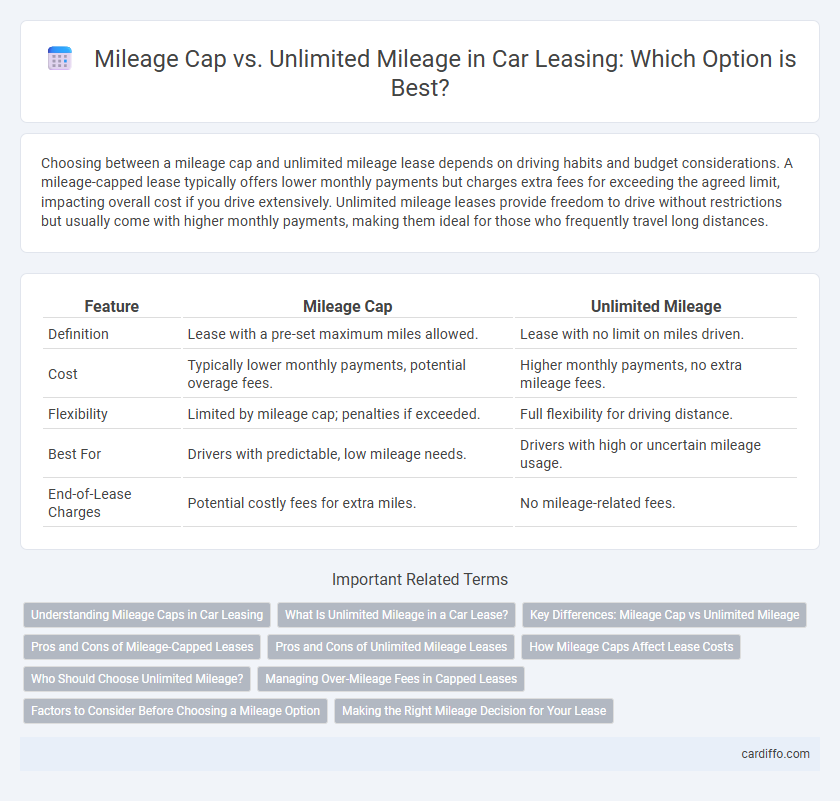
Choosing between a mileage cap and unlimited mileage lease depends on driving habits and budget considerations. A mileage-capped lease typically offers lower monthly payments but charges extra fees for exceeding the agreed limit, impacting overall cost if you drive extensively. Unlimited mileage leases provide freedom to drive without restrictions but usually come with higher monthly payments, making them ideal for those who frequently travel long distances.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mileage Cap | Unlimited Mileage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lease with a pre-set maximum miles allowed. | Lease with no limit on miles driven. |
| Cost | Typically lower monthly payments, potential overage fees. | Higher monthly payments, no extra mileage fees. |
| Flexibility | Limited by mileage cap; penalties if exceeded. | Full flexibility for driving distance. |
| Best For | Drivers with predictable, low mileage needs. | Drivers with high or uncertain mileage usage. |
| End-of-Lease Charges | Potential costly fees for extra miles. | No mileage-related fees. |
Understanding Mileage Caps in Car Leasing
Mileage caps in car leasing define the maximum number of miles a lessee can drive annually without incurring extra charges, typically ranging from 10,000 to 15,000 miles per year. Exceeding these limits results in additional fees calculated per mile, often between $0.15 to $0.30, significantly impacting the total lease cost. Choosing an appropriate mileage cap based on estimated usage helps avoid unexpected expenses and ensures lease terms align with driving habits.
What Is Unlimited Mileage in a Car Lease?
Unlimited mileage in a car lease allows lessees to drive the vehicle without worrying about exceeding preset mileage limits, eliminating excess mileage fees. This option suits drivers covering long distances, such as business commuters or road trip enthusiasts, providing greater flexibility and peace of mind. Choosing unlimited mileage can increase monthly payments but avoids costly penalties tied to excess mileage charges at lease-end.
Key Differences: Mileage Cap vs Unlimited Mileage
Mileage cap in a lease limits the number of miles driven annually, typically ranging from 10,000 to 15,000 miles, with excess miles incurring additional fees. Unlimited mileage leases allow unrestricted driving without penalties, providing greater flexibility but often at a higher monthly cost. Choosing between mileage cap and unlimited mileage depends on driving habits and budget considerations.
Pros and Cons of Mileage-Capped Leases
Mileage-capped leases typically offer lower monthly payments compared to unlimited mileage leases, appealing to drivers who predict stable or low annual mileage. However, exceeding the mileage cap results in costly penalties per mile, often ranging from 15 to 30 cents, which can significantly increase the total lease cost. This leasing option suits individuals with predictable driving habits but can be financially disadvantageous for those with fluctuating or high mileage needs.
Pros and Cons of Unlimited Mileage Leases
Unlimited mileage leases offer the advantage of unrestricted driving distance, eliminating fees for excess miles and providing flexibility for high-mileage drivers. However, these leases typically come with higher monthly payments and may reduce the vehicle's resale value due to accelerated wear and tear. Choosing unlimited mileage is ideal for those who regularly exceed standard lease limits or require long-distance travel without penalty.
How Mileage Caps Affect Lease Costs
Mileage caps in vehicle leases limit the number of miles driven annually, directly impacting the overall lease cost by reducing the monthly payment compared to unlimited mileage options. Exceeding the mileage cap incurs costly per-mile penalties, often ranging from $0.15 to $0.30 per mile, which increase the total expense upon lease termination. Choosing a lower mileage cap typically lowers the lease's upfront and monthly costs but requires careful mileage forecasting to avoid significant overage fees.
Who Should Choose Unlimited Mileage?
Unlimited mileage leases are ideal for drivers who cover extensive distances annually, typically exceeding 15,000 to 20,000 miles, and want to avoid costly excess mileage fees. Business professionals, long-distance commuters, and road trip enthusiasts benefit significantly from the financial predictability and flexibility that unlimited mileage offers. Opting for unlimited mileage ensures peace of mind by eliminating concerns about overage charges, making it a practical choice for high-mileage users.
Managing Over-Mileage Fees in Capped Leases
Managing over-mileage fees in capped leases requires careful tracking of the vehicle's mileage against the agreed cap to avoid costly penalties. Lease agreements typically charge a predetermined fee per mile exceeded, which can significantly increase overall leasing costs if not monitored closely. Utilizing mileage tracking tools and adjusting driving habits can help lessees stay within limits and minimize unexpected overage charges.
Factors to Consider Before Choosing a Mileage Option
Choosing between a mileage cap and unlimited mileage lease depends on your expected annual driving distance and potential excess mileage fees. Consider your lifestyle, commuting habits, and how frequently you take long trips to avoid costly penalties or overpaying for unnecessary miles. Evaluating your historical driving data and lease terms helps optimize cost efficiency and aligns the lease agreement with your usage patterns.
Making the Right Mileage Decision for Your Lease
Choosing between a mileage cap and unlimited mileage lease hinges on accurately estimating your annual driving needs to avoid costly overage fees or higher monthly payments. A capped mileage lease typically offers lower monthly rates but charges steep penalties for exceeding limits, while unlimited mileage leases provide flexibility at a premium cost. Evaluating your driving habits against lease terms ensures a cost-effective decision that aligns with your travel frequency and budget.
Mileage Cap vs Unlimited Mileage Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com