The Green Vehicle Tax Credit offers significant financial incentives for purchasing electric and hybrid cars, promoting eco-friendly transportation and reducing carbon emissions. In contrast, the Gasoline Car Tax Credit is generally smaller and less common, reflecting the environmental impact of fossil fuel consumption. Choosing a green vehicle not only benefits the environment but also provides substantial tax savings compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars.
Table of Comparison
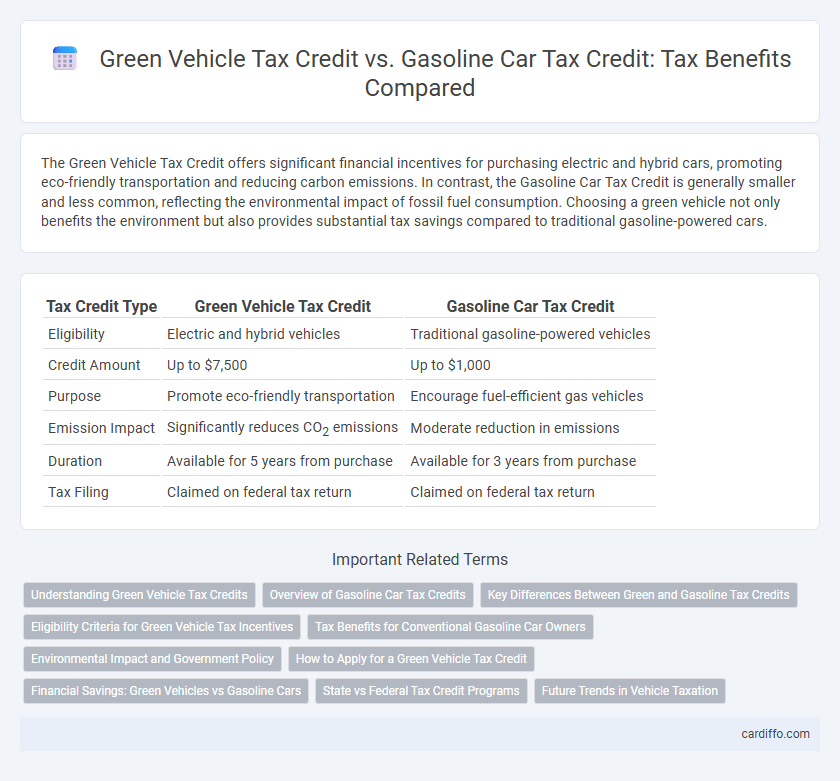
| Tax Credit Type | Green Vehicle Tax Credit | Gasoline Car Tax Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Electric and hybrid vehicles | Traditional gasoline-powered vehicles |
| Credit Amount | Up to $7,500 | Up to $1,000 |
| Purpose | Promote eco-friendly transportation | Encourage fuel-efficient gas vehicles |
| Emission Impact | Significantly reduces CO2 emissions | Moderate reduction in emissions |
| Duration | Available for 5 years from purchase | Available for 3 years from purchase |
| Tax Filing | Claimed on federal tax return | Claimed on federal tax return |
Understanding Green Vehicle Tax Credits
Green vehicle tax credits provide financial incentives to promote the adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles by reducing the upfront cost through government rebates or deductions. These credits often vary by country and state, with specific eligibility requirements based on battery capacity, vehicle type, and price limits. Understanding green vehicle tax credits helps consumers maximize savings compared to traditional gasoline car tax credits, which typically offer fewer benefits and are geared towards fuel efficiency rather than emissions reduction.
Overview of Gasoline Car Tax Credits
Gasoline car tax credits primarily aim to incentivize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by offering rebates or deductions based on miles per gallon (MPG) ratings or purchase of hybrid models. These credits vary significantly by state and federal programs, often providing smaller financial benefits compared to green vehicle tax credits for electric or plug-in hybrid vehicles. Understanding eligibility criteria and credit limits is essential for maximizing tax benefits on gasoline-powered vehicles.
Key Differences Between Green and Gasoline Tax Credits
Green Vehicle Tax Credits primarily incentivize electric, hybrid, and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles by offering substantial deductions based on battery capacity and vehicle price, promoting environmentally friendly transportation. Gasoline Car Tax Credits, in contrast, are less common and typically focus on fuel efficiency improvements or alternative fuels, offering smaller credits that directly relate to gasoline consumption reductions. The key differences lie in the eligibility criteria, credit amounts, and the underlying environmental goals, with green vehicle credits aiming to reduce carbon emissions significantly while gasoline credits encourage marginal improvements in fuel economy.
Eligibility Criteria for Green Vehicle Tax Incentives
Eligibility criteria for green vehicle tax incentives typically require that the vehicle be fully electric, plug-in hybrid, or hydrogen fuel cell-powered, with a minimum battery capacity often set around 4 kWh. Qualifying vehicles must meet manufacturer-specific MSRP thresholds and comply with assembly location requirements within North America to ensure access to federal tax credits. Consumers must also meet income limits and purchase new vehicles directly from authorized dealers to claim the green vehicle tax credit, distinguishing it from gasoline car tax credits, which are generally less common and less generous.
Tax Benefits for Conventional Gasoline Car Owners
Conventional gasoline car owners receive limited tax benefits compared to electric vehicle incentives, with federal tax credits generally capped at lower amounts or unavailable altogether. State-level tax rebates and deductions for gasoline-powered cars often focus on emissions reduction programs and fuel efficiency improvements, rather than direct purchase credits. Understanding these tax structures helps gasoline car owners optimize savings primarily through fuel-related deductions and maintenance cost allowances.
Environmental Impact and Government Policy
Green Vehicle Tax Credits incentivize electric and hybrid vehicles by reducing emissions and promoting sustainable transportation, aligning with government policies targeting carbon footprint reduction. Gasoline Car Tax Credits, less common today, often fail to address air pollution effectively due to higher greenhouse gas emissions. Government policy increasingly favors green vehicle incentives to meet climate goals and enhance environmental health.
How to Apply for a Green Vehicle Tax Credit
To apply for a Green Vehicle Tax Credit, taxpayers must complete IRS Form 8936, which requires details about the qualified electric or plug-in hybrid vehicle, including the make, model, and VIN. The credit amount depends on the battery capacity and phase-out status for the manufacturer, so reviewing up-to-date IRS guidelines is essential. Submitting Form 8936 with the federal tax return claims the credit, reducing the taxpayer's overall federal income tax liability.
Financial Savings: Green Vehicles vs Gasoline Cars
Green vehicle tax credits offer significant financial savings by reducing the upfront cost of electric and hybrid cars, often ranging from $2,500 to $7,500 depending on the battery capacity and manufacturer. In contrast, gasoline car tax incentives are generally limited or non-existent, leading to higher overall fuel and maintenance expenses over time. Consumers choosing green vehicles benefit from lower operating costs and governmental rebates, increasing total cost savings compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars.
State vs Federal Tax Credit Programs
State tax credit programs for green vehicles often provide additional incentives beyond the federal tax credit, varying widely by location and vehicle type. Federal tax credits cover plug-in electric and fuel cell vehicles with standardized amounts up to $7,500, while state credits can include rebates, reduced registration fees, and exemptions from emissions testing. Combining state and federal incentives can significantly lower the upfront cost of green vehicles compared to gasoline car tax credits, which are generally limited and less substantial at both levels.
Future Trends in Vehicle Taxation
Future trends in vehicle taxation emphasize increased incentives for green vehicle tax credits, reflecting global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable transportation. Gasoline car tax credits are expected to diminish as governments implement stricter environmental regulations and higher taxes on fossil fuel consumption. Advances in electric vehicle technology and expanding charging infrastructure will further accelerate the shift towards preferential tax treatment for eco-friendly vehicles.
Green Vehicle Tax Credit vs Gasoline Car Tax Credit Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com