Import duty is a government-imposed fee on goods brought into a country, influencing the overall cost of imported vehicles and products. Local registration tax applies specifically to registering vehicles within the jurisdiction, affecting the total expenses for vehicle owners after importation. Understanding the differences between import duty and local registration tax is crucial for accurate budgeting and compliance with tax regulations.
Table of Comparison
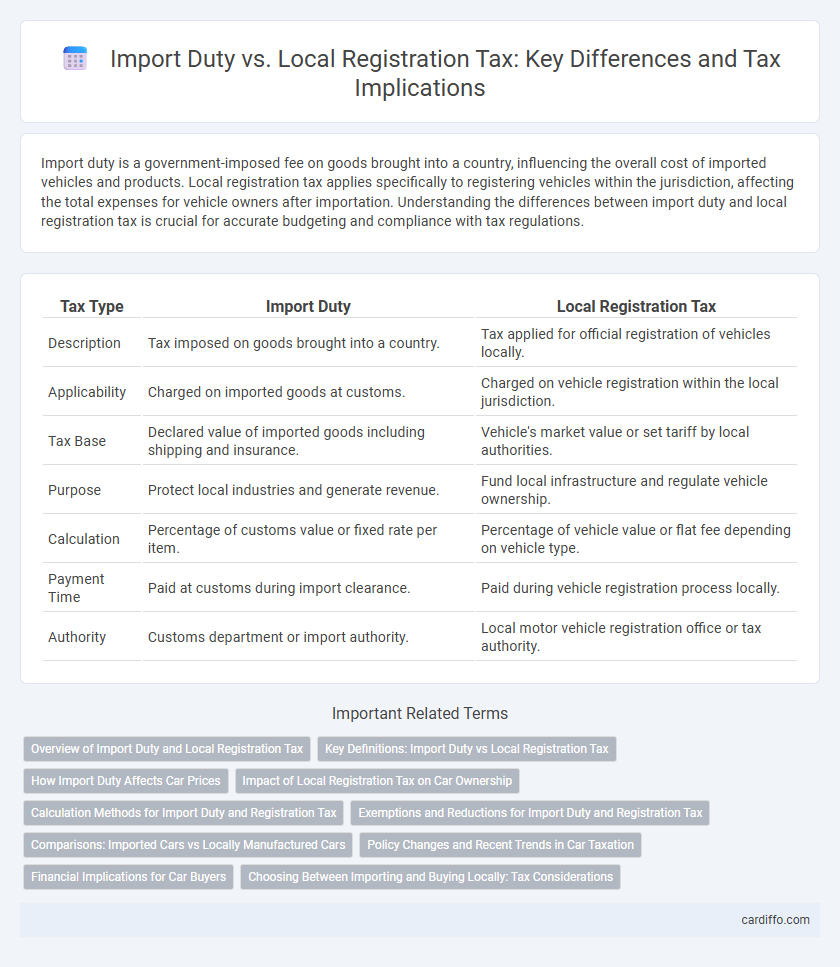
| Tax Type | Import Duty | Local Registration Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Tax imposed on goods brought into a country. | Tax applied for official registration of vehicles locally. |
| Applicability | Charged on imported goods at customs. | Charged on vehicle registration within the local jurisdiction. |
| Tax Base | Declared value of imported goods including shipping and insurance. | Vehicle's market value or set tariff by local authorities. |
| Purpose | Protect local industries and generate revenue. | Fund local infrastructure and regulate vehicle ownership. |
| Calculation | Percentage of customs value or fixed rate per item. | Percentage of vehicle value or flat fee depending on vehicle type. |
| Payment Time | Paid at customs during import clearance. | Paid during vehicle registration process locally. |
| Authority | Customs department or import authority. | Local motor vehicle registration office or tax authority. |
Overview of Import Duty and Local Registration Tax
Import duty is a government-imposed tax on goods brought into a country, calculated based on the product's value, type, and origin to protect domestic industries and generate revenue. Local registration tax applies to vehicles and certain assets upon local registration, often varying by jurisdiction and calculated using factors like vehicle type, engine size, or assessed value. Understanding the distinct calculation methods and purposes of import duty versus local registration tax is essential for compliance and cost management in international trade and asset registration.
Key Definitions: Import Duty vs Local Registration Tax
Import duty is a government-imposed tax on goods brought into a country, calculated based on the item's value, category, and origin. Local registration tax is a domestic fee applied when registering assets such as vehicles or properties within a jurisdiction, often calculated as a percentage of the asset's declared value or market price. Both taxes impact the total cost of ownership but apply at different stages--import duty at entry and local registration tax during official registration.
How Import Duty Affects Car Prices
Import duty significantly increases the final price of cars by adding a percentage cost based on the vehicle's declared import value, directly impacting affordability for consumers. Local registration tax, calculated on factors like engine capacity and emission standards, further influences the total ownership cost but varies regionally. Understanding the cumulative effect of import duty and registration tax is crucial for accurate car price estimation in international markets.
Impact of Local Registration Tax on Car Ownership
Local registration tax significantly increases the overall cost of car ownership, often exceeding the initial import duty paid at customs. This tax varies by region but typically adds a substantial financial burden, influencing buyers' decisions and discouraging the purchase of imported vehicles. High local registration fees reduce market demand and impact the total cost of maintaining a vehicle over time.
Calculation Methods for Import Duty and Registration Tax
Import duty is calculated based on the customs value of the goods, which includes the cost, insurance, and freight (CIF) of the imported items, multiplied by the specific tariff rate set by the importing country. Local registration tax, often applied to vehicles, is computed using factors such as the vehicle's engine capacity, age, and market value, reflecting regional tax policies and depreciation schedules. Both taxes require precise documentation and valuation methods to ensure compliance with local tax authorities and avoid penalties.
Exemptions and Reductions for Import Duty and Registration Tax
Import duty exemptions typically apply to diplomatic imports, essential goods, and specific raw materials, reducing the initial cost burden for eligible importers. Local registration tax reductions are often granted for electric vehicles, vehicles used by persons with disabilities, and vintage cars to encourage sustainability and social inclusion. Both import duty and registration tax exemptions aim to stimulate economic growth while supporting targeted policy goals.
Comparisons: Imported Cars vs Locally Manufactured Cars
Import duty on imported cars significantly increases their overall cost compared to locally manufactured vehicles, as this tax is applied as a percentage of the car's declared value at customs. Local registration tax often varies based on engine size, emissions, and vehicle age, impacting both imported and domestic cars but generally favors locally produced models due to incentive policies. Comparing total tax burdens, imported cars face higher upfront import duties, while locally manufactured cars benefit from reduced or exempted registration fees, resulting in lower overall expenses.
Policy Changes and Recent Trends in Car Taxation
Recent policy changes in car taxation highlight a shift towards higher import duties to protect domestic automotive industries while local registration taxes have been adjusted to promote environmentally friendly vehicles. Governments are increasingly aligning import duty rates with emission standards, incentivizing electric and hybrid car registrations through reduced local taxes. Trends indicate a growing emphasis on sustainable transport, with fiscal measures encouraging consumers to choose low-emission vehicles via strategic import duty hikes and favorable local registration tax structures.
Financial Implications for Car Buyers
Import duty significantly increases the initial cost of purchasing a foreign vehicle, often amounting to 10-30% of the car's value depending on the country's tariff rates. Local registration tax, typically calculated based on vehicle price, engine size, or emissions, can add another substantial financial burden at the time of vehicle registration. Car buyers must assess both import duty and local registration tax as they directly impact the overall cost of ownership and affordability.
Choosing Between Importing and Buying Locally: Tax Considerations
When deciding between importing a vehicle or purchasing locally, understanding the import duty versus local registration tax is crucial to optimizing overall costs. Import duty rates vary based on the vehicle's origin, engine size, and age, often making imported vehicles subject to higher initial taxes compared to local purchases. Local registration tax typically includes roadworthiness fees, emissions standards, and vehicle type categories, which can influence annual expenses and ownership affordability.
Import duty vs local registration tax Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com