A Retail Installment Contract typically involves purchasing a vehicle through a dealership with financing provided by the dealer or a third-party lender, often including added fees and higher interest rates. Direct Auto Loans are arranged directly between the borrower and a bank or credit union, offering potentially lower interest rates and greater transparency. Choosing between the two depends on the buyer's preference for convenience versus cost savings and loan terms.
Table of Comparison
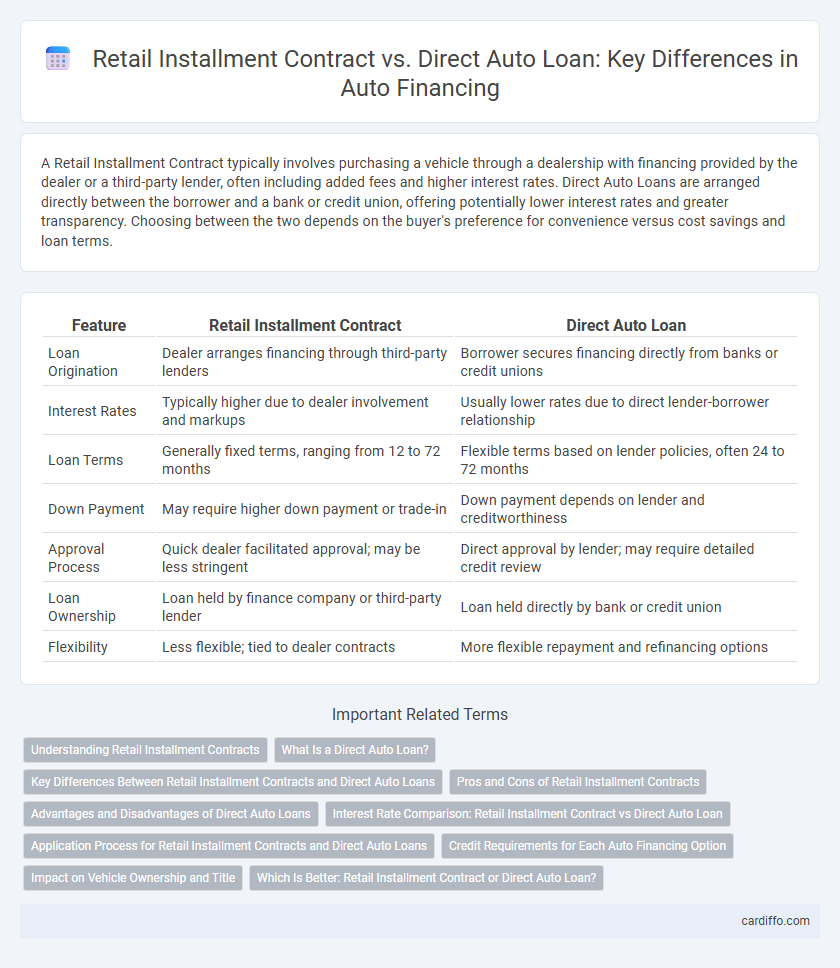
| Feature | Retail Installment Contract | Direct Auto Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Origination | Dealer arranges financing through third-party lenders | Borrower secures financing directly from banks or credit unions |
| Interest Rates | Typically higher due to dealer involvement and markups | Usually lower rates due to direct lender-borrower relationship |
| Loan Terms | Generally fixed terms, ranging from 12 to 72 months | Flexible terms based on lender policies, often 24 to 72 months |
| Down Payment | May require higher down payment or trade-in | Down payment depends on lender and creditworthiness |
| Approval Process | Quick dealer facilitated approval; may be less stringent | Direct approval by lender; may require detailed credit review |
| Loan Ownership | Loan held by finance company or third-party lender | Loan held directly by bank or credit union |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; tied to dealer contracts | More flexible repayment and refinancing options |
Understanding Retail Installment Contracts
Retail Installment Contracts (RIC) involve a buyer financing a vehicle purchase directly through the seller, typically a dealership, with payments made in installments over time. Unlike Direct Auto Loans where the borrower secures financing from a bank or credit union, RICs combine the purchase and loan agreement in a single contract, often including higher interest rates and fees. Understanding the terms, such as the total payment amount and interest rate specified in the Retail Installment Contract, is crucial for buyers to avoid unexpected costs and ensure affordability.
What Is a Direct Auto Loan?
A direct auto loan is a financing option where a consumer borrows money directly from a bank, credit union, or online lender to purchase a vehicle, offering competitive interest rates and flexible terms. Unlike a retail installment contract, which is arranged through the dealership with the dealer often acting as the lender, a direct auto loan allows buyers to negotiate the vehicle price upfront and choose their lender independently. This type of loan provides greater transparency and often lower overall costs by cutting out intermediaries in the vehicle financing process.
Key Differences Between Retail Installment Contracts and Direct Auto Loans
Retail installment contracts involve the buyer making fixed monthly payments directly to the dealership or lender over a specified term, often including interest and fees embedded in the total price of the vehicle. Direct auto loans are secured loans obtained from banks or credit unions, where borrowers receive funds upfront to purchase the vehicle and then repay the lender with interest over time. The key differences lie in the origination sources, payment structures, interest rates, and flexibility, with retail installment contracts generally having higher rates and less borrower control compared to direct auto loans.
Pros and Cons of Retail Installment Contracts
Retail Installment Contracts offer flexible repayment terms and fixed interest rates, making monthly payments predictable and helping borrowers manage budgets effectively. These contracts often include fees and higher interest rates compared to direct auto loans, increasing the overall cost of borrowing. Unlike direct auto loans, retail installment contracts are typically arranged through dealerships, potentially limiting borrower negotiation power and transparency in loan terms.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Direct Auto Loans
Direct auto loans offer lower interest rates compared to retail installment contracts due to fewer intermediaries and quicker approval processes. However, borrowers might face stricter credit requirements and less flexible repayment terms with direct auto loans. These loans provide more transparency in fees and loan conditions but can limit dealership incentives and negotiating power on the vehicle price.
Interest Rate Comparison: Retail Installment Contract vs Direct Auto Loan
Retail Installment Contracts typically feature higher interest rates compared to Direct Auto Loans due to the added risk and convenience offered by dealerships, often ranging from 6% to 12% APR. In contrast, Direct Auto Loans from banks or credit unions generally provide lower interest rates, averaging between 3% and 7% APR, reflecting stricter lending criteria and lower borrower risk. Borrowers seeking the most cost-effective financing should prioritize Direct Auto Loans for their better interest rate terms and potential savings over time.
Application Process for Retail Installment Contracts and Direct Auto Loans
The application process for Retail Installment Contracts typically involves visiting a dealership where the borrower completes financing paperwork with the dealer, who then works with multiple lenders to secure a loan offer. In contrast, Direct Auto Loans require the borrower to apply directly with a bank, credit union, or online lender before shopping for a vehicle, often enabling more control over loan terms and approval criteria. Both processes require credit checks, income verification, and documentation of vehicle details, but Retail Installment Contracts streamline approval through dealer intermediaries.
Credit Requirements for Each Auto Financing Option
Retail installment contracts often have more flexible credit requirements, making them accessible to borrowers with lower credit scores or limited credit history. Direct auto loans typically require higher credit scores and stronger financial profiles, as lenders assess creditworthiness more rigorously to minimize risk. Understanding these differences helps consumers select the best financing option based on their credit status and financial goals.
Impact on Vehicle Ownership and Title
Retail Installment Contracts often involve the lender holding the vehicle title until the loan is fully paid, affecting the borrower's immediate ownership rights and ability to sell the vehicle. Direct Auto Loans typically grant the borrower full ownership and title upon purchase, allowing greater control over the vehicle from the outset. Understanding the differences in title retention and ownership impact is crucial when choosing between these financing options for a vehicle purchase.
Which Is Better: Retail Installment Contract or Direct Auto Loan?
Retail Installment Contracts often include dealer add-ons and may have higher interest rates, making monthly payments potentially more expensive compared to Direct Auto Loans, which typically offer lower rates through banks or credit unions. Direct Auto Loans provide more control over the financing process and usually require less paperwork, benefiting borrowers looking for transparency and cost efficiency. Choosing between the two depends on priorities such as convenience, interest costs, and willingness to negotiate terms directly with the lender or dealer.
Retail Installment Contract vs Direct Auto Loan Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com