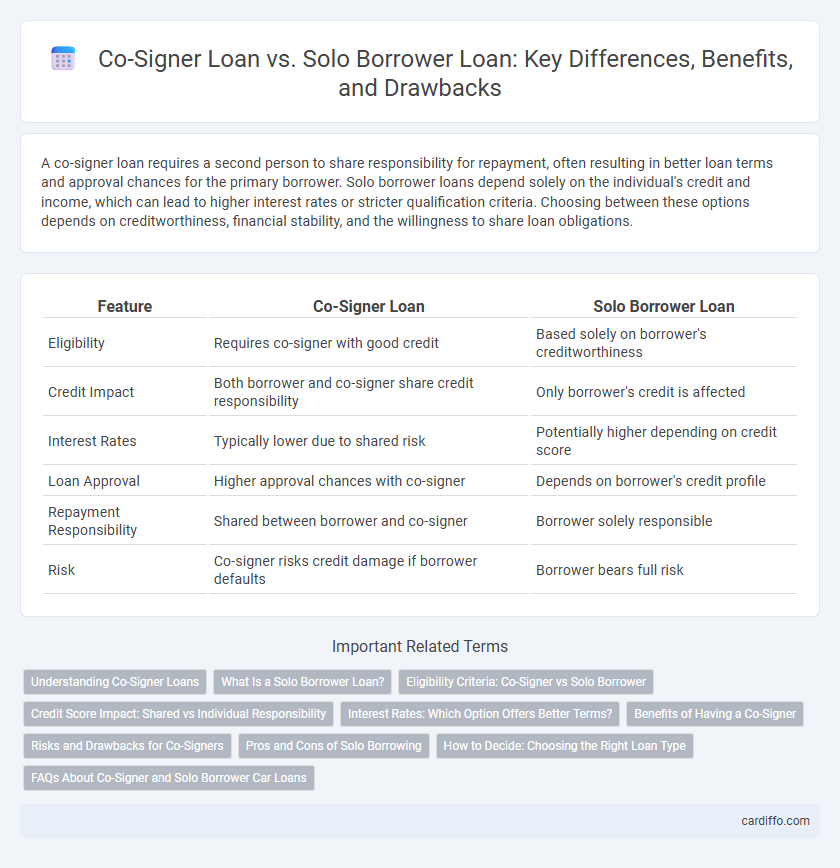
A co-signer loan requires a second person to share responsibility for repayment, often resulting in better loan terms and approval chances for the primary borrower. Solo borrower loans depend solely on the individual's credit and income, which can lead to higher interest rates or stricter qualification criteria. Choosing between these options depends on creditworthiness, financial stability, and the willingness to share loan obligations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Co-Signer Loan | Solo Borrower Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Requires co-signer with good credit | Based solely on borrower's creditworthiness |
| Credit Impact | Both borrower and co-signer share credit responsibility | Only borrower's credit is affected |
| Interest Rates | Typically lower due to shared risk | Potentially higher depending on credit score |
| Loan Approval | Higher approval chances with co-signer | Depends on borrower's credit profile |
| Repayment Responsibility | Shared between borrower and co-signer | Borrower solely responsible |
| Risk | Co-signer risks credit damage if borrower defaults | Borrower bears full risk |
Understanding Co-Signer Loans
Co-signer loans involve a secondary individual who guarantees the loan repayment, reducing lender risk and often enabling better interest rates or higher borrowing limits. The co-signer's credit history directly impacts loan approval and terms, making their financial stability crucial for successful borrowing. Unlike solo borrower loans, co-signer loans require joint accountability, where both parties are legally responsible for ensuring timely payments.
What Is a Solo Borrower Loan?
A solo borrower loan is a type of loan where a single individual is solely responsible for repayment and credit obligations, without the involvement of a co-signer or joint borrower. This loan structure relies exclusively on the solo borrower's creditworthiness, income, and financial history to determine eligibility and loan terms. Solo borrower loans typically offer more straightforward accountability but may require stronger credit profiles compared to co-signer loans.
Eligibility Criteria: Co-Signer vs Solo Borrower
Co-Signer loans require the co-signer to have a strong credit history and stable income to guarantee repayment, improving loan approval chances for the primary borrower. Solo borrower loans necessitate that the individual meets the lender's eligibility criteria independently, including credit score thresholds, income verification, and debt-to-income ratio limits. While a co-signer loan can ease qualification for applicants with weaker credit, a solo borrower loan depends solely on the borrower's financial profile and creditworthiness.
Credit Score Impact: Shared vs Individual Responsibility
Co-signer loans can positively impact both parties' credit scores by sharing repayment responsibility, but missed payments may harm both credit profiles simultaneously. Solo borrower loans tie credit score changes solely to the individual's repayment behavior, placing full responsibility on one person. Lenders assess creditworthiness differently for co-signer loans, often requiring strong credit from both parties to approve loans with favorable terms.
Interest Rates: Which Option Offers Better Terms?
Co-signer loans generally offer lower interest rates compared to solo borrower loans because the presence of a co-signer reduces the lender's risk by adding an additional party responsible for repayment. Solo borrower loans often carry higher interest rates, especially for borrowers with limited credit history or lower credit scores, due to increased risk for lenders. Comparing credit profiles and lender policies is essential, but co-signer loans typically provide better terms in interest rates when the co-signer has strong credit.
Benefits of Having a Co-Signer
Having a co-signer on a loan can significantly improve approval chances and secure lower interest rates, especially for borrowers with limited credit history or lower credit scores. Co-signers provide additional assurance to lenders, reducing the perceived risk and enabling larger loan amounts or better terms. This shared responsibility can also help build the primary borrower's credit profile more quickly when payments are made on time.
Risks and Drawbacks for Co-Signers
Co-signer loans carry significant risks for co-signers, including full legal responsibility for repayment if the primary borrower defaults, which can severely damage the co-signer's credit score and financial stability. Unlike solo borrower loans, co-signers have no control over how loan funds are used but remain liable for the debt, increasing the potential for unexpected financial burdens. The co-signer's credit utilization and debt-to-income ratio can also be adversely affected, limiting future borrowing capacity.
Pros and Cons of Solo Borrowing
Solo borrower loans offer full control over credit management and financial decisions without the need to coordinate with a co-signer, enhancing privacy and accountability. However, solo lending often involves stricter credit requirements and potentially higher interest rates due to the lender assuming full risk without co-signer backing. Borrowers with strong credit profiles can benefit from solo loans by building personal credit history, but those with limited credit may face approval challenges and less favorable loan terms.
How to Decide: Choosing the Right Loan Type
Evaluating credit history and financial stability helps determine if a co-signer loan or solo borrower loan is appropriate for your situation. A co-signer loan may provide better interest rates and approval chances for those with limited credit, while solo borrower loans offer full autonomy and responsibility for repayment. Assess your credit score, income consistency, and willingness to share liability when deciding which loan type aligns with your financial goals.
FAQs About Co-Signer and Solo Borrower Car Loans
A co-signer loan involves a second party who agrees to repay the loan if the primary borrower defaults, improving approval chances and potentially securing lower interest rates. Solo borrower loans require only one individual responsible for the debt, often needing stronger credit qualifications and resulting in higher interest rates if credit is less favorable. Frequently asked questions address eligibility, credit impact, loan approval likelihood, and responsibilities of co-signers versus solo borrowers in auto financing.
Co-Signer Loan vs Solo Borrower Loan Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com