Personal property tax is a levy on movable assets such as vehicles, equipment, and furniture, based on the assessed value of the individual items. Ad valorem tax applies to real estate and is calculated as a percentage of the property's assessed value, reflecting market worth. Both taxes are crucial for local government revenue but differ in their subjects and valuation methods.
Table of Comparison
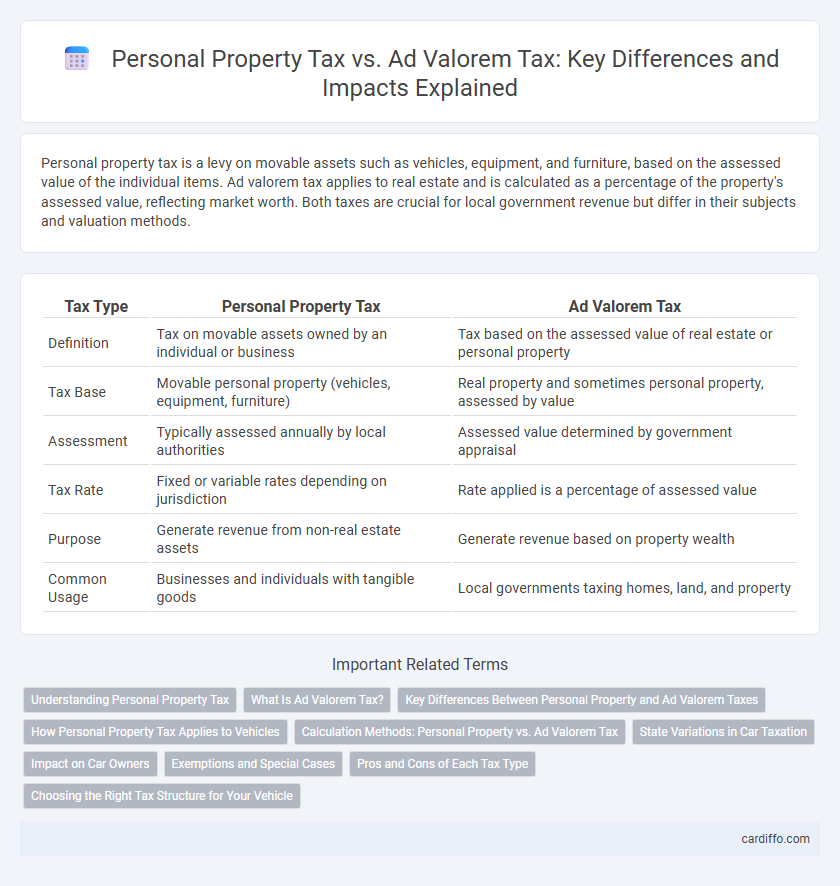
| Tax Type | Personal Property Tax | Ad Valorem Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax on movable assets owned by an individual or business | Tax based on the assessed value of real estate or personal property |
| Tax Base | Movable personal property (vehicles, equipment, furniture) | Real property and sometimes personal property, assessed by value |
| Assessment | Typically assessed annually by local authorities | Assessed value determined by government appraisal |
| Tax Rate | Fixed or variable rates depending on jurisdiction | Rate applied is a percentage of assessed value |
| Purpose | Generate revenue from non-real estate assets | Generate revenue based on property wealth |
| Common Usage | Businesses and individuals with tangible goods | Local governments taxing homes, land, and property |
Understanding Personal Property Tax
Personal Property Tax applies to movable assets like vehicles, machinery, and equipment, assessed based on the value of these tangible items owned by individuals or businesses. This tax differs from Ad Valorem Tax, which is levied proportionally to the assessed value of real estate or immovable property. Understanding Personal Property Tax is essential for accurate asset valuation, compliance with local tax laws, and effective financial planning.
What Is Ad Valorem Tax?
Ad Valorem tax is a property tax based on the assessed value of real estate or personal property, calculated as a percentage of that value. Unlike personal property tax, which specifically targets movable assets such as vehicles and equipment, ad valorem taxes apply broadly to both real and tangible personal property within a jurisdiction. This tax system ensures that property owners pay in proportion to the value of their assets, contributing to local government revenues for public services.
Key Differences Between Personal Property and Ad Valorem Taxes
Personal property tax is a tax levied on movable assets owned by individuals or businesses, such as vehicles, equipment, and furniture, while ad valorem tax is based on the assessed value of real estate or tangible personal property. Personal property tax rates and assessment methods vary by jurisdiction, often focusing on specific categories of movable property, whereas ad valorem tax applies broadly to real estate and is calculated as a percentage of appraised market value. The key difference lies in the taxable subjects: personal property tax targets movable assets separately from land, whereas ad valorem tax primarily targets real estate and can include certain personal properties based on value assessments.
How Personal Property Tax Applies to Vehicles
Personal property tax on vehicles is a tax imposed by local governments based on the assessed value of the vehicle, differing from ad valorem tax which applies more broadly to real estate or other tangible personal property. This tax is calculated annually, reflecting the current market value or depreciation of the vehicle to determine the owed amount. Vehicle owners must pay personal property tax to comply with state laws and avoid penalties, with rates varying by jurisdiction.
Calculation Methods: Personal Property vs. Ad Valorem Tax
Personal Property Tax is calculated based on the assessed value of movable assets like vehicles or equipment, typically using a flat rate or percentage specific to the tax jurisdiction. Ad Valorem Tax is determined by the assessed market value of real estate or tangible personal property, applying a tax rate proportional to the property's value. The key difference lies in Personal Property Tax focusing on specific asset categories, while Ad Valorem Tax broadly targets property value, influencing calculation methods and applicable rates.
State Variations in Car Taxation
State variations in car taxation demonstrate significant differences between personal property tax and ad valorem tax systems. Some states levy a personal property tax based on the vehicle's value annually, while others apply ad valorem tax calculated as a percentage of the car's assessed value at purchase or registration. These disparities affect the overall tax burden on vehicle owners, influencing registration costs and annual tax payments across different jurisdictions.
Impact on Car Owners
Personal Property Tax directly affects car owners by imposing an annual tax based on the vehicle's assessed value, often leading to higher costs for newer or more expensive cars. Ad Valorem Tax, calculated as a percentage of the car's market value, can cause fluctuations in tax amounts depending on changes in vehicle depreciation or market conditions. Understanding these tax types helps car owners anticipate financial obligations and budget accordingly.
Exemptions and Special Cases
Personal property tax often allows exemptions for items such as household goods, tools of the trade, and certain business equipment, reducing the taxable value based on state-specific regulations. Ad valorem tax exemptions commonly include exemptions for primary residences, agricultural land, and nonprofit organizations, which vary by jurisdiction and can significantly lower tax liability. Special cases like tax abatements, circuit breakers, or senior citizen exemptions also apply differently in personal property and ad valorem tax systems, impacting the overall tax burden.
Pros and Cons of Each Tax Type
Personal property tax targets movable assets, offering precise valuation on high-value items but often requires frequent reassessment, causing administrative complexity and potential taxpayer disputes. Ad valorem tax, based on property value, provides a stable revenue stream linked to market value but may lead to inequities during market fluctuations and challenges in accurate appraisal. Evaluating personal property tax versus ad valorem tax involves balancing assessment accuracy against administrative efficiency and fiscal fairness.
Choosing the Right Tax Structure for Your Vehicle
Personal property tax applies specifically to movable assets like vehicles, calculating tax based on the asset's current value annually. Ad valorem tax, a broader category, bases the tax amount on the assessed value of property, including real estate and personal property, often influencing the overall tax burden. Selecting the right tax structure for your vehicle requires understanding local regulations, as personal property tax may vary by jurisdiction and impact total ownership costs more directly than ad valorem tax.
Personal Property Tax vs Ad Valorem Tax Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com