Interest rate represents the cost of borrowing expressed as a percentage of the loan amount, while the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) includes both the interest rate and additional fees, providing a more comprehensive view of the loan's true cost. Borrowers comparing loan offers should prioritize the APR to understand the full financial impact. Understanding the difference helps in making informed decisions to secure the most affordable loan terms.
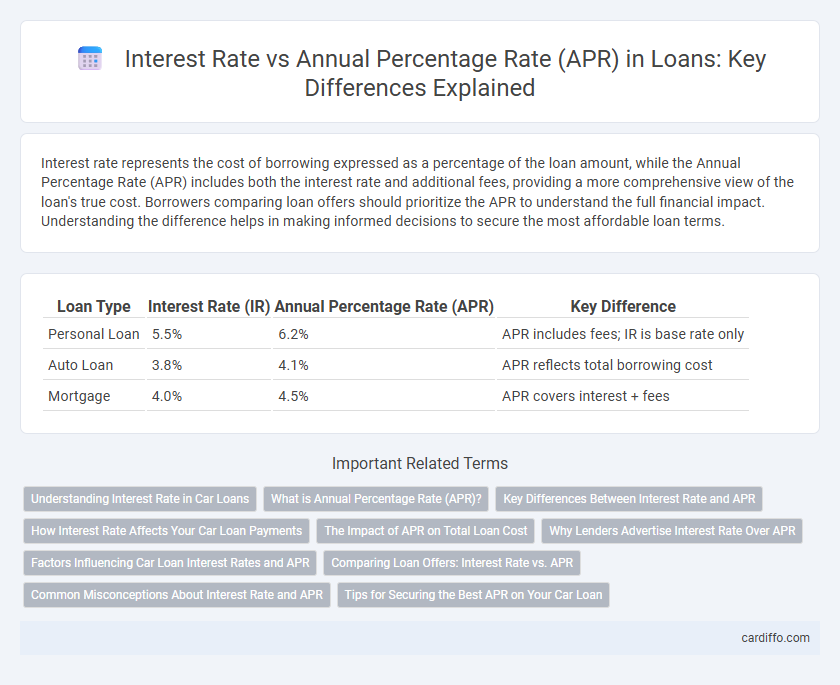
Table of Comparison
| Loan Type | Interest Rate (IR) | Annual Percentage Rate (APR) | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personal Loan | 5.5% | 6.2% | APR includes fees; IR is base rate only |
| Auto Loan | 3.8% | 4.1% | APR reflects total borrowing cost |
| Mortgage | 4.0% | 4.5% | APR covers interest + fees |
Understanding Interest Rate in Car Loans
Interest rate in car loans refers to the percentage charged by lenders on the principal amount borrowed, directly impacting monthly payment amounts. This rate excludes fees and other costs, making it lower than the Annual Percentage Rate (APR), which includes these additional expenses for a more comprehensive loan cost representation. Understanding the interest rate helps borrowers compare basic loan costs and determine affordability before factoring in total loan expenses reflected by the APR.
What is Annual Percentage Rate (APR)?
Annual Percentage Rate (APR) represents the total cost of borrowing, expressed as a yearly percentage, including the interest rate plus any additional fees or costs involved in the loan. Unlike the nominal interest rate, APR provides a more comprehensive measure of the true cost of a loan, enabling borrowers to compare different loan offers accurately. APR is vital for evaluating mortgages, credit cards, personal loans, and auto loans, reflecting the real financial impact over the loan term.
Key Differences Between Interest Rate and APR
Interest rate represents the cost of borrowing the principal loan amount expressed as a percentage annually, excluding fees and other charges. Annual Percentage Rate (APR) includes the interest rate plus additional costs such as origination fees, closing costs, and insurance, providing a more comprehensive view of the total loan expense. Comparing interest rate versus APR helps borrowers accurately assess the true cost of loans and make informed financial decisions.
How Interest Rate Affects Your Car Loan Payments
The interest rate determines the cost of borrowing money for a car loan by directly influencing your monthly payment amount and the total interest paid over the loan term. A lower interest rate reduces monthly installments and overall loan costs, while a higher rate increases both, affecting affordability. The Annual Percentage Rate (APR) includes the interest rate plus fees, providing a more comprehensive measure of the loan's true cost.
The Impact of APR on Total Loan Cost
The Annual Percentage Rate (APR) reflects the total cost of a loan, combining the interest rate with additional fees and charges, providing a more comprehensive measure than the interest rate alone. A higher APR increases the overall expense over the loan's term, affecting monthly payments and the total amount repaid. Understanding APR is crucial for borrowers to compare loan offers accurately and gauge the true financial impact beyond just the nominal interest rate.
Why Lenders Advertise Interest Rate Over APR
Lenders advertise the interest rate over the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) because the interest rate appears lower and more attractive to potential borrowers, making it easier to market loan products. The APR includes additional fees and costs, reflecting the true cost of borrowing, which can deter some consumers. Focusing on the interest rate helps lenders highlight the immediate cost of borrowing, though the APR provides a more comprehensive measure of loan expenses.
Factors Influencing Car Loan Interest Rates and APR
Car loan interest rates and APR are influenced by factors including the borrower's credit score, loan term, and the lender's policies. A higher credit score typically results in lower interest rates, while longer loan terms may increase the APR due to accumulated fees and interest. Market conditions, such as inflation and Federal Reserve rate changes, also impact the calculation of both interest rate and APR for auto loans.
Comparing Loan Offers: Interest Rate vs. APR
When comparing loan offers, the interest rate represents the cost of borrowing as a percentage of the principal, excluding additional fees, while the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) includes both the interest rate and all associated loan fees, providing a more comprehensive measure of the total loan cost. Evaluating APR allows borrowers to accurately assess and compare the true expense of different loan options, considering fees that impact the overall payment amount. Prioritizing APR over the nominal interest rate ensures a clearer understanding of loan affordability and prevents underestimating the financial commitment.
Common Misconceptions About Interest Rate and APR
Many borrowers mistakenly believe that the interest rate reflects the total cost of a loan, while the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) provides a more comprehensive measure by including fees and additional costs. The interest rate only indicates the cost of borrowing the principal amount, excluding other charges such as loan origination fees and closing costs that are incorporated into the APR. Understanding the difference between interest rate and APR is crucial for comparing loan offers accurately and avoiding unexpected expenses over the loan term.
Tips for Securing the Best APR on Your Car Loan
When seeking the best APR on your car loan, compare offers from multiple lenders to identify the lowest rates available, considering both the interest rate and added fees included in the APR calculation. Improve your credit score by paying bills on time and reducing debt to qualify for better loan terms and lower APRs. Opt for shorter loan terms and consider making a larger down payment to decrease the loan amount and secure a more favorable APR.
Interest Rate vs Annual Percentage Rate Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com