A Co-Signer Loan involves a second party agreeing to share responsibility for repayment, which can improve approval chances and secure lower interest rates compared to a Solo Applicant Loan. Borrowers applying solo face stricter credit requirements and may encounter higher interest rates due to increased lender risk. Choosing between these options depends on credit history, financial stability, and willingness to share loan obligations.
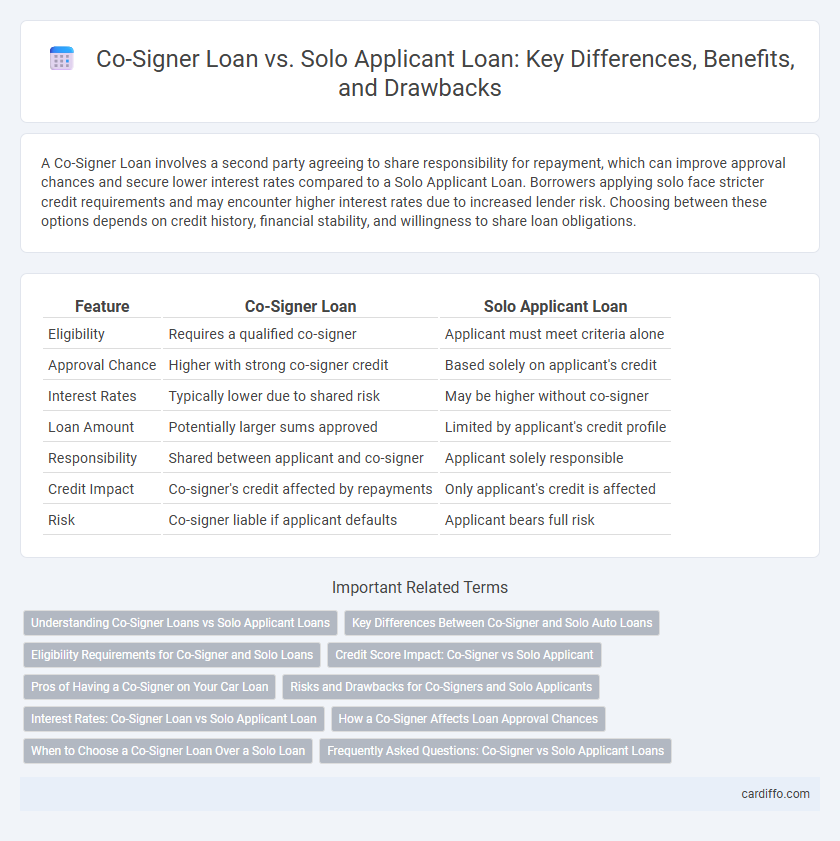
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Co-Signer Loan | Solo Applicant Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Requires a qualified co-signer | Applicant must meet criteria alone |
| Approval Chance | Higher with strong co-signer credit | Based solely on applicant's credit |
| Interest Rates | Typically lower due to shared risk | May be higher without co-signer |
| Loan Amount | Potentially larger sums approved | Limited by applicant's credit profile |
| Responsibility | Shared between applicant and co-signer | Applicant solely responsible |
| Credit Impact | Co-signer's credit affected by repayments | Only applicant's credit is affected |
| Risk | Co-signer liable if applicant defaults | Applicant bears full risk |
Understanding Co-Signer Loans vs Solo Applicant Loans
Co-signer loans involve a second party agreeing to share the responsibility of repayment, which can improve approval chances and secure lower interest rates for borrowers with limited credit history. Solo applicant loans rely solely on the individual's creditworthiness, income, and financial stability, often leading to stricter qualification criteria. Understanding the differences helps borrowers choose the best loan type based on their credit profile and financial needs.
Key Differences Between Co-Signer and Solo Auto Loans
Co-signer auto loans involve a secondary borrower who guarantees loan repayment, reducing risk for lenders and often enabling better interest rates or loan approval for the primary applicant. Solo auto loans are solely under one person's name, placing full responsibility for repayment on that individual, which may result in stricter qualification criteria and potentially higher interest rates. Key differences include credit impact, eligibility requirements, and potential loan terms, with co-signer loans offering benefits for borrowers with limited or poor credit history.
Eligibility Requirements for Co-Signer and Solo Loans
Eligibility requirements for co-signer loans typically include a strong credit score, stable income, and low debt-to-income ratio to support the primary borrower's application, while solo applicant loans rely solely on the individual's financial credentials. Co-signers must often demonstrate the ability to repay the loan if the primary borrower defaults, which can improve approval chances and secure better interest rates. Solo applicants face stricter criteria since the lender assesses only their creditworthiness and income stability for loan approval.
Credit Score Impact: Co-Signer vs Solo Applicant
A co-signer loan can improve approval chances and possibly secure a lower interest rate by leveraging the co-signer's higher credit score, but both parties' credit scores are affected by timely or missed payments. Solo applicant loans solely impact the borrower's credit score, placing all responsibility and risk on the individual's credit behavior. Lenders often view co-signed loans as less risky, potentially benefiting the primary applicant's credit profile if managed well, while solo loans emphasize independent creditworthiness.
Pros of Having a Co-Signer on Your Car Loan
Having a co-signer on your car loan can significantly improve your chances of approval, especially if your credit history is limited or poor. A co-signer with a strong credit profile often helps secure lower interest rates and better loan terms, reducing the overall cost of the loan. Lenders view co-signed loans as less risky, which increases the likelihood of higher loan amounts and flexible repayment options.
Risks and Drawbacks for Co-Signers and Solo Applicants
Co-signer loans carry significant risks for co-signers, including full legal responsibility for repayment if the primary borrower defaults, which can severely impact their credit score and financial stability. Solo applicant loans place all repayment responsibility on one individual, increasing the risk of default if income streams become unstable, but offer greater autonomy without risking another's credit. Both options involve potential credit damage and financial strain, with co-signers facing added liability and solo applicants shouldering full burden alone.
Interest Rates: Co-Signer Loan vs Solo Applicant Loan
Co-signer loans typically offer lower interest rates compared to solo applicant loans due to the added security a co-signer provides, reducing lender risk. Solo applicants often face higher interest rates since the loan approval and creditworthiness rely solely on their financial profile. Lenders prefer co-signer loans when the primary borrower has limited credit history or lower credit scores, resulting in more favorable interest terms.
How a Co-Signer Affects Loan Approval Chances
A co-signer significantly improves loan approval chances by adding their creditworthiness and income to the application, reducing the lender's risk. Lenders often view co-signed loans as lower risk, potentially leading to better interest rates and higher loan amounts compared to solo applicant loans. This shared responsibility provides a financial safety net, making it easier for applicants with limited credit history or lower income to secure approval.
When to Choose a Co-Signer Loan Over a Solo Loan
Choose a co-signer loan over a solo applicant loan when your credit score is below the lender's minimum requirement or your income is insufficient to qualify independently. A co-signer with strong credit can increase the chances of loan approval and secure better interest rates. This option is ideal for first-time borrowers or those rebuilding credit who need financial backing to access favorable loan terms.
Frequently Asked Questions: Co-Signer vs Solo Applicant Loans
Co-signer loans require an additional borrower to guarantee repayment, often improving approval chances and securing lower interest rates for applicants with limited credit history. Solo applicant loans rely solely on the creditworthiness and income of the primary borrower, making qualification stricter but the loan solely tied to one individual's financial responsibility. Common questions include eligibility criteria, impact on credit scores, and how default or late payments affect both co-signers and solo applicants.
Co-Signer Loan vs Solo Applicant Loan Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com