Private car tax rates differ significantly from commercial vehicle tax, reflecting the distinct usage and economic impact of each. While private car taxes are typically calculated based on factors like engine size, emissions, and vehicle age, commercial vehicle taxes often consider payload capacity and business usage. Understanding these differences helps optimize tax liabilities for both individual owners and businesses.
Table of Comparison
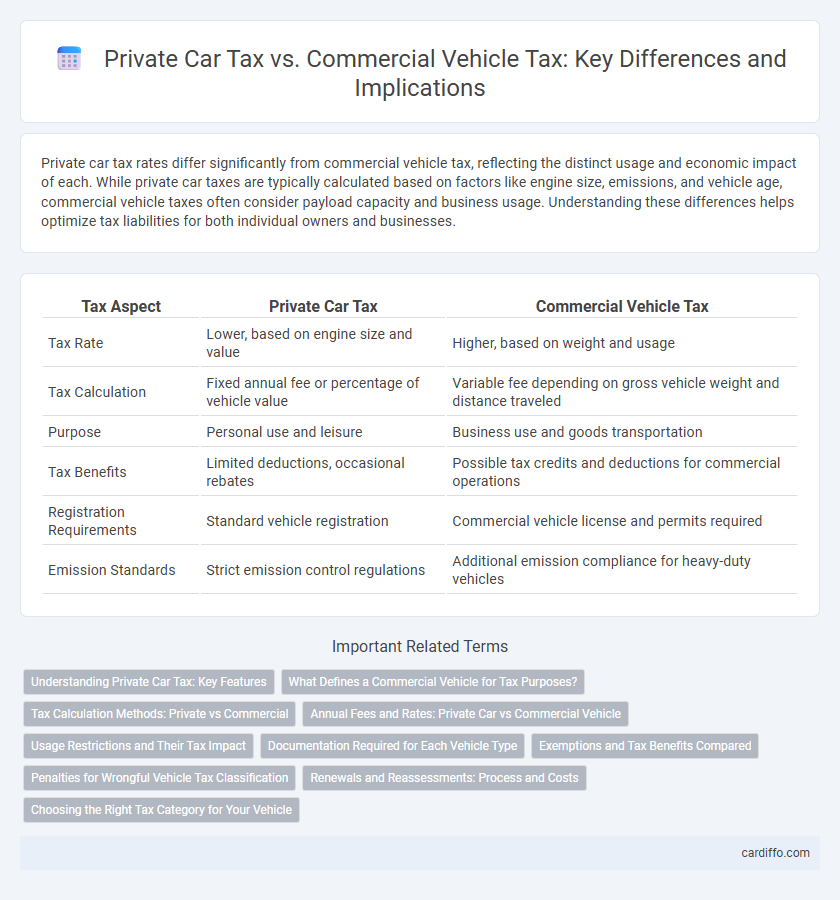
| Tax Aspect | Private Car Tax | Commercial Vehicle Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Rate | Lower, based on engine size and value | Higher, based on weight and usage |
| Tax Calculation | Fixed annual fee or percentage of vehicle value | Variable fee depending on gross vehicle weight and distance traveled |
| Purpose | Personal use and leisure | Business use and goods transportation |
| Tax Benefits | Limited deductions, occasional rebates | Possible tax credits and deductions for commercial operations |
| Registration Requirements | Standard vehicle registration | Commercial vehicle license and permits required |
| Emission Standards | Strict emission control regulations | Additional emission compliance for heavy-duty vehicles |
Understanding Private Car Tax: Key Features
Private Car Tax primarily applies to vehicles used for personal transportation, with rates typically based on engine size, vehicle value, and emissions. Key features include lower tax rates compared to commercial vehicles and specific exemptions for environmentally friendly models, such as hybrids and electric cars. These tax policies aim to promote personal vehicle ownership while encouraging eco-friendly choices through financial incentives.
What Defines a Commercial Vehicle for Tax Purposes?
A commercial vehicle for tax purposes is defined by its primary use in business activities, such as transporting goods or passengers for profit, rather than personal use. Tax regulations often classify vehicles based on factors like weight, registration, and purpose, distinguishing commercial vehicles to enforce different tax rates and deductions. Understanding these definitions impacts tax liabilities, with commercial vehicles typically subject to higher or specialized tax rates compared to private cars.
Tax Calculation Methods: Private vs Commercial
Private car tax calculations typically rely on engine size, CO2 emissions, or vehicle value, with rates varying by region and vehicle age to incentivize eco-friendly choices. Commercial vehicle tax is often based on weight, usage, and the number of axles, reflecting the vehicle's impact on infrastructure and its business purpose. Differences in tax brackets and exemptions between private and commercial categories ensure fair taxation aligned with vehicle function and road wear.
Annual Fees and Rates: Private Car vs Commercial Vehicle
Private cars typically incur an annual tax fee based on engine capacity and vehicle age, with rates varying by state or country regulations. Commercial vehicles face higher annual tax rates reflecting their heavier usage and commercial purpose, often including additional charges such as weight-based fees or environmental levies. These differentiated rates ensure that commercial vehicles contribute proportionally more to road maintenance and infrastructure funding compared to private cars.
Usage Restrictions and Their Tax Impact
Private car tax rates are generally lower due to limited usage restrictions, as these vehicles primarily serve personal transportation purposes. Commercial vehicle tax is higher, reflecting their extensive use in business operations, cargo transport, and passenger services, which leads to increased wear and road usage. Usage restrictions such as mileage limits and zonal access further influence tax assessment, with commercial vehicles often subject to stricter regulations and higher tax liabilities.
Documentation Required for Each Vehicle Type
Private car tax documentation requires proof of ownership such as a vehicle registration certificate, valid insurance papers, and a recent emissions test report. Commercial vehicle tax demands more extensive documentation including vehicle registration, commercial insurance policy, permits for goods or passenger transport, and compliance certificates for safety and emission standards. Accurate and complete documentation ensures proper assessment and payment of taxes for both private and commercial vehicles.
Exemptions and Tax Benefits Compared
Private car tax exemptions often include benefits such as reduced rates for electric vehicles and senior citizen discounts, promoting environmentally friendly choices and social equity. Commercial vehicle tax exemptions typically cover goods transport vehicles used in agriculture or essential services, encouraging business growth and economic efficiency. Understanding these exemptions helps taxpayers optimize tax liabilities by leveraging specific benefits based on vehicle classification and intended use.
Penalties for Wrongful Vehicle Tax Classification
Misclassifying a private car as a commercial vehicle or vice versa can result in significant penalties including fines, back taxes, and interest charges assessed by tax authorities. Incorrect classification may trigger audits and legal consequences under tax compliance regulations, increasing financial liability for vehicle owners. Proper vehicle tax classification ensures adherence to state and federal tax codes, avoiding costly penalties and maintaining eligibility for related tax benefits.
Renewals and Reassessments: Process and Costs
Private car tax renewals typically require annual payment based on vehicle age and emissions, with straightforward reassessment procedures generally handled online or at local tax offices. Commercial vehicle tax renewals often involve higher fees, incorporating factors like vehicle weight, usage type, and emission standards, with more frequent and detailed reassessments to reflect operational changes. Costs for commercial vehicle tax reassessments are usually higher due to stricter regulatory compliance and additional documentation requirements compared to private car tax processes.
Choosing the Right Tax Category for Your Vehicle
Selecting the appropriate tax category hinges on your vehicle's primary use, with private car tax rates typically lower for personal transportation compared to commercial vehicle tax applied to vehicles used for business purposes. Understanding the distinction between these tax categories ensures compliance and optimal tax benefits, as commercial vehicle taxes often include higher fees and different exemption criteria. Accurate classification based on vehicle usage prevents penalties and leverages possible deductions or incentives aligned with private or commercial tax regulations.
Private Car Tax vs Commercial Vehicle Tax Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com