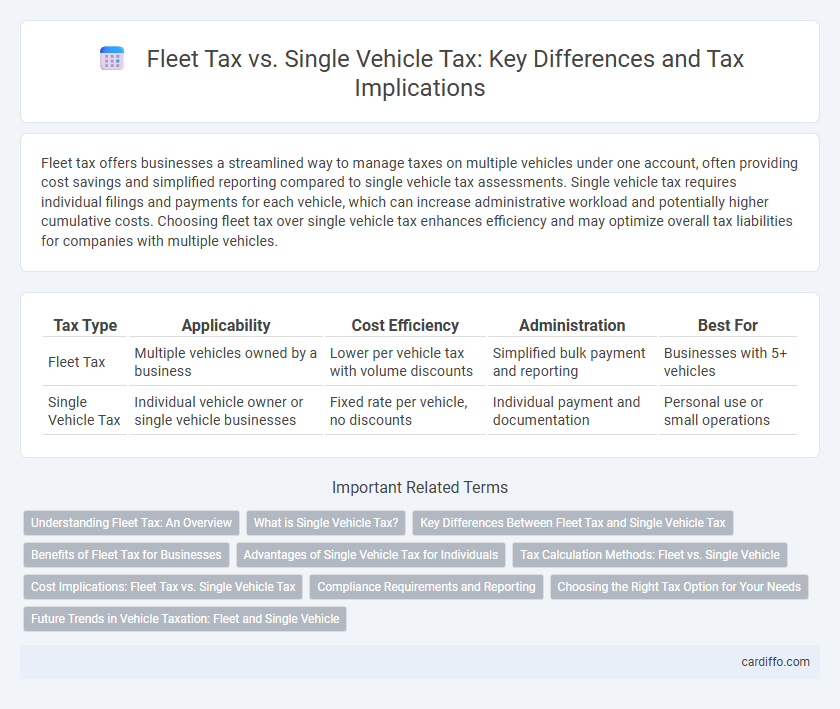
Fleet tax offers businesses a streamlined way to manage taxes on multiple vehicles under one account, often providing cost savings and simplified reporting compared to single vehicle tax assessments. Single vehicle tax requires individual filings and payments for each vehicle, which can increase administrative workload and potentially higher cumulative costs. Choosing fleet tax over single vehicle tax enhances efficiency and may optimize overall tax liabilities for companies with multiple vehicles.
Table of Comparison
| Tax Type | Applicability | Cost Efficiency | Administration | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fleet Tax | Multiple vehicles owned by a business | Lower per vehicle tax with volume discounts | Simplified bulk payment and reporting | Businesses with 5+ vehicles |
| Single Vehicle Tax | Individual vehicle owner or single vehicle businesses | Fixed rate per vehicle, no discounts | Individual payment and documentation | Personal use or small operations |
Understanding Fleet Tax: An Overview
Fleet tax applies to companies or individuals owning multiple vehicles, providing a streamlined payment process and often discounted rates compared to taxing each vehicle individually. This tax system simplifies accounting and compliance for businesses with extensive vehicle inventories. Understanding fleet tax helps optimize tax liabilities and ensures efficient management of transportation expenses.
What is Single Vehicle Tax?
Single Vehicle Tax is a mandatory tax imposed on individual vehicles, calculated based on factors such as engine size, vehicle weight, and emissions. This tax differs from fleet tax, which applies collectively to a group of vehicles owned by a single entity, often with varying rates and regulations. Understanding Single Vehicle Tax is crucial for individuals as it directly affects vehicle registration fees and ongoing ownership costs.
Key Differences Between Fleet Tax and Single Vehicle Tax
Fleet tax applies to multiple vehicles owned by a single entity and is often calculated based on total fleet size, weight, or usage, offering potential bulk rate advantages. Single vehicle tax is assessed individually on each vehicle, considering factors like engine size, emissions, and registration type. Key differences highlight fleet tax's aggregated approach versus the personalized assessment inherent in single vehicle tax calculations.
Benefits of Fleet Tax for Businesses
Fleet tax offers businesses significant cost savings by consolidating multiple vehicle taxes into a single, streamlined payment, reducing administrative burdens. It simplifies accounting processes and improves cash flow management, allowing companies to allocate resources more efficiently. Moreover, fleet tax often provides volume-based discounts and enhanced compliance tracking, resulting in long-term financial benefits.
Advantages of Single Vehicle Tax for Individuals
Single Vehicle Tax offers individuals greater flexibility by allowing them to pay taxes based solely on the number of vehicles they own, reducing unnecessary costs associated with fleet-wide assessments. This tax structure simplifies budgeting for private vehicle owners, as charges are directly proportional to their personal vehicle usage rather than a collective fleet. Individualized taxation also facilitates easier compliance and administrative management by local authorities.
Tax Calculation Methods: Fleet vs. Single Vehicle
Fleet tax calculation aggregates the total taxable value of all vehicles within a company's fleet, often applying volume-based discounts and tiered tax rates to optimize overall tax liability. Single vehicle tax calculation assesses each vehicle individually based on factors such as weight, engine size, and emissions, resulting in precise but potentially higher cumulative costs. Companies managing multiple vehicles benefit from fleet taxation methods that provide streamlined assessments and potential cost savings compared to single vehicle tax computations.
Cost Implications: Fleet Tax vs. Single Vehicle Tax
Fleet tax typically offers cost advantages as it consolidates multiple vehicles under one tax payment, reducing administrative expenses and often qualifying for bulk discounts. Single vehicle tax requires individual payments for each vehicle, leading to higher cumulative costs and increased paperwork. Businesses managing numerous vehicles find fleet tax more economical and efficient compared to single vehicle tax.
Compliance Requirements and Reporting
Fleet tax requires businesses to maintain detailed records for all vehicles, including mileage, usage, and maintenance logs, to ensure compliance with tax regulations. Single vehicle tax compliance involves tracking and reporting information specific to an individual vehicle, such as registration details, fuel usage, and tax payment status. Accurate reporting in both cases is essential to avoid penalties, with fleet tax often demanding more comprehensive data management systems due to the volume of vehicles involved.
Choosing the Right Tax Option for Your Needs
Fleet tax offers a streamlined approach for businesses managing multiple vehicles, providing cost savings through consolidated payments and simplified administration. Single vehicle tax suits individual owners or businesses with limited vehicles, allowing precise management of tax liabilities per vehicle. Evaluate the size of your fleet, usage patterns, and budget constraints to choose the most efficient tax strategy that minimizes expenses and compliance efforts.
Future Trends in Vehicle Taxation: Fleet and Single Vehicle
Future trends in vehicle taxation indicate a shift towards dynamic pricing models that factor in environmental impact, vehicle usage, and real-time data for both fleet and single vehicle taxes. Fleet tax systems are increasingly integrating advanced telematics and AI to optimize tax rates based on collective emissions and mileage patterns, while single vehicle taxes are evolving to include personalized assessments reflecting individual driver behavior and eco-efficiency. Governments are prioritizing sustainable transportation incentives, encouraging fleets to adopt electric vehicles through reduced tax rates and implementing stricter emission-based taxes for single vehicles to support climate goals.
fleet tax vs single vehicle tax Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com