Refinancing replaces an existing loan with a new one, often securing a lower interest rate or better terms to reduce monthly payments or loan duration. Loan modification alters the original loan agreement without replacing it, typically adjusting interest rates, payment schedules, or principal amounts to make repayments more manageable for the borrower. Both options help improve financial stability, but refinancing usually requires qualifying for a new loan, while modification directly negotiates changes with the existing lender.
Table of Comparison
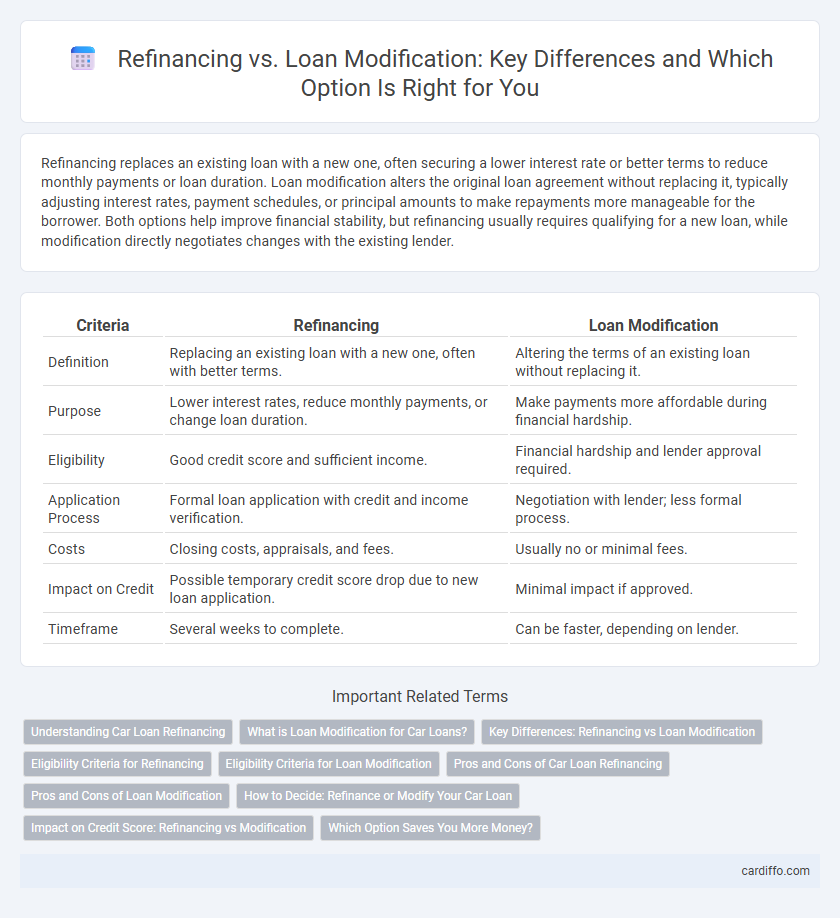
| Criteria | Refinancing | Loan Modification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Replacing an existing loan with a new one, often with better terms. | Altering the terms of an existing loan without replacing it. |
| Purpose | Lower interest rates, reduce monthly payments, or change loan duration. | Make payments more affordable during financial hardship. |
| Eligibility | Good credit score and sufficient income. | Financial hardship and lender approval required. |
| Application Process | Formal loan application with credit and income verification. | Negotiation with lender; less formal process. |
| Costs | Closing costs, appraisals, and fees. | Usually no or minimal fees. |
| Impact on Credit | Possible temporary credit score drop due to new loan application. | Minimal impact if approved. |
| Timeframe | Several weeks to complete. | Can be faster, depending on lender. |
Understanding Car Loan Refinancing
Car loan refinancing involves replacing your current auto loan with a new one, typically to secure a lower interest rate or better terms, whereas loan modification changes the existing loan's conditions without replacing it. Refinancing can reduce monthly payments and overall interest costs by leveraging improved credit scores or market rates, while loan modification is often pursued during financial hardship to lower payments temporarily. Understanding these differences helps borrowers make informed decisions about managing car loan debt effectively.
What is Loan Modification for Car Loans?
Loan modification for car loans involves altering the original terms of the loan agreement to provide more manageable payment options without refinancing. This process may include extending the loan term, reducing the interest rate, or temporarily lowering monthly payments to prevent default. Loan modification helps borrowers facing financial hardship retain their vehicle while avoiding foreclosure or repossession.
Key Differences: Refinancing vs Loan Modification
Refinancing replaces an existing loan with a new loan, often to secure a lower interest rate or better terms, potentially extending the loan term and altering monthly payments. Loan modification adjusts the terms of the current loan without replacing it, typically through changes in interest rate, loan duration, or principal balance to make payments more affordable. Refinancing usually requires credit approval and closing costs, whereas loan modification is often offered by lenders to prevent foreclosure and does not involve starting a new loan process.
Eligibility Criteria for Refinancing
Eligibility criteria for refinancing typically include a strong credit score, stable income, and sufficient home equity to secure a lower interest rate or better loan terms. Lenders require a debt-to-income ratio within acceptable limits, usually below 43%, to ensure the borrower's ability to repay the new loan. Documentation such as recent pay stubs, tax returns, and credit history verification is essential to qualify for refinancing.
Eligibility Criteria for Loan Modification
Loan modification eligibility primarily depends on the borrower's demonstrated financial hardship, such as reduced income or increased expenses, which must be documented and verified by the lender. The property securing the loan often needs to be the borrower's primary residence, and the loan must be at risk of default or foreclosure to qualify. Lenders also evaluate borrower's payment history and loan status to determine if modification can improve repayment terms and prevent foreclosure.
Pros and Cons of Car Loan Refinancing
Car loan refinancing offers lower interest rates and reduced monthly payments, improving cash flow and potentially saving money over the loan term. However, refinancing may extend the loan duration, increasing total interest paid and possibly leading to additional fees like application or title transfer costs. Borrowers should weigh immediate financial relief against long-term expenses when considering refinancing as an alternative to loan modification.
Pros and Cons of Loan Modification
Loan modification offers borrowers the advantage of adjusting existing loan terms such as interest rates, repayment periods, or principal amounts to avoid foreclosure and reduce monthly payments. However, loan modifications can negatively impact credit scores and often require extensive documentation and lender approval, making the process time-consuming and not guaranteed. Unlike refinancing, loan modification does not involve obtaining a new loan but rather restructures the current loan under potentially less favorable conditions.
How to Decide: Refinance or Modify Your Car Loan
Choosing between refinancing and modifying your car loan depends on your current financial situation and goals. Refinance offers lower interest rates and better terms by replacing your existing loan with a new one, while loan modification adjusts the original loan's terms to provide temporary relief without a new contract. Evaluate factors like credit score, interest rate differences, loan duration, and lender policies to determine the most cost-effective and feasible option for your car loan management.
Impact on Credit Score: Refinancing vs Modification
Refinancing a loan often results in a hard credit inquiry, which can temporarily lower your credit score, but it may improve your financial profile long-term by securing better terms. Loan modification typically does not involve a credit check, minimizing immediate impact on your credit score, although missed payments prior to modification can have lasting negative effects. Both options influence credit rating differently, with refinancing potentially rebuilding credit through new payment history while modification focuses on avoiding default during financial hardship.
Which Option Saves You More Money?
Refinancing a loan typically lowers your interest rate and monthly payments by replacing your existing loan with a new one, often saving more money over time if market rates have dropped. Loan modification adjusts the terms of your current loan, such as extending the repayment period or reducing interest rates, providing immediate relief but usually less overall savings than refinancing. Evaluating your credit score, loan-to-value ratio, and current interest rates helps determine whether refinancing or loan modification offers the best financial advantage.
Refinancing vs Loan Modification Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com