Lease buyout allows the lessee to purchase the vehicle at the end of the lease term, converting the lease into ownership and potentially saving money compared to leasing a new car. Lease transfer involves shifting the remaining lease obligations to another party, offering flexibility for those who want to exit a lease early without penalties. Understanding the costs, fees, and credit requirements is essential for making an informed decision between these two options.
Table of Comparison
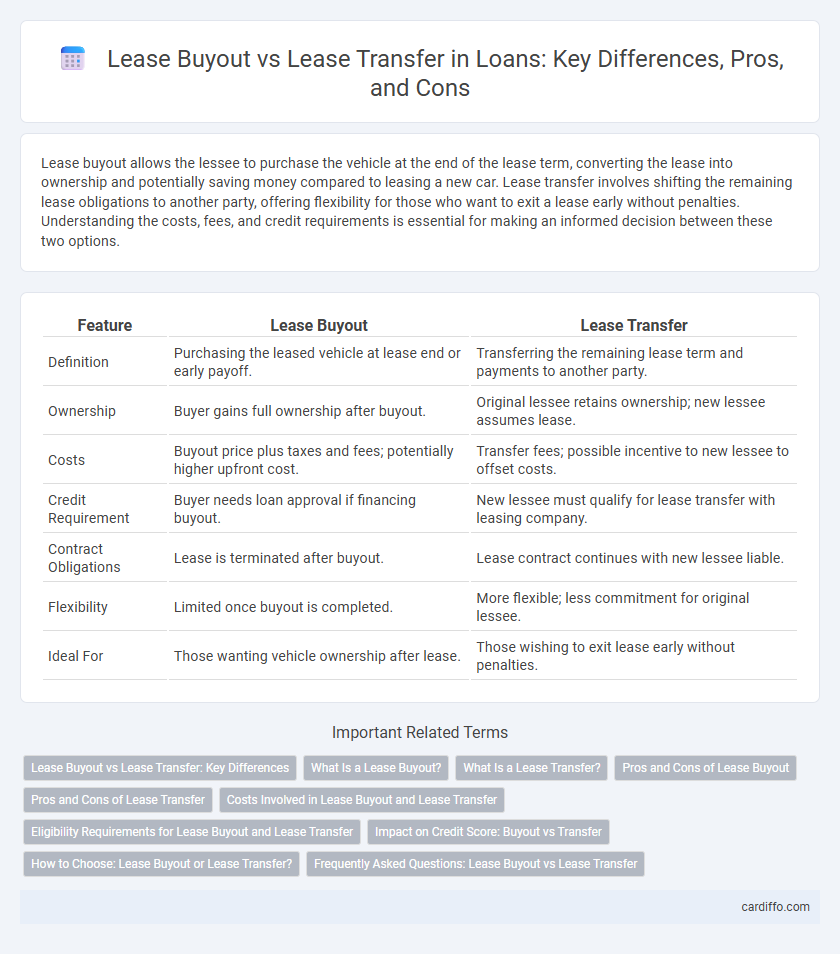
| Feature | Lease Buyout | Lease Transfer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Purchasing the leased vehicle at lease end or early payoff. | Transferring the remaining lease term and payments to another party. |
| Ownership | Buyer gains full ownership after buyout. | Original lessee retains ownership; new lessee assumes lease. |
| Costs | Buyout price plus taxes and fees; potentially higher upfront cost. | Transfer fees; possible incentive to new lessee to offset costs. |
| Credit Requirement | Buyer needs loan approval if financing buyout. | New lessee must qualify for lease transfer with leasing company. |
| Contract Obligations | Lease is terminated after buyout. | Lease contract continues with new lessee liable. |
| Flexibility | Limited once buyout is completed. | More flexible; less commitment for original lessee. |
| Ideal For | Those wanting vehicle ownership after lease. | Those wishing to exit lease early without penalties. |
Lease Buyout vs Lease Transfer: Key Differences
Lease buyout involves purchasing the leased vehicle at the end or during the lease term, allowing ownership transfer to the lessee. Lease transfer, also known as lease assumption, permits the lessee to transfer the remaining term and payments to another party without owning the vehicle. Key differences include ownership transfer only through buyout, while lease transfer merely shifts contractual obligations without changing ownership.
What Is a Lease Buyout?
A lease buyout occurs when a lessee purchases the leased asset, typically a vehicle, either at the end of the lease term or before it expires, paying the predetermined residual value or market price. This option allows the lessee to own the asset outright, avoiding mileage penalties and lease-end fees. Lease buyouts can be financed through auto loans, offering flexibility compared to lease transfers where the lease obligation shifts to another party.
What Is a Lease Transfer?
A lease transfer, also known as a lease assumption, allows a lessee to transfer their remaining lease obligations to another party, relieving themselves from future payments and responsibilities. This process requires approval from the leasing company and involves the new lessee taking over the lease term, mileage limits, and condition requirements. Lease transfers are often used to avoid lease termination fees and provide flexibility when the original lessee wants to exit the lease early.
Pros and Cons of Lease Buyout
Lease buyout offers the advantage of owning the vehicle outright after the lease term, eliminating mileage limits and end-of-lease fees. It requires a substantial upfront payment or financing, potentially resulting in higher monthly costs compared to continuing the lease or transferring it. However, lease buyout can lead to long-term savings if the vehicle's residual value is lower than its market value.
Pros and Cons of Lease Transfer
Lease transfer allows the original lessee to transfer remaining lease obligations to a new party, eliminating future payments and avoiding early termination fees. This option offers flexibility and financial relief but can be limited by lease agreements, potential credit impacts for both parties, and the challenge of finding an eligible transferee. It avoids the upfront costs of a lease buyout but requires approval from the leasing company and may not always cover remaining lease value.
Costs Involved in Lease Buyout and Lease Transfer
Lease buyout typically involves paying the residual value of the vehicle plus any applicable fees and taxes, which can be costly upfront but leads to ownership. Lease transfer usually requires a transfer fee and possibly covering the remaining lease payments, often resulting in lower initial costs but no ownership at the end. Understanding these cost differences is crucial for making informed decisions about managing leased vehicles.
Eligibility Requirements for Lease Buyout and Lease Transfer
Eligibility requirements for a lease buyout typically include having a current lease agreement in good standing, with no outstanding payments or violations, and often require lender approval based on creditworthiness and financial stability. Lease transfer eligibility generally mandates that the current lessee must obtain consent from the leasing company, and the new lessee must meet specific credit and income criteria to assume the lease obligations. Both options require thorough review of lease terms and conditions to ensure compliance with lease-end obligations and transfer or buyout fees.
Impact on Credit Score: Buyout vs Transfer
A lease buyout typically has a more significant impact on your credit score as it involves taking out a new loan or using savings to purchase the vehicle, which increases your overall debt and affects credit utilization. Lease transfers usually have minimal effect since the original lease is simply reassigned to another party, avoiding new debt on your credit report. Understanding how each option influences your credit score helps in making informed decisions about managing auto financing and maintaining a healthy credit profile.
How to Choose: Lease Buyout or Lease Transfer?
Choosing between a lease buyout and a lease transfer depends on your financial situation and vehicle needs. Opt for a lease buyout if you want to keep the car long-term and can handle the remaining payments or financing. Select a lease transfer to avoid future payments and fees by passing the lease to another party, which requires approval from the leasing company and may involve transfer fees.
Frequently Asked Questions: Lease Buyout vs Lease Transfer
Lease buyout allows the lessee to purchase the vehicle at the end or during the lease term by paying the residual value plus fees, providing ownership and eliminating mileage limits. Lease transfer involves transferring the remaining lease obligations to another party, often requiring credit approval and reducing or eliminating remaining payments for the original lessee. Common questions include eligibility criteria, transfer fees, and financial impact on credit scores, highlighting the importance of understanding both options before deciding.
Lease buyout vs Lease transfer Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com