | VAT on office supplies, raw materials. | VAT charged on product sales, service fees. |
Introduction to Input VAT Reclaim and Output VAT Liability
Input VAT reclaim allows businesses to recover the value-added tax paid on purchases used for taxable supplies, reducing overall tax costs and improving cash flow. Output VAT liability arises from VAT charged on sales or services provided, which businesses must remit to tax authorities. Understanding the distinction between Input VAT reclaim and Output VAT liability is crucial for accurate VAT reporting and compliance.
Understanding Input VAT in Car Type Tax
Input VAT in car type tax refers to the value-added tax paid on the purchase or lease of vehicles used for business purposes, which can be reclaimed if the car is primarily used for taxable activities. Businesses must accurately track and document the proportion of business versus private use to determine the eligible amount of input VAT reclaim. Understanding the distinctions between reclaimable input VAT and output VAT liability is essential for compliance with tax regulations and minimizing overall VAT costs.
Defining Output VAT and Its Implications
Output VAT refers to the value-added tax a business charges on its sales of goods or services, which must be reported and paid to tax authorities. This tax creates a VAT liability that a company owes, influencing cash flow management and compliance obligations. Understanding output VAT is essential to accurately calculate net VAT position when offsetting input VAT reclaim against output VAT liability.
Key Differences: Input VAT vs Output VAT
Input VAT represents the Value Added Tax paid on business purchases and is recoverable from tax authorities, reducing a company's VAT payable. Output VAT is the tax charged on sales of goods or services, which businesses must remit to the tax authorities. The key difference lies in their roles in VAT accounting: input VAT is a reclaimable expense, while output VAT is a tax liability owed to the government.
Eligibility Criteria for Input VAT Reclaim on Cars
Input VAT reclaim on cars is subject to strict eligibility criteria, including the vehicle's exclusive use for business purposes and proper documentation such as valid VAT invoices. Personal or mixed-use vehicles generally disqualify businesses from reclaiming input VAT unless a detailed logbook demonstrating 100% business use is maintained. Compliance with local tax authority regulations and accurate record-keeping are essential to substantiate the eligibility for input VAT recovery on automotive assets.
Common Scenarios Impacting Output VAT Liability
Common scenarios impacting output VAT liability include sales that are zero-rated, exempt, or standard-rated, which determine the amount of VAT payable to tax authorities. Adjustments such as credit notes, debit notes, and bad debt write-offs can alter output VAT calculations, affecting the overall VAT liability. Transactions involving exports, intra-community supplies, or reverse charge mechanisms also influence output VAT liability by shifting the VAT payment responsibility or applying special VAT rates.
Documentation Required for Input VAT Reclaim
Proper documentation is crucial for Input VAT reclaim, including valid tax invoices that clearly state the supplier's VAT registration number, invoice date, and detailed description of goods or services purchased. Maintaining accurate records such as purchase orders, delivery receipts, and proof of payment supports the legitimacy of the claim and ensures compliance with tax authorities. Failure to provide comprehensive documentation may result in denied Input VAT credits and increased scrutiny during tax audits.
Practical Examples of Input VAT Reclaim and Output VAT Liability
Input VAT reclaim allows businesses to recover VAT paid on purchases used for taxable supplies, such as reclaiming EUR1,000 VAT on office equipment bought for a VAT-registered company. Output VAT liability arises when a business sells goods or services subject to VAT, for example, charging EUR2,000 VAT on a EUR10,000 sale to a customer. The practical impact is seen in VAT returns where reclaimed input VAT reduces the total VAT payable, offsetting the output VAT liability owed to the tax authorities.
Compliance and Reporting Requirements
Input VAT reclaim and output VAT liability require meticulous compliance with tax regulations to ensure accurate reporting and avoid penalties. Businesses must maintain detailed records of purchase invoices for input VAT reclaim while accurately calculating and reporting output VAT liabilities on sales within prescribed deadlines. Electronic filing systems and periodic VAT returns submission are essential for meeting regulatory requirements and facilitating audit trails.
Best Practices to Optimize VAT Position for Car Purchases
To optimize VAT position on car purchases, businesses should accurately distinguish between input VAT reclaim eligibility and output VAT liability obligations, ensuring all invoices are properly documented and meet tax authority requirements. Implementing a stringent audit process of vehicle usage logs can validate the proportion of business to private use, directly impacting reclaim limits and reducing potential VAT exposure. Maintaining up-to-date knowledge of local VAT regulations and rates, including any sector-specific exemptions or restrictions, is essential for maximizing allowable input VAT recovery while minimizing output VAT liabilities.
Input VAT Reclaim vs Output VAT Liability Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com