Exempt vehicles are those specifically excluded from road tax due to their use, such as emergency service vehicles, agricultural machinery, or electric cars that qualify for green incentives. Taxable vehicles include private cars, commercial trucks, and motorcycles that require registration and annual tax payment to fund road maintenance and infrastructure. Understanding the distinction ensures compliance with tax regulations and potential savings for eligible vehicle owners.
Table of Comparison
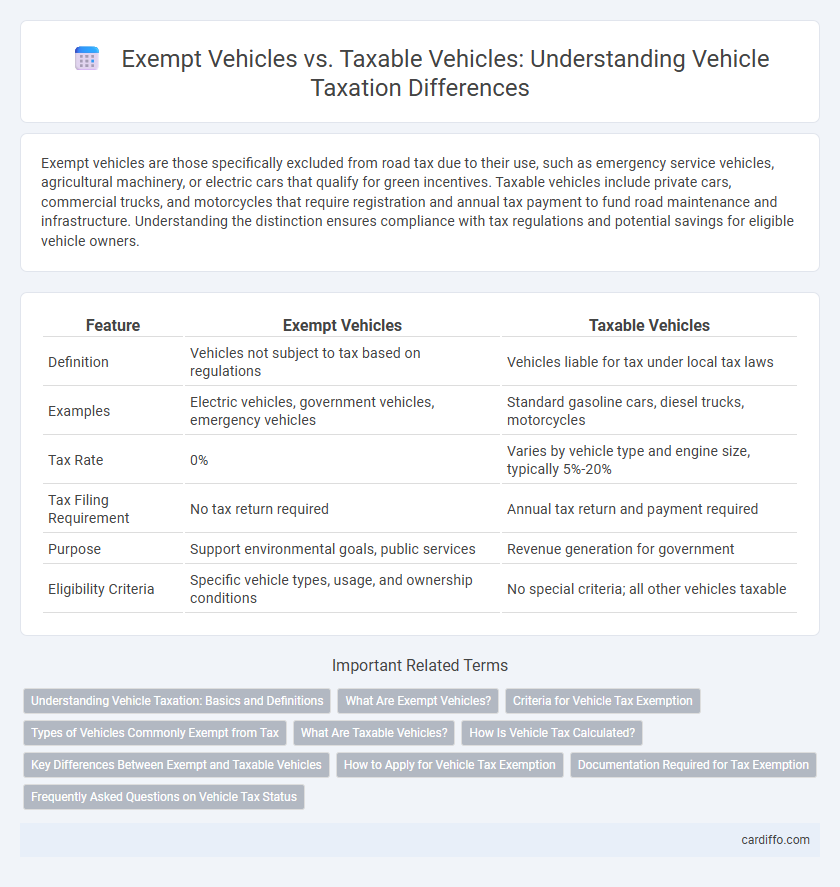
| Feature | Exempt Vehicles | Taxable Vehicles |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Vehicles not subject to tax based on regulations | Vehicles liable for tax under local tax laws |
| Examples | Electric vehicles, government vehicles, emergency vehicles | Standard gasoline cars, diesel trucks, motorcycles |
| Tax Rate | 0% | Varies by vehicle type and engine size, typically 5%-20% |
| Tax Filing Requirement | No tax return required | Annual tax return and payment required |
| Purpose | Support environmental goals, public services | Revenue generation for government |
| Eligibility Criteria | Specific vehicle types, usage, and ownership conditions | No special criteria; all other vehicles taxable |
Understanding Vehicle Taxation: Basics and Definitions
Exempt vehicles typically include those used for specific purposes such as agricultural, emergency, or government services, which qualify for tax relief or complete exemption under local tax laws. Taxable vehicles, in contrast, encompass personal, commercial, and non-exempt government vehicles that incur vehicle excise duties, registration taxes, or sales taxes based on factors like weight, engine size, or emissions. Understanding these classifications is crucial for compliance, avoiding penalties, and optimizing tax liabilities related to vehicle ownership and use.
What Are Exempt Vehicles?
Exempt vehicles refer to specific categories of vehicles that are not subject to certain taxes, such as registration or road use taxes, often based on their purpose, usage, or owner status. Common examples include government-owned vehicles, emergency service vehicles, agricultural vehicles, and electric vehicles in some jurisdictions benefiting from tax incentives. Understanding the criteria for vehicle exemption helps owners determine eligibility and avoid unnecessary tax liabilities.
Criteria for Vehicle Tax Exemption
Vehicles qualify for tax exemption based on specific criteria such as government or emergency service use, electric or zero-emission vehicle status, and eligibility under disability or veteran exemptions. Commercial vehicles exceeding a certain weight threshold or used for business purposes typically fall under taxable categories. Documentation proving vehicle usage, ownership, and compliance with local tax codes is essential for exemption validation.
Types of Vehicles Commonly Exempt from Tax
Vehicles commonly exempt from tax include those used for agricultural purposes such as tractors and harvesters, as well as emergency vehicles like ambulances and fire trucks. Government-owned vehicles and certain non-commercial electric vehicles may also qualify for tax exemptions. These exemptions aim to support critical public services and promote environmental sustainability.
What Are Taxable Vehicles?
Taxable vehicles refer to motor vehicles subject to government-imposed taxes such as sales tax, registration fees, and excise taxes upon purchase or use. These typically include passenger cars, trucks, motorcycles, and commercial vehicles that do not qualify for any exemptions based on purpose, ownership, or usage. Taxable vehicles require proper documentation and payment to comply with state and federal tax regulations.
How Is Vehicle Tax Calculated?
Vehicle tax is calculated based on factors such as engine size, fuel type, CO2 emissions, and vehicle age. Exempt vehicles, including electric cars, classic cars over 40 years old, and disabled passenger vehicles, are not subject to these charges. Taxable vehicles incur fees determined by their emissions levels and registered date, with higher taxes applied to vehicles producing more pollution.
Key Differences Between Exempt and Taxable Vehicles
Exempt vehicles, such as government-owned cars, emergency response vehicles, and certain agricultural machinery, are not subject to standard vehicle taxes due to their specific use or ownership status. Taxable vehicles typically include privately owned passenger cars, commercial trucks, and motorcycles, which must comply with registration fees, excise taxes, and annual road taxes. The key differences hinge on ownership classification, intended use, and relevant tax legislation that determines eligibility for tax exemptions or liabilities.
How to Apply for Vehicle Tax Exemption
To apply for a vehicle tax exemption, submit a completed exemption form along with required documents such as proof of eligibility, vehicle registration, and identification to the local tax authority or motor vehicle department. Eligibility criteria often include vehicles used for agricultural purposes, emergency services, or owned by disabled individuals, requiring specific certifications or official letters. Processing times vary, and maintaining updated records ensures continued exemption from annual vehicle tax payments.
Documentation Required for Tax Exemption
Tax exemption for vehicles requires specific documentation to verify eligibility, including proof of ownership, exemption certificates, and relevant identification such as government-issued IDs or organizational certifications. Exempt vehicles often include those used for charitable, educational, or governmental purposes, which must provide detailed records demonstrating their non-commercial use. Ensuring all documentation aligns with local tax authority regulations is critical to maintain compliance and avoid penalties.
Frequently Asked Questions on Vehicle Tax Status
Exempt vehicles include government-owned cars, emergency vehicles, and agricultural machinery, which are not subject to standard vehicle tax due to their specific use or ownership. Taxable vehicles generally encompass private passenger cars, commercial trucks, and motorcycles, requiring regular vehicle tax payments based on factors such as engine size and emissions. Common FAQs address how to verify a vehicle's tax status, procedures for applying exemptions, and penalties for driving untaxed vehicles.
Exempt Vehicles vs Taxable Vehicles Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com