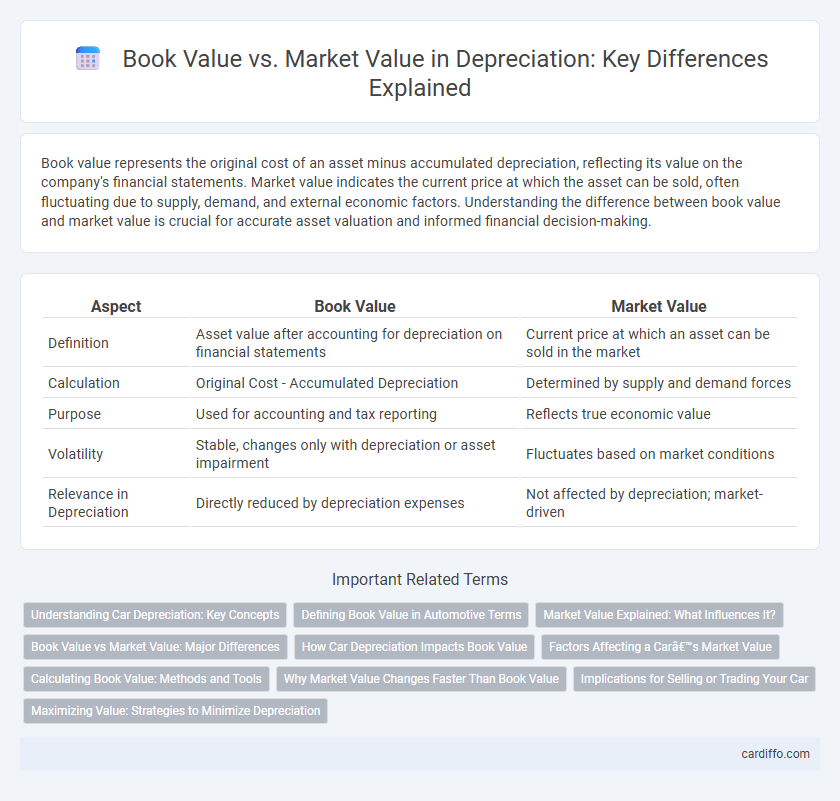
Book value represents the original cost of an asset minus accumulated depreciation, reflecting its value on the company's financial statements. Market value indicates the current price at which the asset can be sold, often fluctuating due to supply, demand, and external economic factors. Understanding the difference between book value and market value is crucial for accurate asset valuation and informed financial decision-making.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Book Value | Market Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Asset value after accounting for depreciation on financial statements | Current price at which an asset can be sold in the market |
| Calculation | Original Cost - Accumulated Depreciation | Determined by supply and demand forces |
| Purpose | Used for accounting and tax reporting | Reflects true economic value |
| Volatility | Stable, changes only with depreciation or asset impairment | Fluctuates based on market conditions |
| Relevance in Depreciation | Directly reduced by depreciation expenses | Not affected by depreciation; market-driven |
Understanding Car Depreciation: Key Concepts
Car depreciation significantly impacts the difference between book value and market value, as book value reflects the asset's original cost minus accumulated depreciation, while market value is the current price buyers are willing to pay. Understanding that book value often underestimates true market value early in a vehicle's life helps owners make informed decisions about resale or trade-in timing. Realizing the rapid initial depreciation rate of cars, often 20-30% in the first year, is crucial for accurately assessing both financial worth and insurance considerations.
Defining Book Value in Automotive Terms
Book value in automotive terms refers to the original purchase price of a vehicle minus accumulated depreciation, reflecting its accounting value on financial statements. It serves as a baseline for calculating depreciation expenses and tax deductions. This value often differs from market value, which is influenced by factors like demand, condition, and market trends.
Market Value Explained: What Influences It?
Market value represents the current price at which an asset can be bought or sold in the open market, influenced by factors such as supply and demand, economic conditions, and investor sentiment. Unlike book value, which is based on the original cost minus accumulated depreciation, market value reflects real-time perceptions of an asset's worth. Changes in interest rates, market trends, and future earning potential also play crucial roles in determining an asset's market value.
Book Value vs Market Value: Major Differences
Book value represents the asset's original cost minus accumulated depreciation, reflecting its value on the balance sheet, while market value denotes the current price an asset can fetch in the open market. Book value is based on historical data and accounting principles, often differing significantly from market value, which fluctuates with supply, demand, and economic conditions. Understanding the major differences between book value and market value is crucial for accurate financial analysis and investment decisions.
How Car Depreciation Impacts Book Value
Car depreciation directly reduces the book value, which represents the original cost minus accumulated depreciation over time. Market value fluctuates based on demand, condition, and external factors, often deviating from the book value. Understanding how depreciation lowers book value helps in assessing asset worth, tax implications, and resale potential.
Factors Affecting a Car’s Market Value
A car's market value is influenced by factors such as age, mileage, condition, and demand, which differ from its book value calculated through depreciation schedules. While book value reflects the asset's original cost minus accumulated depreciation, market value fluctuates based on real-time buyer interest, economic conditions, and vehicle desirability. External elements like regional market trends and technological advancements also play crucial roles in shaping a car's resale price.
Calculating Book Value: Methods and Tools
Calculating book value involves deducting accumulated depreciation from the asset's original cost using methods such as straight-line, declining balance, or units of production. Accurate tools like depreciation schedules and accounting software streamline this process by tracking asset lifespan and periodic expense allocation. These calculations provide a reliable metric for financial reporting, distinct from fluctuating market value which reflects current asset demand.
Why Market Value Changes Faster Than Book Value
Market value fluctuates rapidly due to external factors like supply and demand, economic conditions, and investor sentiment, while book value changes slowly as it is based on historical cost minus accumulated depreciation. Depreciation methods spread asset costs evenly over useful life, causing book value to decline predictably despite market volatility. This disparity explains why market value often diverges significantly from book value at any point in time.
Implications for Selling or Trading Your Car
Book value reflects the car's depreciated cost based on accounting methods, while market value indicates the price a buyer is willing to pay in the current market. When selling or trading your car, understanding the disparity between book value and market value helps set realistic price expectations and negotiate effectively. A vehicle's book value may underestimate its worth during high demand periods, impacting trade-in offers and resale negotiations.
Maximizing Value: Strategies to Minimize Depreciation
Maximizing value involves regularly updating asset maintenance schedules and implementing proactive repairs to slow depreciation rates, effectively preserving book value closer to market value. Accurate asset revaluation and timely disposal of underperforming assets prevent significant value erosion in financial statements. Leveraging technology such as asset tracking software enhances decision-making, optimizing asset utilization and minimizing depreciation losses.
Book Value vs Market Value Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com