New car loans often come with lower interest rates and manufacturer incentives, making them attractive for buyers seeking the latest models and warranty coverage. Used car loans typically have higher interest rates but lower principal amounts, offering more affordable monthly payments for budget-conscious buyers. Understanding the trade-offs between depreciation rates and financing terms is crucial when choosing between new or used car loans.
Table of Comparison
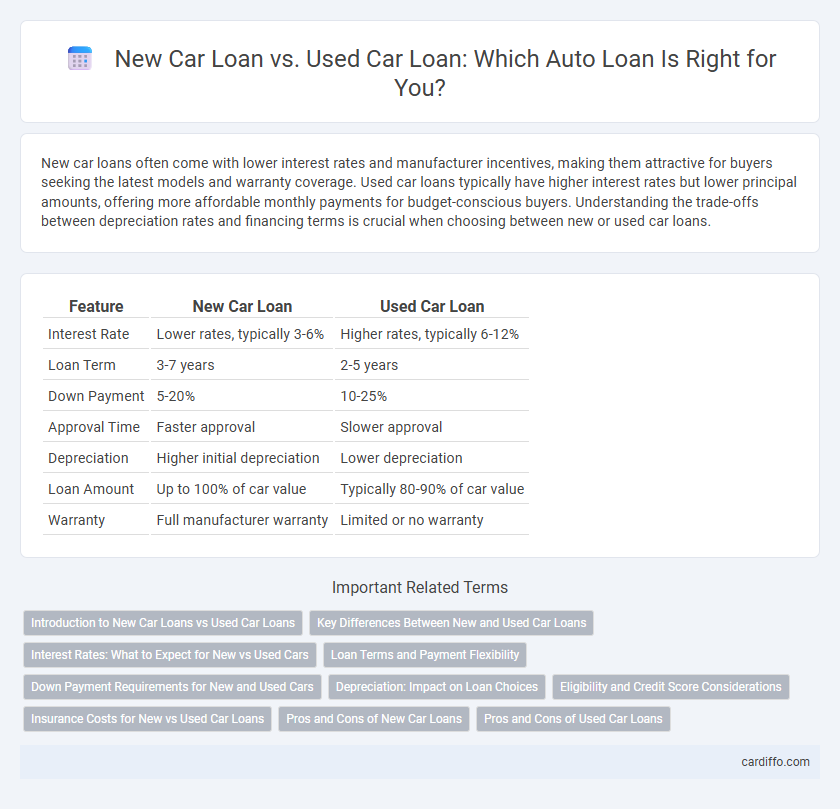
| Feature | New Car Loan | Used Car Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Lower rates, typically 3-6% | Higher rates, typically 6-12% |
| Loan Term | 3-7 years | 2-5 years |
| Down Payment | 5-20% | 10-25% |
| Approval Time | Faster approval | Slower approval |
| Depreciation | Higher initial depreciation | Lower depreciation |
| Loan Amount | Up to 100% of car value | Typically 80-90% of car value |
| Warranty | Full manufacturer warranty | Limited or no warranty |
Introduction to New Car Loans vs Used Car Loans
New car loans typically offer lower interest rates and longer repayment terms compared to used car loans, reflecting the higher value and lower risk of new vehicles. Used car loans often have higher interest rates and shorter terms due to increased depreciation and potential maintenance costs. Understanding these differences helps borrowers choose the best financing option based on their budget and vehicle preferences.
Key Differences Between New and Used Car Loans
New car loans typically offer lower interest rates and longer repayment terms due to the higher value and better collateral of new vehicles. Used car loans often come with higher interest rates and shorter loan durations because of increased risk and faster depreciation of pre-owned cars. Loan-to-value ratios differ, with new car loans usually providing more favorable terms compared to used car loans, reflecting the car's condition and market value.
Interest Rates: What to Expect for New vs Used Cars
Interest rates for new car loans typically range from 3% to 6%, reflecting lower risk and higher lender confidence in the vehicle's value and condition. Used car loan interest rates are generally higher, often between 5% and 12%, due to greater depreciation and potential for maintenance issues, which pose increased risk for lenders. Borrowers with strong credit scores may secure rates closer to the lower end of these ranges for both new and used car loans.
Loan Terms and Payment Flexibility
New car loans typically offer longer loan terms, often up to 72 months, providing lower monthly payments but higher total interest costs. Used car loans usually have shorter terms, around 36 to 60 months, which can result in higher monthly payments but less interest paid overall. Payment flexibility may be greater with new car loans due to manufacturer promotions, including deferred payments or lower interest rates, whereas used car loans often have stricter payment schedules.
Down Payment Requirements for New and Used Cars
New car loans typically require a higher down payment, often around 10% to 20% of the vehicle's purchase price, reflecting the car's higher value and depreciation rates. Used car loans generally have lower down payment requirements, sometimes as low as 5%, due to the reduced market value and increased lender risk associated with older vehicles. Lenders may also adjust down payment expectations based on credit score, loan term, and vehicle condition for both new and used car loans.
Depreciation: Impact on Loan Choices
New car loans often come with higher interest rates due to rapid depreciation, as a new vehicle can lose up to 20% of its value within the first year. Used car loans may offer lower financing costs because the slower depreciation rate preserves the car's value longer, reducing the lender's risk. Understanding depreciation trends helps borrowers select loan terms that align with vehicle value retention and minimize negative equity risk.
Eligibility and Credit Score Considerations
Lenders typically require higher credit scores for new car loans, with minimums around 650, while used car loans may accept scores as low as 600 due to higher risk. Eligibility for new car loans often includes proof of stable income and employment, whereas used car loans might demand additional collateral or a larger down payment to offset potential depreciation. Credit history impacts interest rates directly; borrowers with strong credit scores receive lower rates on new car loans, whereas used car loans generally carry higher rates reflecting increased lender risk.
Insurance Costs for New vs Used Car Loans
Insurance costs for new car loans are generally higher due to the higher value and replacement expenses of new vehicles. Used car loans often come with lower insurance premiums since used cars depreciate faster and typically have lower market value. Lenders may also require comprehensive and collision coverage for new car loans, increasing overall insurance costs compared to used car loans.
Pros and Cons of New Car Loans
New car loans typically offer lower interest rates and come with manufacturer warranties that reduce repair costs, making them a financially safer option for buyers. However, new cars depreciate rapidly within the first few years, leading to higher monthly payments and potential negative equity. Borrowers should weigh the benefits of reliability and lower maintenance against the faster depreciation and higher overall loan amounts when considering new car loans.
Pros and Cons of Used Car Loans
Used car loans often feature lower principal amounts due to reduced vehicle prices, making monthly payments more affordable, yet they tend to have higher interest rates compared to new car loans, increasing overall borrowing costs. The accelerated depreciation and increased maintenance costs associated with used cars can reduce long-term value and elevate ownership expenses. Limited warranty coverage for used vehicles requires buyers to consider potential repair risks, impacting loan appeal and financial planning.
New Car Loan vs Used Car Loan Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com