Gap insurance covers the difference between your vehicle's actual cash value and the outstanding balance on your lease if your car is totaled or stolen. Personal insurance, such as comprehensive and collision coverage, pays for damages to your vehicle regardless of your lease balance but does not cover the deficiency gap. Choosing gap insurance protects you from financial loss in case your leased car's value depreciates faster than your payments.
Table of Comparison
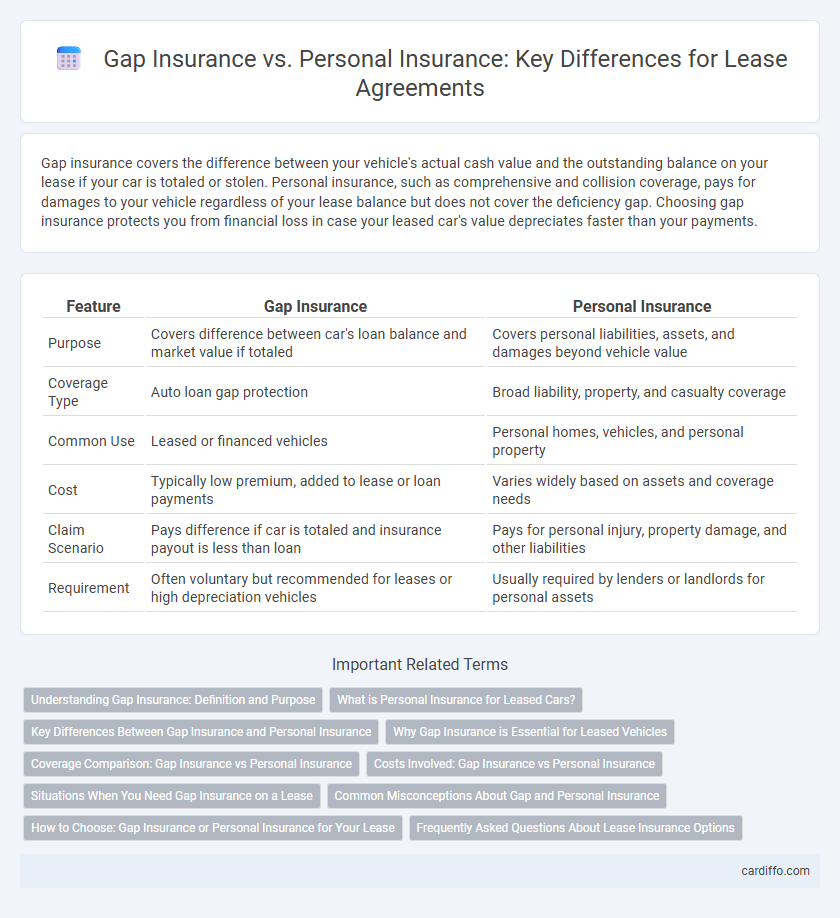
| Feature | Gap Insurance | Personal Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Covers difference between car's loan balance and market value if totaled | Covers personal liabilities, assets, and damages beyond vehicle value |
| Coverage Type | Auto loan gap protection | Broad liability, property, and casualty coverage |
| Common Use | Leased or financed vehicles | Personal homes, vehicles, and personal property |
| Cost | Typically low premium, added to lease or loan payments | Varies widely based on assets and coverage needs |
| Claim Scenario | Pays difference if car is totaled and insurance payout is less than loan | Pays for personal injury, property damage, and other liabilities |
| Requirement | Often voluntary but recommended for leases or high depreciation vehicles | Usually required by lenders or landlords for personal assets |
Understanding Gap Insurance: Definition and Purpose
Gap insurance covers the difference between your vehicle's actual cash value and the remaining balance on your lease, protecting you from financial loss if your car is totaled or stolen. Personal insurance typically covers liability and physical damage but may not cover the full lease payoff amount, making gap insurance essential in lease agreements. Understanding this distinction helps ensure adequate financial protection throughout the lease term.
What is Personal Insurance for Leased Cars?
Personal insurance for leased cars provides coverage tailored to protect the driver's liability and the leased vehicle itself, complying with lease agreement requirements. It typically includes liability, collision, and comprehensive coverage, ensuring that damages or theft are financially covered beyond the scope of gap insurance. Lease contracts often mandate maintaining specific insurance levels to safeguard both the lessee and the leasing company against potential losses.
Key Differences Between Gap Insurance and Personal Insurance
Gap insurance covers the difference between a vehicle's actual cash value and the remaining lease balance in case of total loss, ensuring financial protection during the lease term. Personal insurance typically includes liability, collision, and comprehensive coverage that protects against damages or injuries, but does not cover the gap between loan or lease payoff and the vehicle's depreciated value. Understanding these distinctions helps lessees avoid out-of-pocket expenses when their leased vehicle is totaled or stolen.
Why Gap Insurance is Essential for Leased Vehicles
Gap Insurance is essential for leased vehicles because it covers the difference between the vehicle's actual cash value and the remaining lease balance in case of total loss or theft. Unlike personal insurance, which typically only reimburses the vehicle's market value, gap insurance prevents financial liabilities that exceed standard coverage. This protection ensures that lessees are not responsible for out-of-pocket expenses on the remaining lease payments, providing critical financial security.
Coverage Comparison: Gap Insurance vs Personal Insurance
Gap Insurance covers the difference between your vehicle's actual cash value and the remaining balance on your lease or loan if your car is totaled or stolen, providing financial protection against depreciation losses. Personal Insurance, typically comprehensive and collision coverage within your auto insurance policy, pays for repairs or replacement of your vehicle but may not cover the full amount owed on a lease in case of a total loss. Gap Insurance specifically targets lease or loan payoff gaps, while personal insurance focuses on vehicle repair costs and liability coverage.
Costs Involved: Gap Insurance vs Personal Insurance
Gap insurance typically involves a one-time premium or a small fee added to your auto lease payments, offering cost-effectiveness by covering the difference between your car's market value and the lease payoff amount in case of total loss. Personal insurance premiums vary widely based on factors like driving record, coverage limits, and deductibles, often resulting in higher ongoing costs without covering the lease balance gap. Choosing gap insurance can minimize out-of-pocket expenses after a total loss, whereas relying solely on personal insurance may leave lessees responsible for significant remaining lease payments.
Situations When You Need Gap Insurance on a Lease
Gap insurance is essential for leaseholders when the vehicle's market value depreciates faster than the remaining lease balance, creating a financial shortfall in case of total loss or theft. Personal insurance typically covers the vehicle's current value but does not account for the outstanding lease payoff amount, leaving the lessee responsible for the difference. Situations such as accidents, theft, or severe damage highlight the importance of gap insurance in protecting against costly out-of-pocket expenses during the lease term.
Common Misconceptions About Gap and Personal Insurance
Gap insurance is often misunderstood as a substitute for personal insurance, but it specifically covers the difference between the car's actual cash value and the remaining lease balance in case of total loss. Personal insurance, such as comprehensive or collision coverage, protects against damage or theft but does not cover the financial gap that occurs when a leased vehicle is totaled. Many lessees mistakenly believe personal insurance alone will cover all costs, leading to unexpected out-of-pocket expenses without gap insurance.
How to Choose: Gap Insurance or Personal Insurance for Your Lease
Choosing between gap insurance and personal insurance for your lease depends on the coverage needs and financial risk tolerance. Gap insurance covers the difference between the car's actual cash value and the lease payoff amount in case of total loss, making it essential for leased vehicles with high depreciation. Personal insurance, often a comprehensive policy, protects against damages and liability but may not cover the gap, so reviewing your lease contract and insurer's terms is critical to avoid out-of-pocket expenses.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lease Insurance Options
Gap insurance covers the difference between your vehicle's actual cash value and the outstanding lease balance if the car is totaled or stolen, providing financial protection during the lease term. Personal insurance, including comprehensive and collision coverage, protects against damages or loss to the vehicle but does not cover the lease payoff amount. Lessees often ask whether gap insurance is mandatory, how it affects monthly payments, and if personal insurance suffices without gap coverage; understanding these distinctions is crucial for informed lease insurance decisions.
Gap Insurance vs Personal Insurance Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com