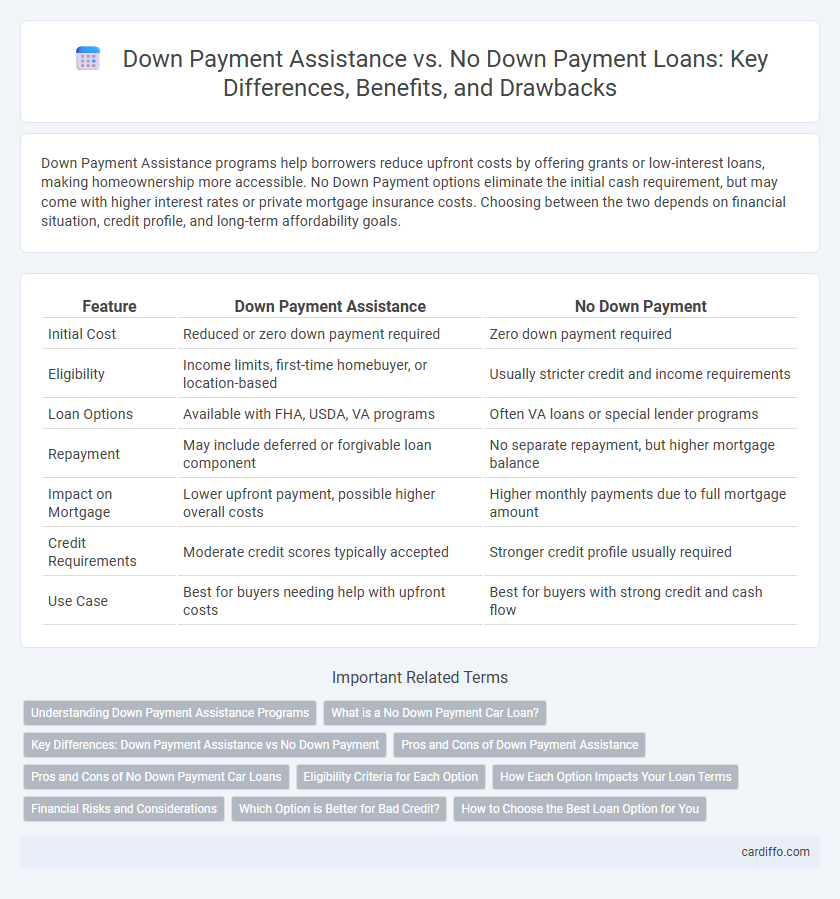
Down Payment Assistance programs help borrowers reduce upfront costs by offering grants or low-interest loans, making homeownership more accessible. No Down Payment options eliminate the initial cash requirement, but may come with higher interest rates or private mortgage insurance costs. Choosing between the two depends on financial situation, credit profile, and long-term affordability goals.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Down Payment Assistance | No Down Payment |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Reduced or zero down payment required | Zero down payment required |
| Eligibility | Income limits, first-time homebuyer, or location-based | Usually stricter credit and income requirements |
| Loan Options | Available with FHA, USDA, VA programs | Often VA loans or special lender programs |
| Repayment | May include deferred or forgivable loan component | No separate repayment, but higher mortgage balance |
| Impact on Mortgage | Lower upfront payment, possible higher overall costs | Higher monthly payments due to full mortgage amount |
| Credit Requirements | Moderate credit scores typically accepted | Stronger credit profile usually required |
| Use Case | Best for buyers needing help with upfront costs | Best for buyers with strong credit and cash flow |
Understanding Down Payment Assistance Programs
Down payment assistance programs provide borrowers with financial support to cover a portion or the entirety of the upfront payment required to secure a loan, often through grants, forgivable loans, or deferred payment options. These programs target first-time homebuyers, low-to-moderate income families, and veterans, reducing the initial cash burden and improving loan eligibility. Understanding the specific terms, eligibility criteria, and repayment obligations is crucial to maximizing the benefits of down payment assistance compared to no down payment loan options.
What is a No Down Payment Car Loan?
A no down payment car loan allows buyers to finance the full purchase price of a vehicle without an initial upfront payment, making it easier for those with limited savings to afford a car. This type of loan often requires higher credit scores or results in increased monthly payments and total interest due to the increased loan amount. Compared to down payment assistance programs, no down payment loans do not provide external funds but instead offer financing options that eliminate the need for an upfront cash contribution.
Key Differences: Down Payment Assistance vs No Down Payment
Down payment assistance programs provide borrowers with funds or grants to cover part or all of the initial payment, reducing upfront financial barriers, whereas no down payment loans eliminate the need for any initial payment but may come with stricter credit requirements or higher interest rates. Down payment assistance enables buyers, especially first-time homeowners, to enter the market with lower initial costs while no down payment options are typically aimed at qualified buyers who can afford recurring costs without upfront equity. The key difference lies in the source of funds for the down payment--assistance programs supplement borrower resources, whereas no down payment loans waive this requirement entirely but often incorporate the cost into loan terms.
Pros and Cons of Down Payment Assistance
Down payment assistance programs offer financial support to homebuyers, reducing upfront costs and making homeownership more accessible, especially for first-time buyers. These programs often come with specific eligibility requirements and may increase the total loan amount or include additional fees, impacting long-term affordability. Unlike no down payment loans, which eliminate initial costs but sometimes require higher interest rates or private mortgage insurance, down payment assistance provides immediate cash relief but can complicate the mortgage process.
Pros and Cons of No Down Payment Car Loans
No down payment car loans eliminate the initial financial burden, making vehicle ownership more accessible and preserving cash flow for other expenses. However, these loans often come with higher interest rates and larger monthly payments, increasing the total cost over time. Borrowers may also face stricter qualification criteria and limited lender options compared to loans requiring a down payment.
Eligibility Criteria for Each Option
Down payment assistance programs typically require applicants to meet specific eligibility criteria such as income limits, first-time homebuyer status, or purchasing within targeted areas. No down payment loans often have different qualifications, including higher credit score requirements and stricter debt-to-income ratios, but do not mandate upfront cash for the home purchase. Understanding these criteria helps borrowers choose the best loan option based on financial situation and homeownership goals.
How Each Option Impacts Your Loan Terms
Down payment assistance programs reduce the upfront cash required, allowing borrowers to preserve savings while potentially increasing the loan amount and monthly payments. Opting for no down payment loans eliminates the initial payment but often results in higher interest rates and mortgage insurance premiums, impacting overall loan costs. Evaluating how each option affects loan-to-value (LTV) ratios and monthly affordability is crucial for optimal financial planning.
Financial Risks and Considerations
Down payment assistance programs reduce upfront costs but may increase overall loan expenses through higher interest rates or additional fees. Choosing no down payment loans often leads to higher monthly payments and greater financial vulnerability if property values decline. Assessing credit impact, loan terms, and potential long-term costs is essential for managing financial risks effectively.
Which Option is Better for Bad Credit?
Down payment assistance programs can provide crucial support for borrowers with bad credit by reducing the upfront cost barrier, making homeownership more accessible despite credit challenges. Loans with no down payment requirements often come with stricter credit qualifications or higher interest rates, which can increase overall borrowing costs for individuals with poor credit. For bad credit borrowers, down payment assistance offers a more feasible path by lowering initial expenses without necessarily intensifying credit risk factors.
How to Choose the Best Loan Option for You
Choosing the best loan option depends on your financial stability, credit score, and long-term homeownership goals. Down payment assistance programs can ease initial costs and improve affordability, especially for first-time buyers with limited savings, while no down payment loans might increase monthly payments and require private mortgage insurance. Evaluating your budget, loan terms, and eligibility criteria helps determine whether a down payment assistance or no down payment loan aligns with your financial strategy.
Down Payment Assistance vs No Down Payment Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com