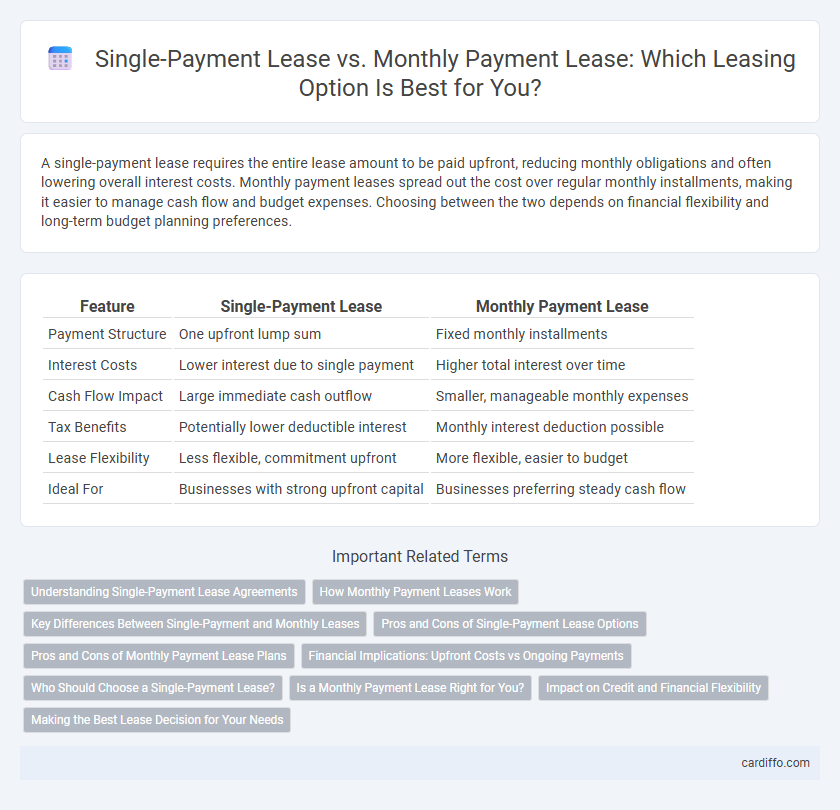
A single-payment lease requires the entire lease amount to be paid upfront, reducing monthly obligations and often lowering overall interest costs. Monthly payment leases spread out the cost over regular monthly installments, making it easier to manage cash flow and budget expenses. Choosing between the two depends on financial flexibility and long-term budget planning preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Single-Payment Lease | Monthly Payment Lease |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Structure | One upfront lump sum | Fixed monthly installments |
| Interest Costs | Lower interest due to single payment | Higher total interest over time |
| Cash Flow Impact | Large immediate cash outflow | Smaller, manageable monthly expenses |
| Tax Benefits | Potentially lower deductible interest | Monthly interest deduction possible |
| Lease Flexibility | Less flexible, commitment upfront | More flexible, easier to budget |
| Ideal For | Businesses with strong upfront capital | Businesses preferring steady cash flow |
Understanding Single-Payment Lease Agreements
Single-payment lease agreements require the lessee to pay the entire lease amount upfront, often resulting in lower overall costs compared to monthly payment leases. This type of lease minimizes administrative fees and interest charges, making it an attractive option for businesses with available capital. Understanding the terms of single-payment leases, such as depreciation schedules and potential tax benefits, is essential for maximizing financial efficiency.
How Monthly Payment Leases Work
Monthly payment leases spread the total lease cost into affordable monthly installments, making vehicle use more budget-friendly without a large upfront expense. This type of lease typically includes depreciation, interest, and fees, calculated over the lease term to determine consistent monthly payments. Lessees benefit from easier budgeting and potential tax advantages, while ownership returns to the lessor at lease end.
Key Differences Between Single-Payment and Monthly Leases
Single-payment leases require the lessee to pay the entire lease amount upfront, resulting in lower overall costs due to reduced financing fees. Monthly payment leases spread the cost over the lease term, offering greater cash flow flexibility but potentially higher total payments due to interest. Single-payment leases often include discounts or incentives, while monthly leases provide convenience and easier budgeting for businesses or individuals.
Pros and Cons of Single-Payment Lease Options
Single-payment leases offer the advantage of reduced overall interest costs, often resulting in lower total payments compared to monthly payment leases, making them cost-effective for those with available funds upfront. They eliminate the risk of missed monthly payments, providing convenience and potentially improving credit scores by consistent on-time payment reporting. However, single-payment leases require a significant initial capital outlay, which can strain cash flow and reduce financial flexibility, and they may limit refunds or adjustments if the lessee decides to terminate the lease early.
Pros and Cons of Monthly Payment Lease Plans
Monthly payment lease plans offer flexibility by spreading the cost over time, making it easier for businesses and individuals to manage cash flow without a large upfront payment. However, these plans often result in higher total costs due to interest or finance charges included in each installment. The convenience of predictable monthly expenses is balanced against potentially higher long-term financial commitments compared to single-payment leases.
Financial Implications: Upfront Costs vs Ongoing Payments
A single-payment lease requires a substantial upfront payment that covers the entire lease term, reducing monthly financial obligations and often lowering overall interest costs. In contrast, a monthly payment lease spreads the total cost over regular installments, resulting in manageable monthly expenses but potentially higher cumulative costs due to interest and fees. Choosing between these options depends on cash flow preferences and the ability to handle large initial expenses versus steady monthly budgeting.
Who Should Choose a Single-Payment Lease?
Individuals with sufficient upfront funds seeking to reduce overall lease costs and avoid monthly billing cycles should consider a Single-Payment Lease, as it often results in lower total payments due to early settlement discounts. Customers aiming for convenience and financial predictability benefit from paying a lump sum rather than managing monthly payments, particularly those with stable cash flow and minimal short-term expenses. Single-Payment Leases are ideal for business owners or lessees prioritizing cost savings, simpler budgeting, and eliminating administrative fees associated with multiple payments.
Is a Monthly Payment Lease Right for You?
A monthly payment lease offers predictable, manageable installments, making it ideal for individuals seeking consistent budgeting without a large upfront cost. This option provides flexibility and potential tax benefits for business users who prefer regular expense tracking. Evaluating your financial stability and usage needs helps determine if a monthly lease aligns with your long-term vehicle or equipment management strategy.
Impact on Credit and Financial Flexibility
A single-payment lease can positively affect credit by reducing monthly obligations and demonstrating strong financial responsibility, potentially improving credit utilization ratios. In contrast, monthly payment leases provide consistent credit activity, which helps build a positive payment history but may limit financial flexibility due to ongoing monthly commitments. Choosing between these options impacts credit scores differently and requires assessing one's cash flow and long-term financial goals.
Making the Best Lease Decision for Your Needs
Choosing between a single-payment lease and a monthly payment lease depends on your financial goals and cash flow preferences. A single-payment lease offers lower overall costs by paying the entire lease amount upfront, reducing interest and fees, while a monthly payment lease provides more manageable monthly expenses and greater budget flexibility. Evaluating your budget, credit score, and long-term usage will help determine the optimal leasing option tailored to your specific needs.
Single-Payment Lease vs Monthly Payment Lease Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com