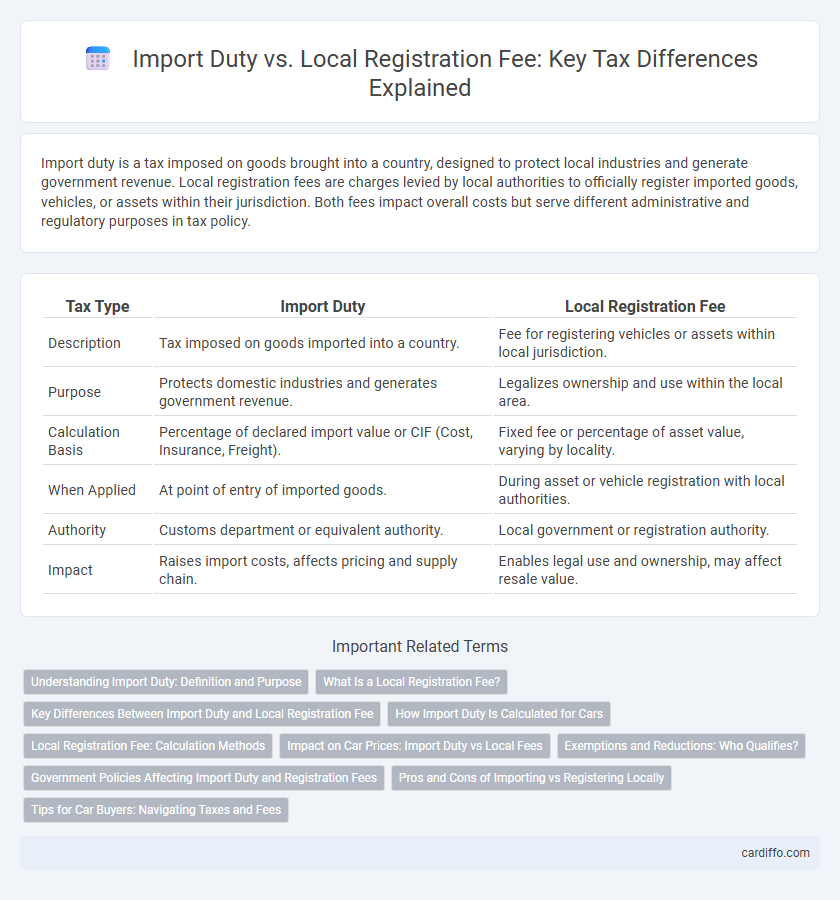
Import duty is a tax imposed on goods brought into a country, designed to protect local industries and generate government revenue. Local registration fees are charges levied by local authorities to officially register imported goods, vehicles, or assets within their jurisdiction. Both fees impact overall costs but serve different administrative and regulatory purposes in tax policy.
Table of Comparison
| Tax Type | Import Duty | Local Registration Fee |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Tax imposed on goods imported into a country. | Fee for registering vehicles or assets within local jurisdiction. |
| Purpose | Protects domestic industries and generates government revenue. | Legalizes ownership and use within the local area. |
| Calculation Basis | Percentage of declared import value or CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight). | Fixed fee or percentage of asset value, varying by locality. |
| When Applied | At point of entry of imported goods. | During asset or vehicle registration with local authorities. |
| Authority | Customs department or equivalent authority. | Local government or registration authority. |
| Impact | Raises import costs, affects pricing and supply chain. | Enables legal use and ownership, may affect resale value. |
Understanding Import Duty: Definition and Purpose
Import duty, a tax imposed by governments on goods brought into a country, aims to protect domestic industries and generate revenue. This fee is calculated based on the product's value, type, and origin, influencing the final cost of imported items. Understanding import duty is crucial for businesses and consumers to anticipate expenses and ensure compliance with customs regulations.
What Is a Local Registration Fee?
A local registration fee is a mandatory charge imposed by government authorities for officially recording ownership of a vehicle within a specific jurisdiction. Unlike import duties, which are taxes levied on goods brought into a country, the local registration fee covers administrative costs related to vehicle identification, licensing, and compliance with local regulations. This fee varies by region and is essential for legal vehicle operation on public roads.
Key Differences Between Import Duty and Local Registration Fee
Import duty is a government-imposed tax on goods brought into a country, calculated as a percentage of the item's customs value to regulate trade and generate revenue. Local registration fee is a charge levied by municipal or regional authorities for officially registering a product, vehicle, or property within a jurisdiction, reflecting administrative costs. Key differences lie in their purpose--import duty targets cross-border transactions to protect domestic industries, while local registration fees fund local governance and provide legal recognition within the community.
How Import Duty Is Calculated for Cars
Import duty for cars is calculated based on the vehicle's customs value, which includes the purchase price, shipping, and insurance costs. The duty rate varies depending on the country of import and the vehicle type, often expressed as a percentage of the customs value. This calculation does not include local registration fees, which are separately assessed by local authorities based on factors such as vehicle age, engine size, and environmental impact.
Local Registration Fee: Calculation Methods
Local registration fees are typically calculated based on the vehicle's engine capacity, age, and market value, varying significantly across jurisdictions. Some regions apply a flat rate, while others use a percentage of the assessed value or taxable base to determine the fee. Accurate assessment and classification of the vehicle attributes ensure precise calculation and compliance with local tax regulations.
Impact on Car Prices: Import Duty vs Local Fees
Import duty significantly raises the initial cost of imported vehicles by applying a percentage-based tax on the car's value, often making foreign cars substantially more expensive. Local registration fees add a fixed or variable charge based on regional regulations but generally have a smaller impact on the overall price compared to import duty. The combined effect of high import duties and local fees can sharply increase the final retail price, influencing consumer preferences toward locally manufactured vehicles.
Exemptions and Reductions: Who Qualifies?
Import duty exemptions primarily apply to diplomatic missions, charitable organizations, and essential goods under international trade agreements, reducing the cost burden on imported items. Local registration fee reductions are often granted to residents with disabilities, veterans, or low-income individuals, facilitating affordable access to vehicle ownership and property transactions. Both tax relief measures aim to promote economic fairness by targeting specific groups eligible based on legal and socioeconomic criteria.
Government Policies Affecting Import Duty and Registration Fees
Government policies significantly influence import duty rates and local registration fees by establishing tariffs designed to protect domestic industries and generate revenue. Import duties are typically adjusted based on trade agreements, economic strategies, and sector-specific regulations, while local registration fees are determined by municipal or state authorities to cover administrative costs and compliance. Changes in international trade policies, such as free trade agreements or sanctions, directly impact the cost structure of imported goods, affecting overall tax liabilities and consumer prices.
Pros and Cons of Importing vs Registering Locally
Import duty often involves a significant upfront cost based on the declared value of the imported goods, which can increase the total expense of acquisition; however, it may provide access to potentially higher-quality or specialized products not available locally. Local registration fees are typically lower and support compliance with domestic regulations, simplifying tax administration and ensuring faster market entry for vehicles or equipment. Importing may face longer processing times and customs complexities, whereas local registration offers streamlined procedures but limited product variety.
Tips for Car Buyers: Navigating Taxes and Fees
Car buyers should carefully compare import duty rates with local registration fees to understand the total cost of vehicle acquisition. Import duties vary based on vehicle type, engine size, and country of origin, often representing a significant upfront cost. Local registration fees may include road taxes and insurance surcharges, making it essential to calculate both to budget accurately before purchasing.
Import Duty vs Local Registration Fee Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com