Choosing between fixed rate and variable rate loans depends on your risk tolerance and financial stability. Fixed rate loans provide predictable monthly payments and protection against interest rate increases, while variable rate loans often start with lower rates that may fluctuate based on market conditions, potentially lowering or raising your payment amounts. Evaluating your budget flexibility and market trends can help determine which loan type aligns with your long-term financial goals.
Table of Comparison
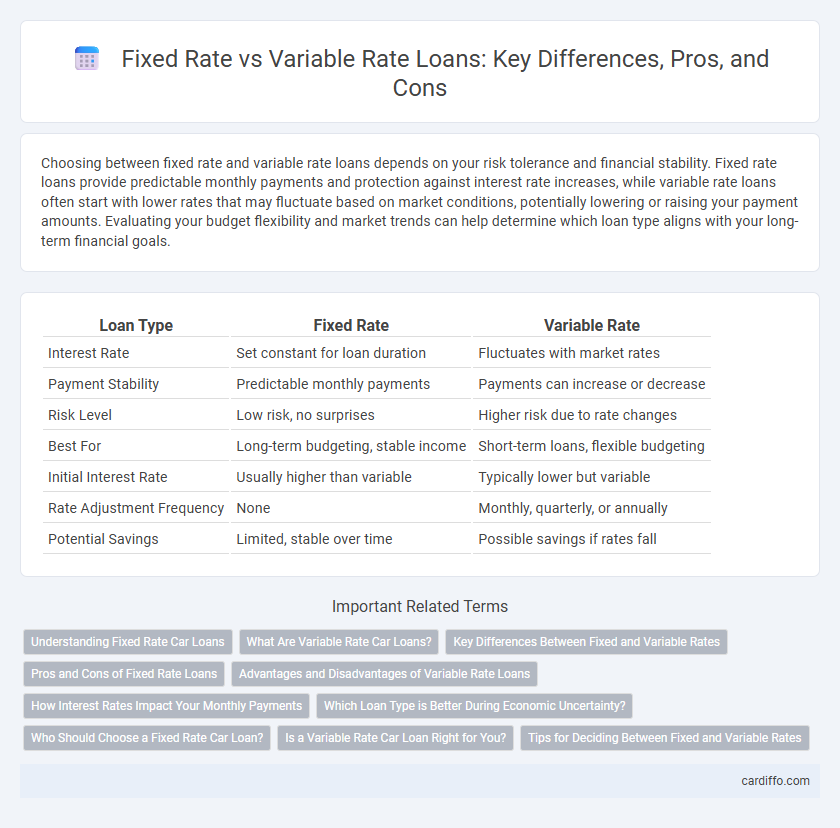
| Loan Type | Fixed Rate | Variable Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Set constant for loan duration | Fluctuates with market rates |
| Payment Stability | Predictable monthly payments | Payments can increase or decrease |
| Risk Level | Low risk, no surprises | Higher risk due to rate changes |
| Best For | Long-term budgeting, stable income | Short-term loans, flexible budgeting |
| Initial Interest Rate | Usually higher than variable | Typically lower but variable |
| Rate Adjustment Frequency | None | Monthly, quarterly, or annually |
| Potential Savings | Limited, stable over time | Possible savings if rates fall |
Understanding Fixed Rate Car Loans
Fixed rate car loans offer borrowers a consistent monthly payment by locking in an interest rate for the entire loan term, providing financial predictability and protection against market fluctuations. These loans are ideal for individuals who prefer budgeting certainty and want to avoid the risk of interest rate increases. Choosing a fixed rate loan can result in higher initial interest rates compared to variable rate loans, but it shields borrowers from rising costs over time.
What Are Variable Rate Car Loans?
Variable rate car loans feature interest rates that fluctuate based on market conditions or an underlying benchmark, such as the prime rate. This type of loan offers lower initial rates compared to fixed rate car loans but carries the risk of increased payments if rates rise. Borrowers often choose variable rate loans to benefit from potential rate decreases while accepting payment variability.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Variable Rates
Fixed-rate loans maintain a constant interest rate throughout the loan term, providing predictable monthly payments and budgeting ease. Variable-rate loans, also known as adjustable-rate loans, fluctuate with market interest rate changes, potentially lowering initial payments but increasing risk over time. Key differences include payment stability, interest cost predictability, and exposure to market rate volatility.
Pros and Cons of Fixed Rate Loans
Fixed rate loans offer the advantage of predictable monthly payments, providing borrowers with financial stability and easier budgeting over the loan term. The downside includes typically higher initial interest rates compared to variable rate loans, which can result in greater overall interest costs if market rates decline. Fixed rates are ideal for borrowers seeking long-term certainty and protection from inflation-driven rate increases.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Variable Rate Loans
Variable rate loans offer the advantage of lower initial interest rates compared to fixed rate loans, potentially reducing monthly payments when market rates are low. However, their main disadvantage is the unpredictability of future payments, as interest rates can increase, leading to higher costs and financial uncertainty. Borrowers opting for variable rate loans must be prepared for fluctuating payments and possibly higher overall interest expenses in a rising rate environment.
How Interest Rates Impact Your Monthly Payments
Fixed-rate loans provide consistent monthly payments because the interest rate remains unchanged throughout the loan term, offering predictability and budget stability. Variable-rate loans have interest rates that fluctuate based on market conditions, causing monthly payments to rise or fall over time. Understanding these rate dynamics is crucial for borrowers to manage financial risk and plan monthly cash flow effectively.
Which Loan Type is Better During Economic Uncertainty?
Fixed rate loans offer consistent monthly payments and protect borrowers from rising interest rates during economic uncertainty, providing financial stability. Variable rate loans may start with lower rates but can increase significantly, leading to unpredictable payment amounts and potential financial strain. Borrowers prioritizing budget certainty typically benefit more from fixed rate loans in volatile economic conditions.
Who Should Choose a Fixed Rate Car Loan?
Borrowers seeking stability and predictable monthly payments should opt for a fixed rate car loan, as it locks in an interest rate for the loan term, protecting against market fluctuations. Fixed rate loans are ideal for buyers with a tight budget or those planning to keep the vehicle for several years. Individuals averse to interest rate volatility benefit most from the security of fixed rate financing.
Is a Variable Rate Car Loan Right for You?
A variable rate car loan offers interest rates that fluctuate with market conditions, often starting lower than fixed rates, which can lead to initial savings. Borrowers comfortable with potential rate increases and unpredictable monthly payments may benefit from a variable rate loan's flexibility. Assessing your risk tolerance and financial stability is crucial to determine if the variable interest rate aligns with your long-term budget goals.
Tips for Deciding Between Fixed and Variable Rates
Evaluate your financial stability and risk tolerance before choosing between fixed and variable loan rates. Fixed rates provide predictable monthly payments, ideal for budgeting, while variable rates may offer lower initial rates but fluctuate with market conditions. Analyze interest rate trends, loan term length, and potential rate caps to decide which option aligns with your long-term financial goals.
Fixed Rate vs Variable Rate Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com