A purchase option in a lease agreement allows the lessee to buy the leased asset at a predetermined price before or at the end of the lease term, providing ownership flexibility. Lease extension grants the lessee additional time to use the asset under the original lease terms, often beneficial for maintaining continuity without immediate capital outlay. Evaluating purchase options versus lease extensions depends on factors like asset value, financial goals, and long-term usage plans.
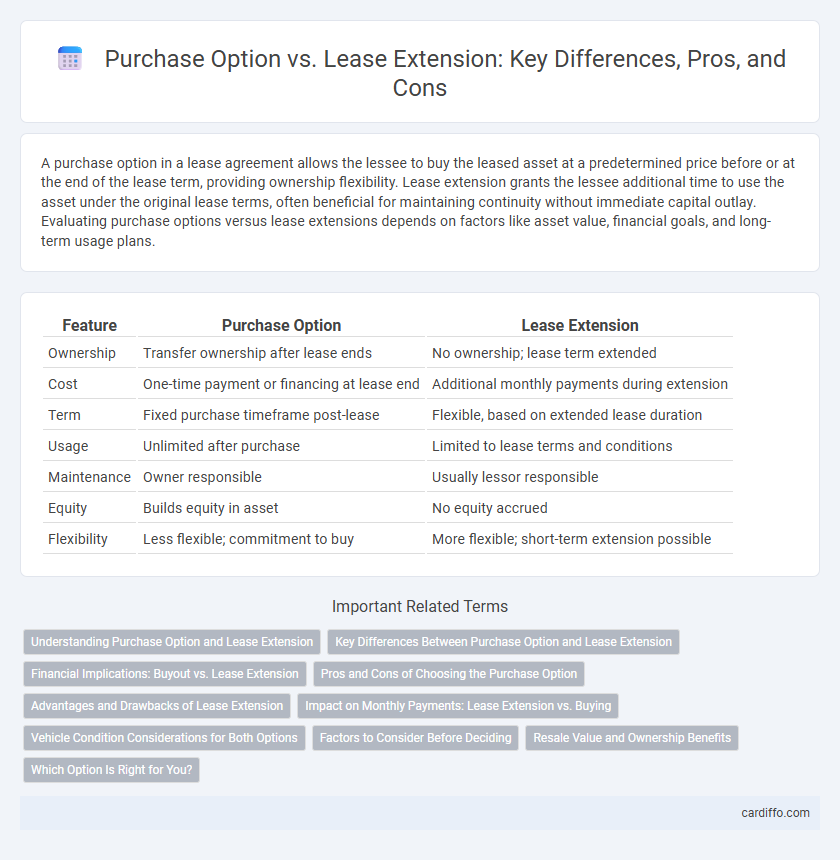
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Purchase Option | Lease Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Transfer ownership after lease ends | No ownership; lease term extended |
| Cost | One-time payment or financing at lease end | Additional monthly payments during extension |
| Term | Fixed purchase timeframe post-lease | Flexible, based on extended lease duration |
| Usage | Unlimited after purchase | Limited to lease terms and conditions |
| Maintenance | Owner responsible | Usually lessor responsible |
| Equity | Builds equity in asset | No equity accrued |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; commitment to buy | More flexible; short-term extension possible |
Understanding Purchase Option and Lease Extension
A purchase option grants tenants the right to buy the leased property at a predetermined price during or at the end of the lease term, providing a clear pathway to ownership. Lease extension allows tenants to prolong their lease period under agreed terms without converting to ownership, offering continued use without immediate purchase obligations. Understanding the distinctions between purchase options and lease extensions is crucial for strategic lease management and financial planning.
Key Differences Between Purchase Option and Lease Extension
A purchase option grants the lessee the right to buy the leased asset at a predetermined price before or at the lease end, providing potential ownership and equity buildup. Lease extension involves prolonging the lease term under agreed conditions without acquiring ownership, maintaining the asset's leased status. Key differences include ownership transfer in purchase options versus continued tenancy in lease extensions, and financial implications such as down payments or adjusted rental rates.
Financial Implications: Buyout vs. Lease Extension
A purchase option in a lease agreement allows tenants to acquire the leased asset at a predetermined price, often resulting in higher upfront costs but potential long-term ownership benefits. Lease extensions typically involve negotiated monthly payments that may be higher than initial lease terms, but avoid the immediate capital expenditure associated with buyouts. Evaluating the financial implications requires analyzing cash flow impact, total cost of ownership, and asset depreciation to determine the most cost-effective strategy.
Pros and Cons of Choosing the Purchase Option
Choosing the purchase option in a lease provides the advantage of eventual ownership, allowing tenants to build equity and potentially benefit from property appreciation. However, this option requires a significant upfront financial commitment and may reduce flexibility compared to lease extensions, which offer continued occupancy without hefty purchase costs. Buyers must carefully evaluate upfront costs, long-term investment potential, and market conditions before opting for purchase over lease extension.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Lease Extension
Lease extension offers the advantage of maintaining tenancy stability without the upfront costs associated with a purchase option, allowing tenants to continue benefiting from predictable rent and terms. However, lease extensions may limit flexibility as tenants remain tied to the property and subject to potential rent increases or landlord-imposed changes. This arrangement reduces immediate financial commitment but lacks the equity-building potential found in a purchase option.
Impact on Monthly Payments: Lease Extension vs. Buying
Choosing a purchase option typically results in higher monthly payments compared to a lease extension due to the acquisition of ownership and associated financing costs. Lease extensions often allow for reduced monthly payments by prolonging the existing lease terms without the need for a substantial down payment. Evaluating monthly payment impact helps lessees decide between continuing lower payments through an extension or committing to larger payments when buying the asset.
Vehicle Condition Considerations for Both Options
When evaluating a purchase option versus a lease extension, vehicle condition plays a critical role in decision-making. For purchase options, thorough inspections and maintenance history are essential, as any existing damage or wear will affect long-term ownership costs. Lease extensions require less stringent condition restrictions but may incur penalties if the vehicle condition exceeds normal wear and tear standards at the lease's end.
Factors to Consider Before Deciding
Evaluating a purchase option versus a lease extension hinges on factors such as the asset's current market value, future depreciation, and the tenant's long-term financial strategy. Assess the total cost implications, including purchase price, lease extension fees, and maintenance expenses, to determine overall affordability. Consider potential tax benefits, changes in property needs, and flexibility requirements before finalizing the decision.
Resale Value and Ownership Benefits
Purchase options in a lease provide lessees the ability to acquire ownership of the asset, enhancing control and potential resale value gains. Lease extensions allow continued use without ownership, which can limit long-term equity accumulation but offer short-term cost efficiency. Ownership through purchase options typically translates to higher resale value benefits and asset control compared to lease extensions.
Which Option Is Right for You?
Choosing between a purchase option and a lease extension depends on your long-term financial goals and asset needs. A purchase option allows you to buy the leased asset at a predetermined price, offering ownership and potential equity benefits, while a lease extension provides continued use of the asset without immediate ownership responsibilities. Evaluate factors such as total cost, asset depreciation, and intended duration of use to determine which option aligns best with your personal or business strategy.
Purchase Option vs Lease Extension Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com