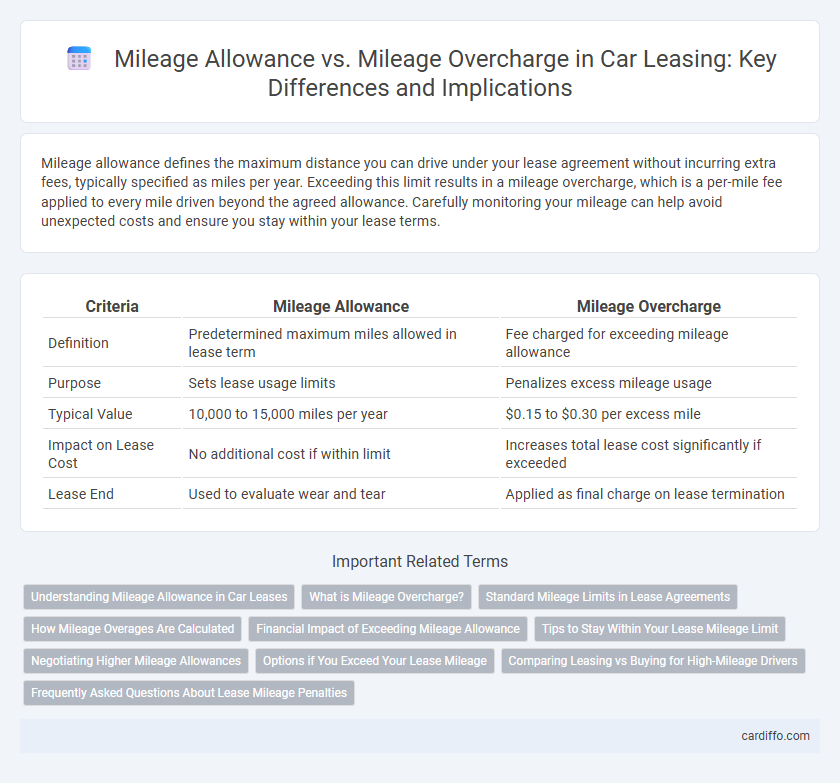
Mileage allowance defines the maximum distance you can drive under your lease agreement without incurring extra fees, typically specified as miles per year. Exceeding this limit results in a mileage overcharge, which is a per-mile fee applied to every mile driven beyond the agreed allowance. Carefully monitoring your mileage can help avoid unexpected costs and ensure you stay within your lease terms.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Mileage Allowance | Mileage Overcharge |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Predetermined maximum miles allowed in lease term | Fee charged for exceeding mileage allowance |
| Purpose | Sets lease usage limits | Penalizes excess mileage usage |
| Typical Value | 10,000 to 15,000 miles per year | $0.15 to $0.30 per excess mile |
| Impact on Lease Cost | No additional cost if within limit | Increases total lease cost significantly if exceeded |
| Lease End | Used to evaluate wear and tear | Applied as final charge on lease termination |
Understanding Mileage Allowance in Car Leases
Mileage allowance in car leases refers to the pre-agreed limit of miles a lessee can drive annually without incurring extra fees. Exceeding this mileage often results in mileage overcharges, which are calculated per additional mile and can significantly increase lease costs. Understanding the specific mileage allowance and its impact on total lease expenses helps lessees avoid unexpected charges and choose the most cost-effective lease terms.
What is Mileage Overcharge?
Mileage overcharge occurs when a lessee exceeds the predetermined mileage limit set in a vehicle lease agreement, resulting in additional fees calculated per excess mile. These charges are specified in the lease contract and often range from $0.15 to $0.30 per mile, significantly impacting the total cost of leasing. Understanding mileage overcharge penalties is essential for managing lease budgets and avoiding unexpected expenses at lease-end.
Standard Mileage Limits in Lease Agreements
Standard mileage limits in lease agreements typically range from 10,000 to 15,000 miles annually, establishing a cap on the vehicle's permitted usage without incurring extra fees. Exceeding these limits results in mileage overcharges, calculated per mile and often ranging from $0.15 to $0.30, significantly increasing the lease's total cost. Understanding these limits and associated fees is crucial for leaseholders to avoid unexpected charges and maintain compliance with their lease terms.
How Mileage Overages Are Calculated
Mileage overages are calculated by subtracting the allowed mileage stated in the lease agreement from the actual miles driven, with the difference multiplied by the predetermined per-mile overage fee. Lease contracts typically specify an annual mileage limit, and exceeding this limit results in charges based on the excess mileage. Accurate tracking of odometer readings at lease inception and termination ensures precise calculation of mileage overcharges.
Financial Impact of Exceeding Mileage Allowance
Exceeding the mileage allowance in a lease agreement results in significant financial charges calculated per additional mile driven, often ranging from $0.15 to $0.30. These overcharges can substantially increase the total cost of leasing, leading to unexpected fees at lease-end. Understanding the mileage cap and closely monitoring usage prevents costly penalties and protects the lessee's budget.
Tips to Stay Within Your Lease Mileage Limit
To avoid mileage overcharge fees on your lease, track your miles regularly using a reliable app or GPS system to ensure you stay within the annual mileage allowance specified in your lease agreement. Plan trips efficiently by consolidating errands and carpooling to reduce unnecessary driving. Opt for maintenance strategies like tire rotation and engine checkups that promote fuel efficiency, helping you get more miles out of every gallon.
Negotiating Higher Mileage Allowances
Negotiating higher mileage allowances in a lease can prevent costly mileage overcharges at the end of the term, often calculated per mile exceeding the contract limit. Lease agreements typically cap mileage between 10,000 to 15,000 miles annually, with excess fees ranging from $0.15 to $0.30 per mile. Securing a higher mileage allowance upfront provides flexibility for increased driving needs and reduces the risk of unexpected fees, making it crucial to discuss this with the lessor before signing.
Options if You Exceed Your Lease Mileage
Exceeding your lease mileage can lead to costly overcharges based on the per-mile rate specified in the contract, often ranging from 15 to 30 cents per mile. To avoid these fees, consider purchasing additional mileage upfront or negotiating a higher mileage allowance before signing the lease. Some leases offer the option to prepay excess miles at a reduced rate or allow lease-end buyouts to cover overages without penalty.
Comparing Leasing vs Buying for High-Mileage Drivers
High-mileage drivers often face significant costs in leasing due to mileage allowance limits, typically ranging from 10,000 to 15,000 miles per year, with penalties averaging 15 to 25 cents per mile over the allowance. In contrast, buying a vehicle eliminates overcharge fees, allowing unlimited mileage without extra costs, making ownership more cost-effective for drivers exceeding these thresholds. Evaluating total expenses, including maintenance and depreciation, helps determine if leasing penalties outweigh the benefits of lower monthly payments for high-mileage usage.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lease Mileage Penalties
Lease mileage penalties often arise when drivers exceed the agreed-upon mileage limit, resulting in mileage overcharges calculated per excess mile. Mileage allowance specifies the maximum miles permitted annually or over the lease term, which is typically between 10,000 and 15,000 miles per year. Understanding the cost difference and negotiating the mileage allowance upfront can help avoid unexpected fees associated with excess mileage at lease-end inspections.
Mileage Allowance vs Mileage Overcharge Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com