New car replacement coverage provides policyholders with a brand-new vehicle if their car is totaled within a specific period, while depreciated value coverage reimburses the current market value, accounting for depreciation. Choosing new car replacement ensures you are not burdened with depreciation costs, offering greater financial protection and peace of mind. Depreciated value insurance generally results in lower premiums but may lead to out-of-pocket expenses for repairs or a new vehicle.
Table of Comparison
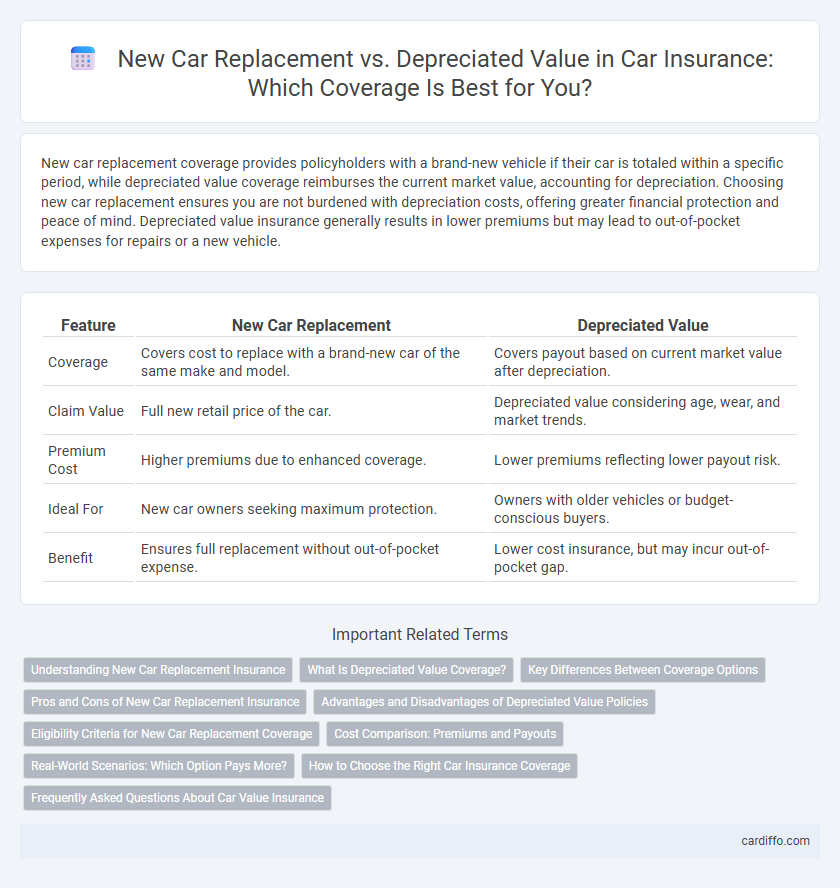
| Feature | New Car Replacement | Depreciated Value |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Covers cost to replace with a brand-new car of the same make and model. | Covers payout based on current market value after depreciation. |
| Claim Value | Full new retail price of the car. | Depreciated value considering age, wear, and market trends. |
| Premium Cost | Higher premiums due to enhanced coverage. | Lower premiums reflecting lower payout risk. |
| Ideal For | New car owners seeking maximum protection. | Owners with older vehicles or budget-conscious buyers. |
| Benefit | Ensures full replacement without out-of-pocket expense. | Lower cost insurance, but may incur out-of-pocket gap. |
Understanding New Car Replacement Insurance
New Car Replacement Insurance covers the cost of replacing your vehicle with a new model if it is stolen or declared a total loss within a specified period, typically the first one to two years of ownership. This coverage eliminates the need to factor in depreciation, providing full reimbursement based on the original purchase price or a comparable new car value. Understanding this difference is crucial compared to standard policies that only pay the depreciated value, significantly impacting your claim settlement amount.
What Is Depreciated Value Coverage?
Depreciated Value Coverage in auto insurance reimburses the vehicle's worth minus depreciation at the time of a claim, reflecting current market value rather than the original purchase price. This means policyholders receive compensation based on the car's age, condition, and mileage, often resulting in lower payouts compared to new car replacement policies. Understanding depreciated value coverage is essential for evaluating potential out-of-pocket expenses when repairing or replacing your vehicle after an accident or total loss.
Key Differences Between Coverage Options
New Car Replacement coverage reimburses the cost of a brand-new vehicle if your car is totaled within a specified time frame, whereas Depreciated Value pays out based on the vehicle's current market value after depreciation. The key difference lies in the payout amount, with New Car Replacement offering full replacement cost without accounting for depreciation, while Depreciated Value reflects wear and tear, reducing the claim amount. Choosing between these options affects financial protection and premium costs, as New Car Replacement typically involves higher premiums due to increased risk for insurers.
Pros and Cons of New Car Replacement Insurance
New Car Replacement insurance offers the advantage of covering the full cost to replace a totaled vehicle with a new one of the same make and model, avoiding depreciation losses common in standard policies. This type of coverage is ideal for owners of new vehicles under three years old, providing peace of mind against rapid value decline. However, premiums tend to be higher compared to depreciated value coverage, and the policy may have limitations on vehicle eligibility and replacement timelines.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Depreciated Value Policies
Depreciated value policies in insurance calculate payouts based on the car's current market value minus depreciation, often resulting in lower compensation compared to new car replacement policies. The primary advantage lies in lower premiums, making it more affordable for policyholders, but a major disadvantage is the risk of insufficient repair or replacement funds following a total loss. This approach can lead to significant out-of-pocket expenses for the insured if the depreciated value falls substantially below the cost of a comparable new vehicle.
Eligibility Criteria for New Car Replacement Coverage
New car replacement coverage eligibility typically requires the insured vehicle to be a brand-new car purchased within the last one to two years, with mileage below a specified threshold, often under 15,000 miles. Policies may also mandate that the vehicle was financed or leased and that the insurance policy includes comprehensive and collision coverage. Verification with the insurer is essential to confirm specific criteria such as vehicle make, model, and condition at the time of the claim.
Cost Comparison: Premiums and Payouts
New car replacement coverage generally results in higher insurance premiums due to the increased payout potential of replacing a vehicle with a new one regardless of depreciation. Depreciated value coverage typically has lower premiums but leads to reduced claim payouts, reflecting the vehicle's diminished market value over time. Policyholders must weigh the upfront cost difference against the potential financial benefit at the time of a claim to determine the most cost-effective option.
Real-World Scenarios: Which Option Pays More?
In real-world insurance claims, new car replacement coverage often pays more than depreciated value policies because it reimburses the cost of a brand-new vehicle rather than the car's current market value, which may be significantly lower due to depreciation. Drivers with new car replacement coverage benefit from full replacement cost without deducting depreciation, especially within the first few years after purchase. Depreciated value policies typically result in lower payouts, reflecting wear and tear and market depreciation, making new car replacement a financially advantageous option for maintaining vehicle value after a total loss.
How to Choose the Right Car Insurance Coverage
Choosing the right car insurance coverage requires understanding the difference between new car replacement and depreciated value policies. New car replacement coverage reimburses the cost of a brand-new vehicle if your car is totaled within a specified period, typically one to two years, offering full financial protection. In contrast, depreciated value insurance compensates based on your car's market value at the time of the claim, which can lead to lower payouts but often reduced premium costs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Car Value Insurance
New car replacement coverage reimburses the cost of a brand new vehicle if your car is totaled within a specified period, while depreciated value coverage pays based on the car's current market value, accounting for depreciation. Policyholders often ask how long new car replacement is available, typically ranging from one to two years after purchase depending on insurers' terms. Another common question concerns whether new car replacement impacts premiums, which generally increase due to the higher potential payout compared to depreciated value coverage.
New Car Replacement vs Depreciated Value Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com