Refinancing a leased pet loan can lower monthly payments by adjusting interest rates and loan terms, offering flexibility without altering ownership. Lease buyout involves purchasing the pet outright at the end of the lease term, providing full ownership and eliminating monthly obligations. Choosing between refinancing and lease buyout depends on your financial goals and desire for pet ownership control.
Table of Comparison
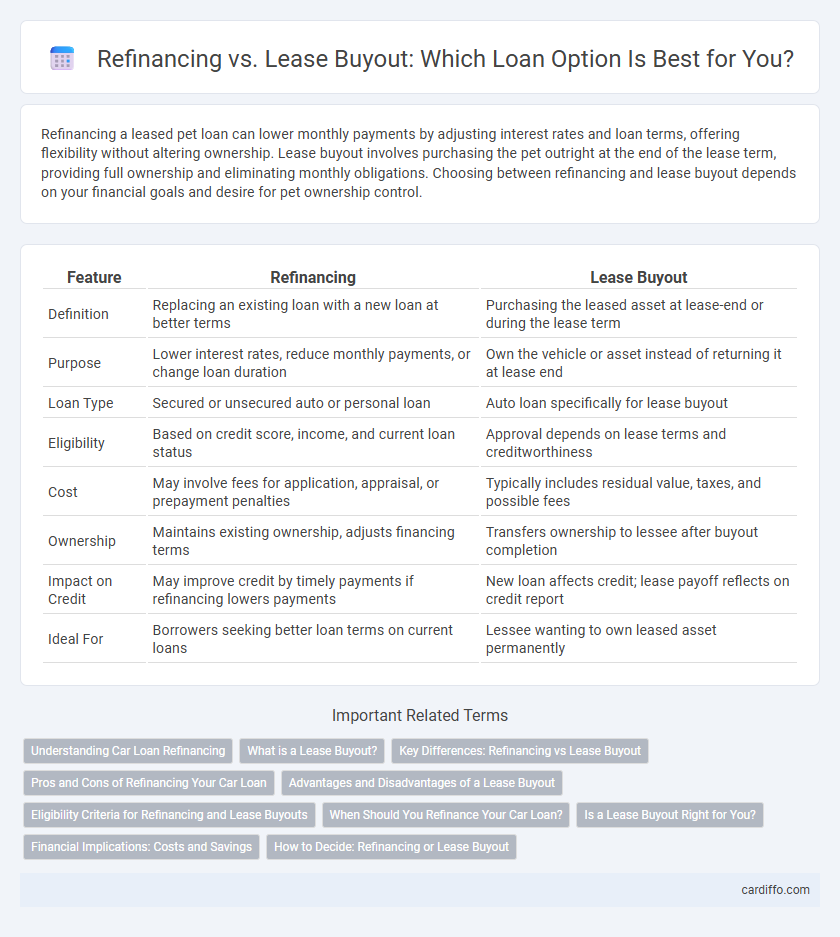
| Feature | Refinancing | Lease Buyout |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Replacing an existing loan with a new loan at better terms | Purchasing the leased asset at lease-end or during the lease term |
| Purpose | Lower interest rates, reduce monthly payments, or change loan duration | Own the vehicle or asset instead of returning it at lease end |
| Loan Type | Secured or unsecured auto or personal loan | Auto loan specifically for lease buyout |
| Eligibility | Based on credit score, income, and current loan status | Approval depends on lease terms and creditworthiness |
| Cost | May involve fees for application, appraisal, or prepayment penalties | Typically includes residual value, taxes, and possible fees |
| Ownership | Maintains existing ownership, adjusts financing terms | Transfers ownership to lessee after buyout completion |
| Impact on Credit | May improve credit by timely payments if refinancing lowers payments | New loan affects credit; lease payoff reflects on credit report |
| Ideal For | Borrowers seeking better loan terms on current loans | Lessee wanting to own leased asset permanently |
Understanding Car Loan Refinancing
Car loan refinancing involves replacing an existing auto loan with a new one, typically offering lower interest rates or better terms to reduce monthly payments and overall loan costs. Unlike a lease buyout, refinancing does not require owning the vehicle outright but improves loan conditions during the repayment period. Understanding factors such as credit score, current interest rates, and loan tenure helps borrowers determine if refinancing is a beneficial option for managing their car financing.
What is a Lease Buyout?
A lease buyout allows the lessee to purchase the vehicle at the end or during the lease term by paying the residual value agreed upon in the lease contract. This option can be financially advantageous compared to refinancing a loan, especially when the car's market value exceeds the buyout price. Understanding the lease buyout process helps consumers decide whether to own the vehicle outright or explore alternative financing solutions.
Key Differences: Refinancing vs Lease Buyout
Refinancing involves replacing an existing loan with a new loan, typically to secure lower interest rates or better terms, while a lease buyout allows the lessee to purchase the leased vehicle by paying the predetermined residual value. Refinancing modifies the terms of a loan on owned assets, impacting monthly payments and loan duration, whereas a lease buyout converts a leased asset into owned property, often at the end of the lease term. Understanding the key differences between refinancing and lease buyout helps consumers make informed decisions based on cost savings, ownership goals, and financial flexibility.
Pros and Cons of Refinancing Your Car Loan
Refinancing your car loan can lower monthly payments and reduce interest rates by leveraging improved credit scores or market conditions, making it a cost-effective option for long-term savings. However, refinancing may extend the loan term, increasing total interest paid, and could involve fees or prepayment penalties that reduce immediate benefits. Evaluating your financial goals, credit status, and loan terms helps determine if refinancing outweighs the simplicity and ownership benefits of a lease buyout.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Lease Buyout
A lease buyout allows borrowers to purchase the leased asset, often leading to ownership without additional financing qualifications. Advantages include avoiding vehicle return fees and potential equity buildup if the asset's value exceeds the buyout amount. Disadvantages involve higher upfront costs compared to regular lease payments and possible obligation to cover repairs and depreciation risks after ownership.
Eligibility Criteria for Refinancing and Lease Buyouts
Eligibility criteria for refinancing typically include a strong credit score, sufficient income to cover new loan payments, and a favorable loan-to-value ratio, ensuring borrowers can secure better interest rates or terms. Lease buyouts generally require the lessee to have met all lease obligations, maintained the vehicle in good condition, and possess sufficient funds or financing approval to cover the buyout amount set by the lease agreement. Both options demand thorough credit assessments and verification of the borrower's financial stability to qualify for refinancing or purchasing the leased asset.
When Should You Refinance Your Car Loan?
Refinance your car loan when you qualify for a significantly lower interest rate, which lowers monthly payments and reduces the total loan cost. Consider refinancing if your credit score has improved since the original loan or if market rates have dropped substantially. Avoid refinancing if the loan term extension outweighs interest savings or if fees and penalties diminish overall benefits.
Is a Lease Buyout Right for You?
A lease buyout may be right for you if you want to avoid mileage penalties, excessive wear-and-tear charges, or if you plan to keep the vehicle long-term after the lease term ends. Refinancing typically reduces monthly payments or interest rates on existing loans but does not transfer ownership like a lease buyout does. Evaluating current vehicle value, lease terms, and financial capacity helps determine whether purchasing the leased vehicle or refinancing is the best loan strategy.
Financial Implications: Costs and Savings
Refinancing a loan often involves lower interest rates and extended payment terms, reducing monthly expenses but potentially increasing total interest paid over time. Lease buyout requires a lump-sum payment or financing the buyout amount, which might include residual value and fees, affecting overall cost compared to continuing lease payments. Evaluating total costs, interest rates, and potential savings helps determine the financially optimal choice between refinancing and lease buyout options.
How to Decide: Refinancing or Lease Buyout
When deciding between refinancing and a lease buyout, evaluate your monthly budget, interest rates, and long-term vehicle goals. Refinancing lowers loan payments or terms by obtaining better rates based on credit score and market conditions. A lease buyout is ideal if you plan to keep the vehicle long-term and want to own it outright after the lease ends.
Refinancing vs Lease Buyout Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com