Gap insurance covers the difference between your car's actual cash value and the balance remaining on your auto loan if your vehicle is totaled, providing financial protection beyond standard coverage. Standard insurance typically reimburses you for the vehicle's market value at the time of the accident, which may leave you responsible for paying the outstanding loan balance. Choosing gap insurance ensures you won't face out-of-pocket expenses when your car's depreciation exceeds your insurance payout.
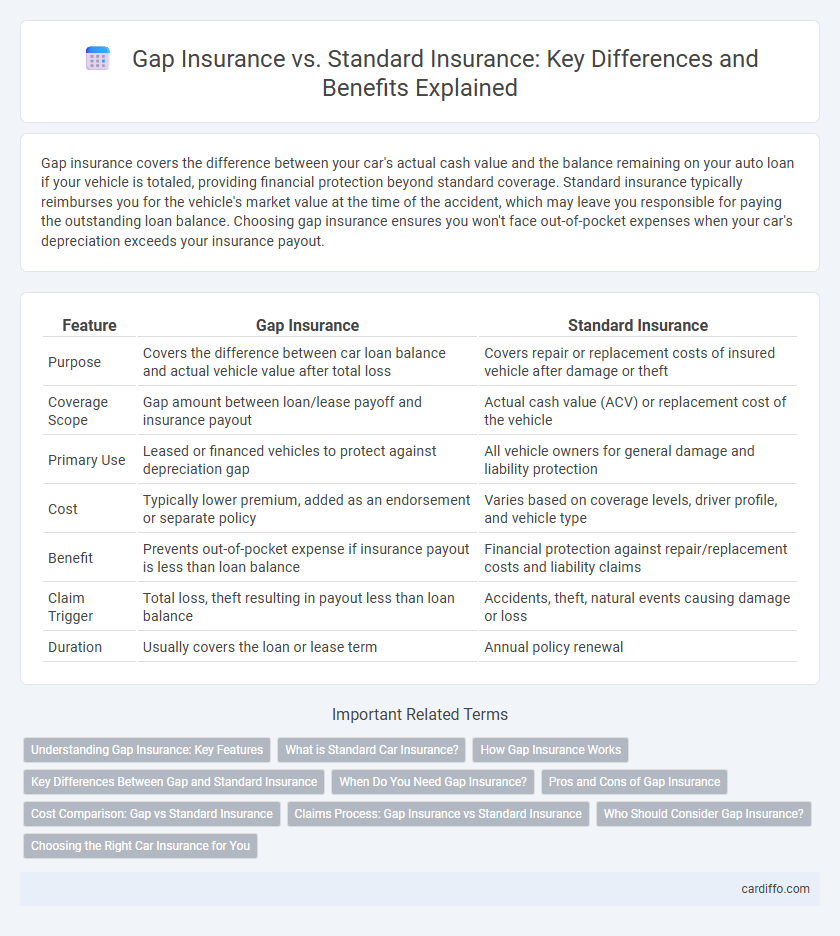
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gap Insurance | Standard Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Covers the difference between car loan balance and actual vehicle value after total loss | Covers repair or replacement costs of insured vehicle after damage or theft |
| Coverage Scope | Gap amount between loan/lease payoff and insurance payout | Actual cash value (ACV) or replacement cost of the vehicle |
| Primary Use | Leased or financed vehicles to protect against depreciation gap | All vehicle owners for general damage and liability protection |
| Cost | Typically lower premium, added as an endorsement or separate policy | Varies based on coverage levels, driver profile, and vehicle type |
| Benefit | Prevents out-of-pocket expense if insurance payout is less than loan balance | Financial protection against repair/replacement costs and liability claims |
| Claim Trigger | Total loss, theft resulting in payout less than loan balance | Accidents, theft, natural events causing damage or loss |
| Duration | Usually covers the loan or lease term | Annual policy renewal |
Understanding Gap Insurance: Key Features
Gap insurance covers the difference between your car's actual cash value and the remaining balance on your auto loan, protecting you from financial loss in case of total vehicle theft or accident. Standard insurance typically covers the current market value of the vehicle, which may leave you responsible for paying off the remaining loan balance if your car is totaled. Key features of gap insurance include coverage for loan balance shortfall, protection during depreciation, and peace of mind for financing or leasing agreements.
What is Standard Car Insurance?
Standard car insurance provides coverage for common risks such as liability, collision, and comprehensive damages, protecting drivers against financial losses from accidents, theft, or natural disasters. It typically covers repair costs, medical expenses, and legal liabilities incurred during an at-fault accident, subject to policy limits and deductibles. Unlike gap insurance, standard insurance does not cover the difference between the car's actual cash value and the remaining loan or lease balance in cases of total loss.
How Gap Insurance Works
Gap insurance covers the difference between the actual cash value of a vehicle and the outstanding loan balance in case of total loss or theft, ensuring the policyholder is not left paying out-of-pocket for the remaining debt. Standard insurance policies typically reimburse only the market value of the vehicle at the time of the claim, which can be significantly lower than the original purchase price. This coverage is especially beneficial for new cars that depreciate rapidly, bridging the financial gap between settlement and loan payoff.
Key Differences Between Gap and Standard Insurance
Gap insurance covers the difference between a vehicle's actual cash value and the outstanding loan balance in case of total loss, whereas standard insurance pays only up to the vehicle's depreciated value. Standard insurance protects against damages or liability, but does not account for any remaining loan amounts exceeding the car's market value. Gap insurance is particularly crucial for drivers with auto loans or leases, minimizing financial loss beyond conventional coverage limits.
When Do You Need Gap Insurance?
Gap insurance is essential when financing or leasing a vehicle, as it covers the difference between the car's actual cash value and the outstanding loan balance in case of total loss. Standard insurance typically reimburses only the depreciated value, which may leave you responsible for paying the loan balance out of pocket. Drivers with high loan-to-value ratios, long loan terms, or rapid depreciation rates benefit most from gap insurance for comprehensive financial protection.
Pros and Cons of Gap Insurance
Gap insurance covers the difference between a vehicle's actual cash value and the amount owed on a loan or lease, protecting policyholders from significant financial loss after total loss or theft. Its main advantage is preventing out-of-pocket expenses when a standard insurance payout is insufficient, but it can add to overall insurance costs and is only beneficial for those with high loan balances or steep depreciation rates. Standard insurance offers broader coverage but may leave borrowers vulnerable to gap exposure, making gap insurance a targeted supplement rather than a replacement.
Cost Comparison: Gap vs Standard Insurance
Gap insurance generally costs between $20 and $40 per year, providing affordable coverage that pays the difference between a vehicle's actual cash value and the remaining loan balance in case of total loss. Standard insurance premiums vary widely based on factors like age, location, driving history, and coverage limits, often ranging from $600 to $1,200 annually for full coverage. While standard insurance covers vehicle damage and liability, gap insurance acts as a cost-effective supplement, reducing out-of-pocket expenses when a vehicle is totaled or stolen.
Claims Process: Gap Insurance vs Standard Insurance
Gap insurance claims process typically involves quicker settlements as it covers the difference between the vehicle's actual cash value and the outstanding loan balance, minimizing the risk of underpayment in total loss scenarios. Standard insurance claims often require detailed damage assessment and depreciation calculations, leading to longer processing times and potentially lower payout amounts. Understanding these differences helps policyholders choose coverage that best fits their financial protection needs after an accident or theft.
Who Should Consider Gap Insurance?
Gap insurance is ideal for new car buyers or individuals with financed or leased vehicles who face rapid depreciation and could owe more than the car's market value. Drivers with low down payments or long loan terms benefit significantly from gap coverage, which covers the difference between the car's actual cash value and the remaining loan balance after a total loss. Standard insurance alone typically covers the car's current market value, leaving a potential financial gap that gap insurance specifically addresses.
Choosing the Right Car Insurance for You
Gap insurance covers the difference between your car's current market value and the amount you still owe on your loan or lease, protecting you from financial loss if your vehicle is totaled or stolen. Standard car insurance typically includes liability, collision, and comprehensive coverage, addressing damage to your vehicle and property, but it does not cover loan or lease gaps. Evaluating your vehicle's depreciation, loan balance, and financial situation is essential to determine if gap insurance complements your standard policy for optimal protection.
Gap Insurance vs Standard Insurance Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com