Electric vehicles benefit from lower tax rates compared to petrol vehicles due to incentives aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainability. Petrol vehicles are subject to higher fuel taxes and emission-related levies, reflecting their environmental impact and fuel consumption. Tax policies increasingly favor electric vehicles to accelerate the transition to greener transportation and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Table of Comparison
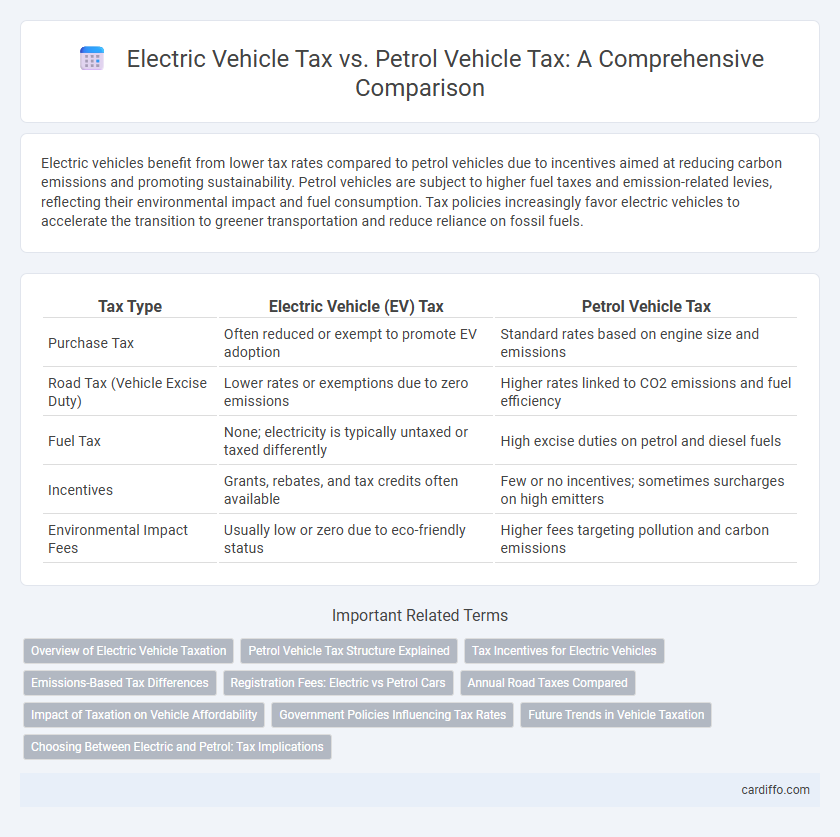
| Tax Type | Electric Vehicle (EV) Tax | Petrol Vehicle Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Purchase Tax | Often reduced or exempt to promote EV adoption | Standard rates based on engine size and emissions |
| Road Tax (Vehicle Excise Duty) | Lower rates or exemptions due to zero emissions | Higher rates linked to CO2 emissions and fuel efficiency |
| Fuel Tax | None; electricity is typically untaxed or taxed differently | High excise duties on petrol and diesel fuels |
| Incentives | Grants, rebates, and tax credits often available | Few or no incentives; sometimes surcharges on high emitters |
| Environmental Impact Fees | Usually low or zero due to eco-friendly status | Higher fees targeting pollution and carbon emissions |
Overview of Electric Vehicle Taxation
Electric vehicle (EV) taxation often includes incentives such as reduced registration fees, tax credits, and exemptions from road taxes to promote environmental sustainability. In contrast, petrol vehicles are typically subject to higher fuel taxes and pollution levies aimed at discouraging carbon emissions. Governments worldwide are increasingly adjusting tax structures to balance revenue needs with the urgent shift towards cleaner transportation technologies.
Petrol Vehicle Tax Structure Explained
Petrol vehicle tax is structured around fuel excise duties, value-added tax (VAT), and registration fees, with excise duties based on liters of fuel consumed, directly impacting running costs. Higher road taxes are often imposed on petrol vehicles due to their carbon emissions, promoting environmental sustainability through fiscal measures. This contrasts with the electric vehicle tax framework, which typically emphasizes lower or zero fuel excise duties to incentivize cleaner transportation alternatives.
Tax Incentives for Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) benefit from substantial tax incentives including federal tax credits up to $7,500 and state-level rebates, significantly reducing overall ownership costs compared to petrol vehicles. Petrol vehicles are typically subject to higher fuel excise taxes and lack comparable tax credits, increasing their long-term expense. These tax incentives for EVs aim to promote environmentally friendly transportation and accelerate the transition away from fossil fuel dependence.
Emissions-Based Tax Differences
Electric vehicle (EV) taxes are structured to incentivize low emissions, often featuring reduced registration fees or tax credits compared to petrol vehicles, which face higher taxes due to their greater carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. Emission-based tax systems use CO2 output measured in grams per kilometer to determine the tax rate, resulting in petrol vehicles incurring higher fees aligned with their environmental impact. This differentiation promotes electric vehicle adoption by lowering ownership costs linked to emissions, thereby supporting national carbon reduction targets.
Registration Fees: Electric vs Petrol Cars
Electric vehicle registration fees are often lower than those for petrol vehicles as governments promote cleaner transportation options through financial incentives. Some regions implement reduced or waived registration fees for electric cars to encourage adoption and offset higher upfront costs. Petrol vehicle registrations typically incur higher fees reflecting environmental impact and fuel consumption policies.
Annual Road Taxes Compared
Annual road taxes for electric vehicles (EVs) are significantly lower than those for petrol vehicles due to government incentives aimed at reducing carbon emissions. Petrol vehicles face higher road tax rates based on engine size and CO2 emissions, resulting in increased annual costs. This tax disparity supports the adoption of electric vehicles by making them more economically attractive over time.
Impact of Taxation on Vehicle Affordability
Electric vehicle (EV) tax incentives significantly reduce the purchase cost, making EVs more affordable compared to petrol vehicles, which often face higher fuel taxes and vehicle excise duties. Governments implement lower or zero emissions-based taxes on EVs, leading to long-term savings on ownership costs through reduced fuel and maintenance expenses. Higher taxation on petrol vehicles increases overall expenses, discouraging their purchase and accelerating the shift toward environmentally friendly transportation.
Government Policies Influencing Tax Rates
Government policies significantly influence tax rates for electric vehicles (EVs) and petrol vehicles, often favoring EVs through tax incentives such as credits, rebates, and reduced registration fees to promote environmental sustainability. Petrol vehicles typically face higher fuel taxes, carbon levies, and stricter emission compliance costs aimed at discouraging fossil fuel consumption and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Tax frameworks vary by jurisdiction but commonly include differential VAT rates, excise taxes, and import duties designed to accelerate the transition to cleaner transportation options.
Future Trends in Vehicle Taxation
Future vehicle taxation trends emphasize increased tax incentives for electric vehicles to accelerate the transition to sustainable transportation. Governments worldwide are progressively implementing higher taxes and stricter emissions regulations on petrol vehicles to discourage fossil fuel consumption. Data from the International Energy Agency indicates a steady rise in electric vehicle tax rebates, reflecting policy shifts favoring environmental goals and carbon neutrality commitments by 2030.
Choosing Between Electric and Petrol: Tax Implications
Electric vehicle (EV) taxes often include reduced registration fees, tax credits, and exemptions from fuel taxes, making them financially attractive compared to petrol vehicles that incur higher fuel taxes and emissions-based surcharges. Government incentives for EVs can significantly lower overall ownership costs, while petrol vehicles face increasing taxes aimed at discouraging fossil fuel use and reducing carbon emissions. Evaluating these tax implications is crucial for consumers deciding between electric and petrol vehicles, as it impacts total cost of ownership and environmental compliance.
Electric Vehicle Tax vs Petrol Vehicle Tax Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com