Trade-in value represents the amount a seller can receive when exchanging a pet-related asset for a new one, typically reflecting better condition and market demand compared to scrap value, which is the minimal price obtained by selling the asset purely for parts or disposal. Depreciation significantly impacts the trade-in value, as assets lose worth over time based on use and wear, often making scrap value substantially lower. Understanding the difference between trade-in and scrap value helps pet business owners make informed decisions about asset replacement and financial planning.
Table of Comparison
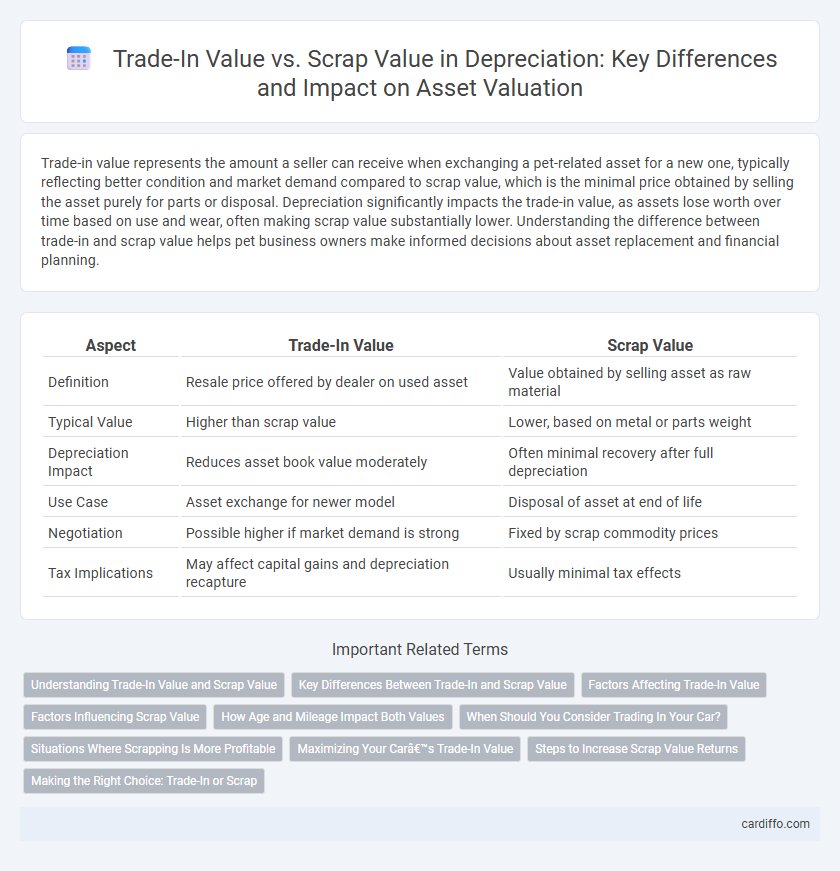
| Aspect | Trade-In Value | Scrap Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Resale price offered by dealer on used asset | Value obtained by selling asset as raw material |
| Typical Value | Higher than scrap value | Lower, based on metal or parts weight |
| Depreciation Impact | Reduces asset book value moderately | Often minimal recovery after full depreciation |
| Use Case | Asset exchange for newer model | Disposal of asset at end of life |
| Negotiation | Possible higher if market demand is strong | Fixed by scrap commodity prices |
| Tax Implications | May affect capital gains and depreciation recapture | Usually minimal tax effects |
Understanding Trade-In Value and Scrap Value
Trade-in value represents the amount a vehicle owner can receive when exchanging a used car for a new one, reflecting current market demand and vehicle condition. Scrap value, also known as salvage value, is the estimated residual price of a vehicle when it is no longer operational, based primarily on recyclable materials like metal weight. Understanding the difference helps in accurately calculating depreciation and making informed decisions about asset disposal or replacement.
Key Differences Between Trade-In and Scrap Value
Trade-in value represents the amount a dealer offers when exchanging an old asset for a new purchase, typically reflecting the asset's current market worth after depreciation. Scrap value, on the other hand, is the residual value of an asset at the end of its useful life, determined by the worth of its raw materials or parts. The key difference lies in trade-in value being influenced by market demand and resale potential, whereas scrap value is based solely on salvageable material worth.
Factors Affecting Trade-In Value
Trade-in value is influenced by factors such as the vehicle's condition, mileage, market demand, and age, whereas scrap value largely depends on the weight and material composition of the car. Economic trends, regional preferences, and the vehicle's maintenance history also play significant roles in determining trade-in value. Unlike scrap value, which is generally static and low, trade-in value varies greatly due to these dynamic market and asset-specific conditions.
Factors Influencing Scrap Value
Scrap value is primarily influenced by the condition of the asset, the type and quality of its materials, and current market demand for recyclable components. Economic factors such as fluctuations in commodity prices, environmental regulations, and advances in recycling technology also play a significant role in determining the scrap value. Depreciation policies and the asset's age further impact the residual value realized through scrapping.
How Age and Mileage Impact Both Values
Age and mileage significantly affect both trade-in value and scrap value, with older vehicles and higher mileage generally reducing trade-in offers due to increased wear and depreciation. Trade-in value tends to decline more sharply as mileage exceeds typical annual averages, reflecting decreased market demand and expected repair costs. Scrap value, however, is less sensitive to mileage and age, primarily depending on the weight and recoverable materials of the vehicle, making it a baseline minimum for aging or heavily-used cars.
When Should You Consider Trading In Your Car?
Trade-in value typically exceeds scrap value when your car remains in good working condition with market demand, making it more beneficial to trade in rather than sell for parts. Consider trading in your car if the trade-in offer covers remaining loan balances or provides a reasonable down payment for a new vehicle, maximizing financial efficiency. Evaluating depreciation rates and current market trends helps determine the optimal timing to trade in, ensuring better value retention compared to scrap value.
Situations Where Scrapping Is More Profitable
Scrapping becomes more profitable than trade-in when the asset has minimal remaining useful life or is severely damaged, reducing its market appeal for resale. In cases where repair or refurbishment costs exceed the trade-in value, selling as scrap maximizes financial recovery by leveraging the salvageable material content. Companies facing obsolete or non-compliant equipment often benefit from scrapping, avoiding additional holding costs and gaining immediate liquidity.
Maximizing Your Car’s Trade-In Value
Maximizing your car's trade-in value involves maintaining its condition through regular servicing and detailing, as buyers prioritize well-kept vehicles over those with cosmetic or mechanical issues. Accurate market research on similar models helps set realistic expectations and negotiate better offers, often yielding higher returns than accepting the lower scrap value. Understanding that trade-in value typically exceeds scrap value unless the vehicle is severely damaged ensures strategic decision-making when planning to replace or sell your car.
Steps to Increase Scrap Value Returns
To increase scrap value returns, first assess and remove all valuable components such as batteries, tires, and catalytic converters to maximize resale value. Thoroughly clean and prepare the vehicle to meet scrap yard requirements, ensuring better offers. Finally, research and compare prices from multiple scrap buyers to secure the highest trade-in value for the scrap material.
Making the Right Choice: Trade-In or Scrap
Evaluating an asset's trade-in value versus its scrap value is crucial in maximizing depreciation recovery and minimizing losses. Trade-in value often exceeds scrap value when the asset retains functional utility or has demand in secondary markets, offering a better financial return. Choosing between trade-in and scrap hinges on assessing market conditions, asset condition, and potential tax implications to optimize the overall cost-benefit outcome.
Trade-In Value vs Scrap Value Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com