Refinancing a loan involves replacing an existing loan with a new one, often to secure better interest rates or improved repayment terms. Unlike the original loan, refinancing can reduce monthly payments, lower the overall interest paid, or extend the loan duration according to the borrower's current financial situation. Carefully comparing the costs and benefits of refinancing versus sticking with the original loan is essential to optimize financial outcomes.
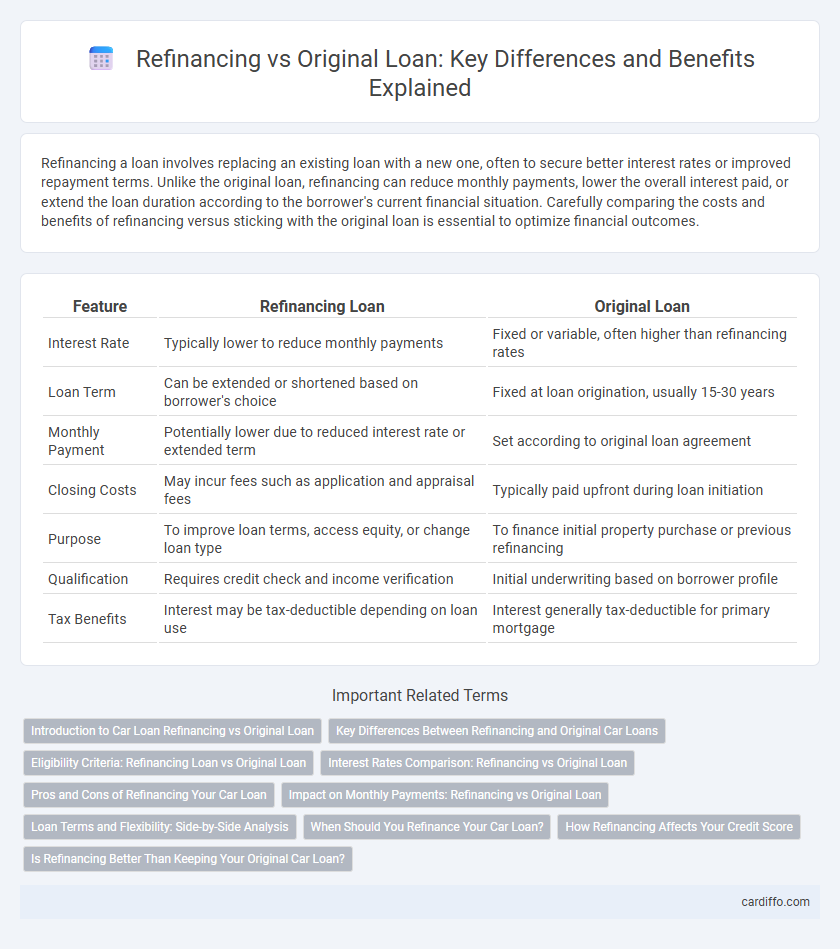
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Refinancing Loan | Original Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Typically lower to reduce monthly payments | Fixed or variable, often higher than refinancing rates |
| Loan Term | Can be extended or shortened based on borrower's choice | Fixed at loan origination, usually 15-30 years |
| Monthly Payment | Potentially lower due to reduced interest rate or extended term | Set according to original loan agreement |
| Closing Costs | May incur fees such as application and appraisal fees | Typically paid upfront during loan initiation |
| Purpose | To improve loan terms, access equity, or change loan type | To finance initial property purchase or previous refinancing |
| Qualification | Requires credit check and income verification | Initial underwriting based on borrower profile |
| Tax Benefits | Interest may be tax-deductible depending on loan use | Interest generally tax-deductible for primary mortgage |
Introduction to Car Loan Refinancing vs Original Loan
Car loan refinancing involves replacing an existing auto loan with a new one, typically featuring better interest rates, terms, or monthly payments. The original car loan establishes the initial borrowing agreement, often with higher interest rates based on credit score and market conditions at the time. Refinancing can reduce total interest costs and improve cash flow by adjusting the loan duration or interest rate compared to the original loan agreement.
Key Differences Between Refinancing and Original Car Loans
Refinancing a car loan involves replacing the original loan with a new one that typically offers better interest rates or terms, potentially lowering monthly payments and total interest paid. Unlike the original car loan, which is based on the vehicle's purchase price and initial credit profile, refinancing takes into account current credit status and vehicle depreciation. Key differences include the opportunity to adjust loan duration, interest rates, and monthly payments based on financial changes since the original loan was issued.
Eligibility Criteria: Refinancing Loan vs Original Loan
Eligibility criteria for refinancing loans typically require a strong credit score, stable income, and a history of timely payments on the original loan, reflecting the borrower's improved financial situation. Original loans often have more lenient eligibility requirements, catering to first-time borrowers with lower credit scores or limited financial history. Lenders assess refinancing applicants based on existing loan performance and current market rates, while original loans rely heavily on initial creditworthiness and income verification.
Interest Rates Comparison: Refinancing vs Original Loan
Refinancing loans often provide lower interest rates compared to original loans, potentially leading to significant monthly savings and reduced total repayment amounts. Original loan interest rates may be higher due to initial credit risk assessments and market conditions at the time of borrowing. Comparing the annual percentage rates (APR) of refinancing options with the original loan rates is crucial to evaluate cost-effectiveness and long-term financial benefits.
Pros and Cons of Refinancing Your Car Loan
Refinancing your car loan can lower interest rates, reduce monthly payments, and improve cash flow, often saving money over the loan term. However, refinancing may lead to longer loan durations, potentially increasing total interest paid, and could involve fees or penalties that offset savings. It's essential to evaluate credit scores, current interest rates, and loan terms to determine if refinancing provides a financial advantage compared to maintaining the original loan.
Impact on Monthly Payments: Refinancing vs Original Loan
Refinancing a loan can significantly reduce monthly payments by securing a lower interest rate or extending the repayment term compared to the original loan. While the original loan's fixed interest and term define consistent payments, refinancing offers flexibility that can lead to immediate cash flow relief. Borrowers should carefully evaluate the new loan's terms to ensure that the impact on monthly payments aligns with their financial goals.
Loan Terms and Flexibility: Side-by-Side Analysis
Refinancing loans typically offer more flexible loan terms compared to original loans, often allowing borrowers to adjust interest rates, repayment periods, and monthly payments to better suit current financial situations. Original loans usually come with fixed terms tailored at the time of borrowing, limiting customization but providing predictable payment schedules. Choosing refinancing can lead to improved cash flow management and potential interest savings while original loans maintain stability and consistency.
When Should You Refinance Your Car Loan?
Refinancing your car loan can lower your interest rate or monthly payments when current rates are significantly lower than your original loan or your credit score has improved. Consider refinancing if you can reduce the loan term without increasing payments, thereby saving on total interest over time. Evaluate your remaining loan balance, fees involved, and how long you plan to keep the vehicle to ensure refinancing provides tangible financial benefits.
How Refinancing Affects Your Credit Score
Refinancing a loan can impact your credit score by triggering a hard inquiry, which may cause a temporary dip. Over time, successfully managing a refinancing loan through timely payments can improve your credit utilization and payment history, boosting your credit score. However, closing the original loan account might reduce the average age of your credit accounts, potentially lowering your score in the short term.
Is Refinancing Better Than Keeping Your Original Car Loan?
Refinancing a car loan can reduce your interest rate, lower monthly payments, or shorten the loan term, potentially saving money over time compared to keeping the original loan. Factors such as current credit score, market interest rates, and remaining loan balance determine if refinancing is advantageous. Carefully evaluating refinancing fees and loan terms ensures this financial strategy maximizes cost efficiency versus maintaining the original car loan agreement.
Refinancing Loan vs Original Loan Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com