Import tax affects the cost and pricing of goods coming into a country, often aimed at protecting local industries by making imported products more expensive. Domestic production tax applies to goods manufactured within the country, influencing the overall production cost and potentially impacting competitiveness. Comparing import tax and domestic production tax helps policymakers balance trade protection with fostering local economic growth.
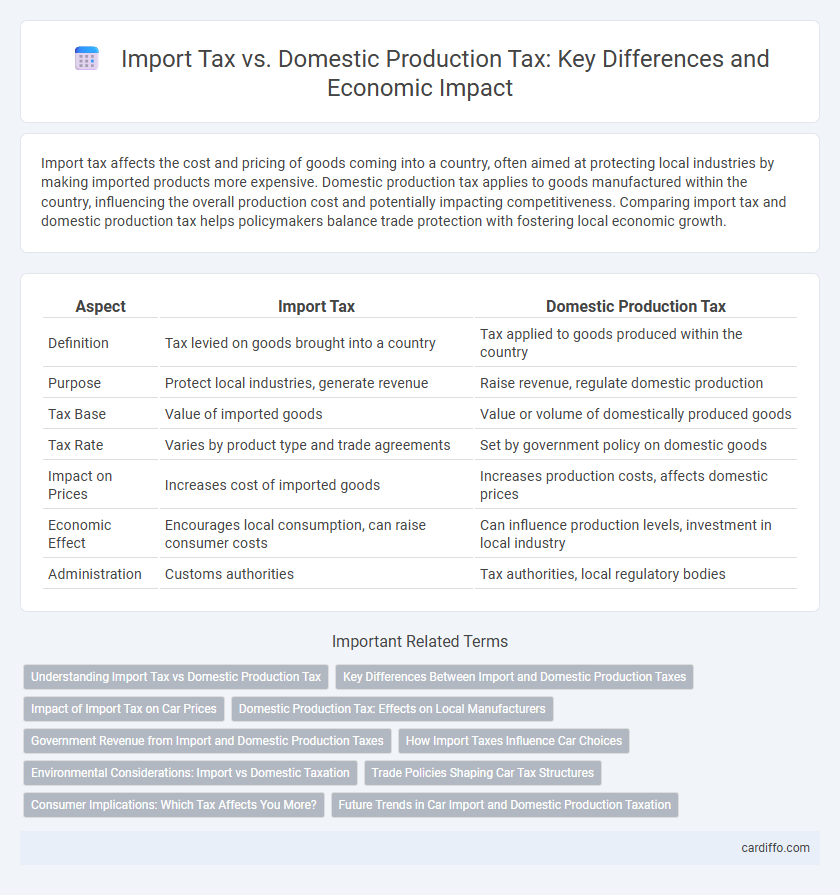
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Import Tax | Domestic Production Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax levied on goods brought into a country | Tax applied to goods produced within the country |
| Purpose | Protect local industries, generate revenue | Raise revenue, regulate domestic production |
| Tax Base | Value of imported goods | Value or volume of domestically produced goods |
| Tax Rate | Varies by product type and trade agreements | Set by government policy on domestic goods |
| Impact on Prices | Increases cost of imported goods | Increases production costs, affects domestic prices |
| Economic Effect | Encourages local consumption, can raise consumer costs | Can influence production levels, investment in local industry |
| Administration | Customs authorities | Tax authorities, local regulatory bodies |
Understanding Import Tax vs Domestic Production Tax
Import tax, also known as customs duty, is levied on goods brought into a country, influencing prices and trade balance by increasing the cost of foreign products. Domestic production tax, such as excise or sales tax, targets goods produced within the country, affecting local manufacturers and consumer prices. Understanding the differences between these taxes helps businesses optimize supply chains and compliance strategies based on cost implications and regulatory environments.
Key Differences Between Import and Domestic Production Taxes
Import taxes are levied on goods brought into a country, primarily aimed at protecting local industries and generating revenue, while domestic production taxes target goods produced within the country to influence local manufacturing activities and fund government expenditures. Import taxes often include tariffs and customs duties, which can vary by product type and trade agreements, whereas domestic production taxes typically encompass excise taxes, value-added taxes (VAT), and production-specific levies. The key differences lie in their economic impact, with import taxes directly affecting international trade flows and prices, whereas domestic production taxes influence local business costs and production decisions.
Impact of Import Tax on Car Prices
Import tax significantly increases the cost of foreign cars, leading to higher retail prices compared to domestically produced vehicles. This tax inflation often discourages consumer demand for imported models, promoting local automotive industry growth through competitive pricing. Domestic production tax policies usually aim to balance revenue generation with affordability, but import taxes directly amplify price disparities in the automotive market.
Domestic Production Tax: Effects on Local Manufacturers
Domestic production tax directly impacts local manufacturers by increasing their operational costs, which can reduce profit margins and hinder competitiveness compared to imported goods. Higher tax rates on domestic production may discourage investment in local industries, slowing innovation and job creation within the manufacturing sector. Adjusting domestic production taxes to balance revenue needs and industry growth is crucial for fostering a sustainable local manufacturing ecosystem.
Government Revenue from Import and Domestic Production Taxes
Government revenue from import taxes often provides a direct and immediate source of funding, leveraging tariffs imposed on imported goods to protect domestic industries and balance trade deficits. Domestic production taxes, such as excise taxes and value-added taxes (VAT), capture ongoing revenue from locally manufactured goods, promoting internal economic activity while ensuring stable tax inflow. Balancing import and domestic production taxes allows governments to optimize revenue streams while supporting local businesses and regulating international trade dynamics.
How Import Taxes Influence Car Choices
Import taxes on vehicles often lead to higher prices for foreign-made cars, pushing consumers toward domestically produced models due to cost considerations. Domestic production taxes, while influential, typically have a more predictable impact on pricing and supply chains within the country. Consequently, elevated import duties can shift consumer demand, affecting market competition and encouraging local automotive industry growth.
Environmental Considerations: Import vs Domestic Taxation
Import taxes often factor in higher environmental costs due to carbon emissions linked to transportation and international logistics, incentivizing lower-carbon imports. Domestic production taxes can include stricter regulations and fees aimed at reducing pollution and promoting sustainable practices within local industries. Comparing both, environmental considerations in import tax encourage greener global supply chains, while domestic taxes target local ecological impacts and resource usage.
Trade Policies Shaping Car Tax Structures
Import tax on vehicles often exceeds domestic production tax, reflecting trade policies aimed at protecting local automakers and promoting national industry growth. Tariffs and import duties reshape car tax structures by increasing costs of foreign-made cars, influencing consumer preferences toward domestically manufactured models. Adjustments in tax rates balance trade competitiveness while supporting economic objectives such as job creation and technological innovation within the automotive sector.
Consumer Implications: Which Tax Affects You More?
Import tax, often levied as tariffs, directly impacts consumer prices by increasing the cost of foreign goods, potentially leading to higher retail prices and reduced product variety. Domestic production tax influences consumer expenses indirectly through its effect on local manufacturers, possibly causing price adjustments if businesses pass on these costs. Understanding which tax affects you more depends on consumption patterns, with import tax impacting consumers of imported goods, while domestic production tax affects those relying on locally produced items.
Future Trends in Car Import and Domestic Production Taxation
Future trends in car import and domestic production taxation are increasingly shaped by environmental regulations and trade policies favoring electric vehicles and low-emission technologies. Governments are expected to adjust import tariffs and domestic excise taxes to incentivize sustainable automotive production and reduce carbon footprints. Enhanced data analytics and blockchain technology will improve tax compliance and enforcement in both imported and domestically produced vehicles.
Import tax vs domestic production tax Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com