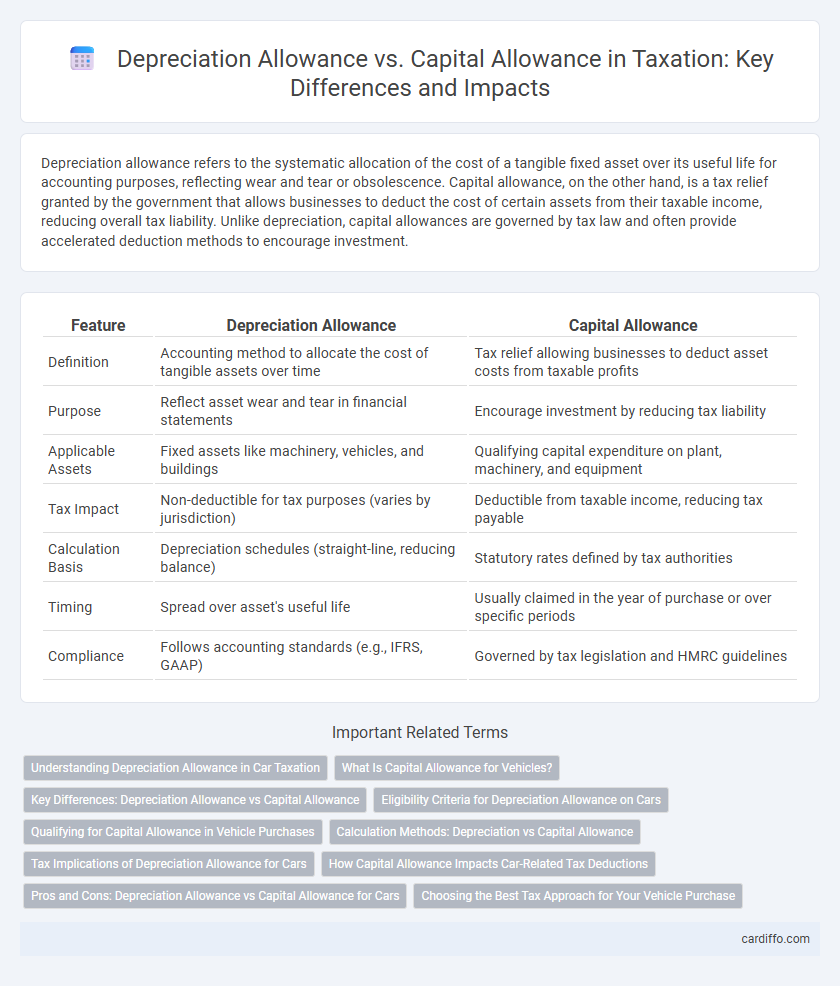
Depreciation allowance refers to the systematic allocation of the cost of a tangible fixed asset over its useful life for accounting purposes, reflecting wear and tear or obsolescence. Capital allowance, on the other hand, is a tax relief granted by the government that allows businesses to deduct the cost of certain assets from their taxable income, reducing overall tax liability. Unlike depreciation, capital allowances are governed by tax law and often provide accelerated deduction methods to encourage investment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Depreciation Allowance | Capital Allowance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting method to allocate the cost of tangible assets over time | Tax relief allowing businesses to deduct asset costs from taxable profits |
| Purpose | Reflect asset wear and tear in financial statements | Encourage investment by reducing tax liability |
| Applicable Assets | Fixed assets like machinery, vehicles, and buildings | Qualifying capital expenditure on plant, machinery, and equipment |
| Tax Impact | Non-deductible for tax purposes (varies by jurisdiction) | Deductible from taxable income, reducing tax payable |
| Calculation Basis | Depreciation schedules (straight-line, reducing balance) | Statutory rates defined by tax authorities |
| Timing | Spread over asset's useful life | Usually claimed in the year of purchase or over specific periods |
| Compliance | Follows accounting standards (e.g., IFRS, GAAP) | Governed by tax legislation and HMRC guidelines |
Understanding Depreciation Allowance in Car Taxation
Depreciation allowance in car taxation refers to the tax relief granted to business owners for the reduction in value of a vehicle over time due to wear and tear. This allowance is often calculated based on the car's purchase price and useful life, helping to offset the cost of using the vehicle for business purposes. Unlike capital allowances, which are tied to specific tax codes and rates, depreciation allowances focus on the gradual loss of value and directly impact taxable income by reducing profits.
What Is Capital Allowance for Vehicles?
Capital Allowance for vehicles enables businesses to deduct the cost of qualifying commercial vehicles from their taxable profits over time, reflecting asset depreciation. This allowance covers cars, vans, lorries, and other business-use vehicles, with specific rates depending on the vehicle's CO2 emissions and type. Claiming Capital Allowance reduces taxable income, helping businesses manage cash flow by spreading the vehicle's purchase cost across several tax years.
Key Differences: Depreciation Allowance vs Capital Allowance
Depreciation allowance refers to the accounting method of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life for financial reporting purposes, while capital allowance is a tax relief permitting businesses to deduct capital expenditure on qualifying assets from their taxable profits. Depreciation is based on accounting standards and does not reduce taxable income, whereas capital allowance is governed by tax laws and directly reduces tax liability. Capital allowances often include specific schemes such as Annual Investment Allowance (AIA) or First-Year Allowances (FYA), which accelerate relief compared to standard depreciation schedules.
Eligibility Criteria for Depreciation Allowance on Cars
Depreciation allowance on cars is typically available to businesses that use vehicles for income-generating activities, with eligibility often requiring the vehicle to be owned and used by the business rather than leased. Tax regulations may specify criteria such as business use percentage, type of vehicle, and cost limits to qualify for depreciation claims. Claimants must maintain accurate records demonstrating the car's role in business operations to meet the stringent requirements for depreciation allowance eligibility.
Qualifying for Capital Allowance in Vehicle Purchases
Qualifying for capital allowance in vehicle purchases requires the vehicle to be used for business purposes and meet specific criteria set by tax authorities, such as being new or having a limited private use percentage. Capital allowances allow businesses to deduct the cost of vehicles over time, often with enhanced first-year allowances for low-emission cars, maximizing tax relief. Depreciation allowance differs as it reflects accounting depreciation without direct tax relief, whereas capital allowance provides a structured tax deduction aligned with government guidelines.
Calculation Methods: Depreciation vs Capital Allowance
Depreciation allowance is calculated based on the asset's wear and tear over its useful life, typically using methods like straight-line or reducing balance to allocate the cost systematically. Capital allowance calculation involves applying specific rates set by tax authorities to the qualifying expenditure on capital assets, allowing businesses to claim tax relief on investments. Unlike depreciation, capital allowance is a tax-based deduction method that follows statutory rules rather than accounting principles.
Tax Implications of Depreciation Allowance for Cars
Depreciation allowance for cars directly reduces taxable profits by allocating the vehicle's cost over its useful life, lowering the immediate tax burden for businesses. Unlike capital allowance, which allows for a more structured tax deduction based on specific asset categories and government schedules, depreciation allowance offers flexibility but may result in different timing of tax benefits. Understanding these distinctions is critical for accurate tax planning and maximizing allowable deductions on car expenses.
How Capital Allowance Impacts Car-Related Tax Deductions
Capital allowance enables businesses to claim tax deductions on the depreciation of vehicle assets, reducing taxable profits by accounting for the car's wear and tear over its effective life. Unlike depreciation allowance, which is an accounting concept, capital allowance has specific tax rates and conditions governed by tax authorities, such as the Annual Investment Allowance or Writing Down Allowance. The utilization of capital allowances on cars directly lowers taxable income, making it a crucial factor in calculating vehicular tax relief and optimizing overall tax liability.
Pros and Cons: Depreciation Allowance vs Capital Allowance for Cars
Depreciation allowance for cars enables businesses to gradually reduce taxable income by accounting for wear and tear, but it often lacks standardized rates, leading to varied deductions and potential disputes with tax authorities. Capital allowance provides fixed percentages for car-related expenditures, offering more predictable tax benefits and compliance simplicity, yet it may limit the total deductible amount compared to actual depreciation values. Choosing between these allowances depends on factors like the vehicle's usage, cost, and the tax jurisdiction's specific rules on asset class and rates.
Choosing the Best Tax Approach for Your Vehicle Purchase
When selecting the best tax approach for your vehicle purchase, understanding the difference between depreciation allowance and capital allowance is crucial. Depreciation allowance accounts for the vehicle's gradual value reduction over time, providing annual tax relief based on wear and tear, while capital allowance offers upfront tax deductions on the initial purchase cost, often accelerating tax savings. Evaluating your business's cash flow, vehicle usage, and long-term financial goals will help determine whether depreciating the asset annually or claiming capital allowances maximizes your tax efficiency.
Depreciation Allowance vs Capital Allowance Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com