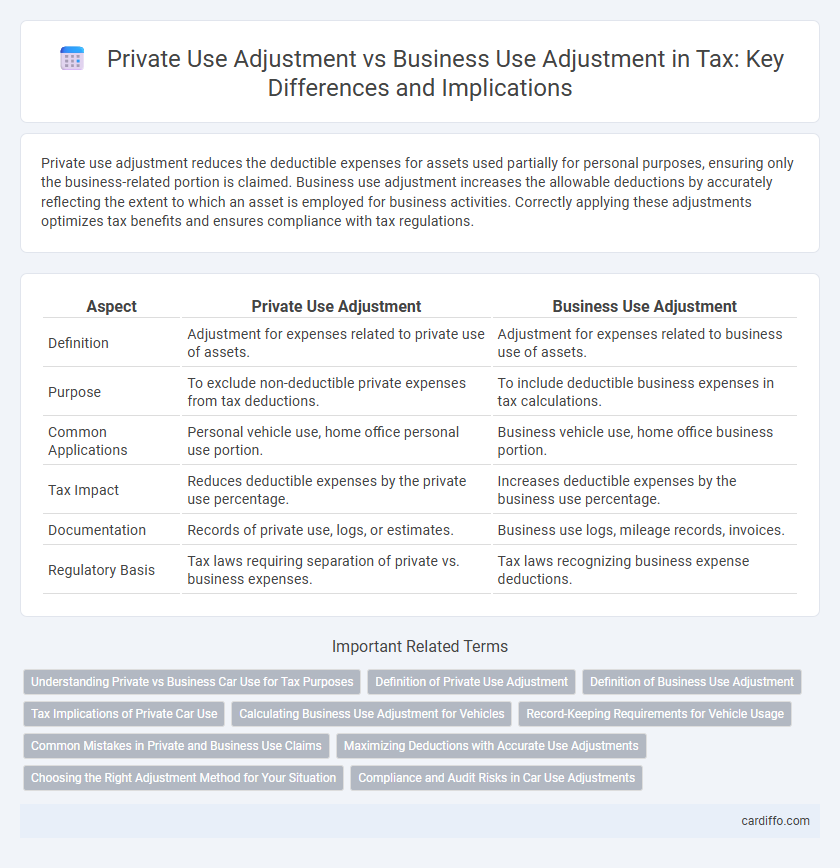
Private use adjustment reduces the deductible expenses for assets used partially for personal purposes, ensuring only the business-related portion is claimed. Business use adjustment increases the allowable deductions by accurately reflecting the extent to which an asset is employed for business activities. Correctly applying these adjustments optimizes tax benefits and ensures compliance with tax regulations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Private Use Adjustment | Business Use Adjustment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjustment for expenses related to private use of assets. | Adjustment for expenses related to business use of assets. |
| Purpose | To exclude non-deductible private expenses from tax deductions. | To include deductible business expenses in tax calculations. |
| Common Applications | Personal vehicle use, home office personal use portion. | Business vehicle use, home office business portion. |
| Tax Impact | Reduces deductible expenses by the private use percentage. | Increases deductible expenses by the business use percentage. |
| Documentation | Records of private use, logs, or estimates. | Business use logs, mileage records, invoices. |
| Regulatory Basis | Tax laws requiring separation of private vs. business expenses. | Tax laws recognizing business expense deductions. |
Understanding Private vs Business Car Use for Tax Purposes
Understanding the distinction between private use adjustment and business use adjustment is crucial for accurate tax reporting on vehicle expenses. Private use adjustment involves reducing deductible expenses to account for non-business mileage, whereas business use adjustment increases the deductible amount based on the percentage of vehicle use related to business activities. Accurate mileage logs and records ensure compliance with tax regulations by clearly separating personal and business kilometers for optimized deductions.
Definition of Private Use Adjustment
Private Use Adjustment refers to the tax calculation applied when an asset or expense is partially used for personal purposes rather than exclusively for business. This adjustment reduces the deductible amount proportionate to the extent of non-business usage, ensuring accurate taxable income reporting. It contrasts with Business Use Adjustment, which typically increases deductions based on the percentage of business-related use.
Definition of Business Use Adjustment
Business use adjustment refers to the process of allocating the deductible expenses or depreciation of an asset based on the percentage of its use for business purposes. This adjustment ensures that only the portion of costs related to generating business income is claimed as a tax deduction. Accurate calculation of business use adjustment is essential for compliance with tax regulations and avoiding penalties.
Tax Implications of Private Car Use
Private use adjustment requires reporting the value of personal use of a business vehicle as a taxable benefit, increasing the individual's assessable income and subjecting it to income tax. Business use adjustment allows deduction of expenses related only to business activities, reducing taxable income but necessitating accurate logbooks and records to substantiate claims. Misclassification or improper adjustments can lead to tax penalties, emphasizing the importance of compliance with tax regulations on private car use.
Calculating Business Use Adjustment for Vehicles
Calculating the Business Use Adjustment for vehicles requires accurately tracking the total kilometers driven and distinguishing between business and private use. The business use percentage is determined by dividing the kilometers driven for business purposes by the total kilometers driven during the fiscal year. This percentage is then applied to vehicle expenses, including depreciation and operating costs, to adjust tax deductions accordingly.
Record-Keeping Requirements for Vehicle Usage
Accurate record-keeping for vehicle usage is essential to distinguish between private use adjustment and business use adjustment in tax reporting. Detailed logs must include dates, mileage, destinations, and purpose of each trip to support the proportion of business versus private use. Failure to maintain precise records can result in incorrect tax deductions and potential penalties during audits.
Common Mistakes in Private and Business Use Claims
Claiming private use expenses as business deductions often leads to inaccuracies due to improper mileage tracking or mixing personal and business expenses without clear documentation. Business use adjustments require detailed record-keeping, such as logs or receipts, to substantiate the percentage of business usage accurately. Failure to separate private from business use can trigger audits and result in denied deductions or penalties from tax authorities.
Maximizing Deductions with Accurate Use Adjustments
Maximizing deductions through precise private use and business use adjustments ensures compliance with tax regulations while optimizing taxable income reductions. Accurately distinguishing between personal and business expenses allows for proper allocation, preventing audit risks and enhancing legitimate deduction claims. Leveraging detailed usage records and applying correct proportional calculations significantly improves the effectiveness of tax deductions related to mixed-use assets.
Choosing the Right Adjustment Method for Your Situation
Selecting the appropriate adjustment method depends on accurately tracking the proportion of private versus business use of assets, such as vehicles or equipment. Business use adjustment typically requires detailed logs or records to substantiate claims, while private use adjustment often relies on standard approximations or flat rates established by tax authorities. Understanding the specific tax regulations and documentation requirements for each method ensures compliance and maximizes allowable deductions.
Compliance and Audit Risks in Car Use Adjustments
Private use adjustments require meticulous record-keeping to differentiate personal mileage from business mileage, reducing the risk of non-compliance with tax regulations. Business use adjustments must accurately reflect actual vehicle use supported by detailed logs, ensuring proper deduction claims and minimizing potential audit discrepancies. Inconsistent or incomplete documentation in either adjustment type can trigger audits, penalties, and increased scrutiny from tax authorities.
Private use adjustment vs business use adjustment Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com