Fleet depreciation spreads the loss of value evenly across a group of vehicles, allowing for more predictable budgeting and streamlined asset management. Individual car depreciation varies significantly based on factors like make, model, usage, and maintenance, leading to unpredictable financial impacts. Understanding the differences between fleet and individual car depreciation is essential for optimizing cost efficiency and asset longevity in vehicle management.
Table of Comparison
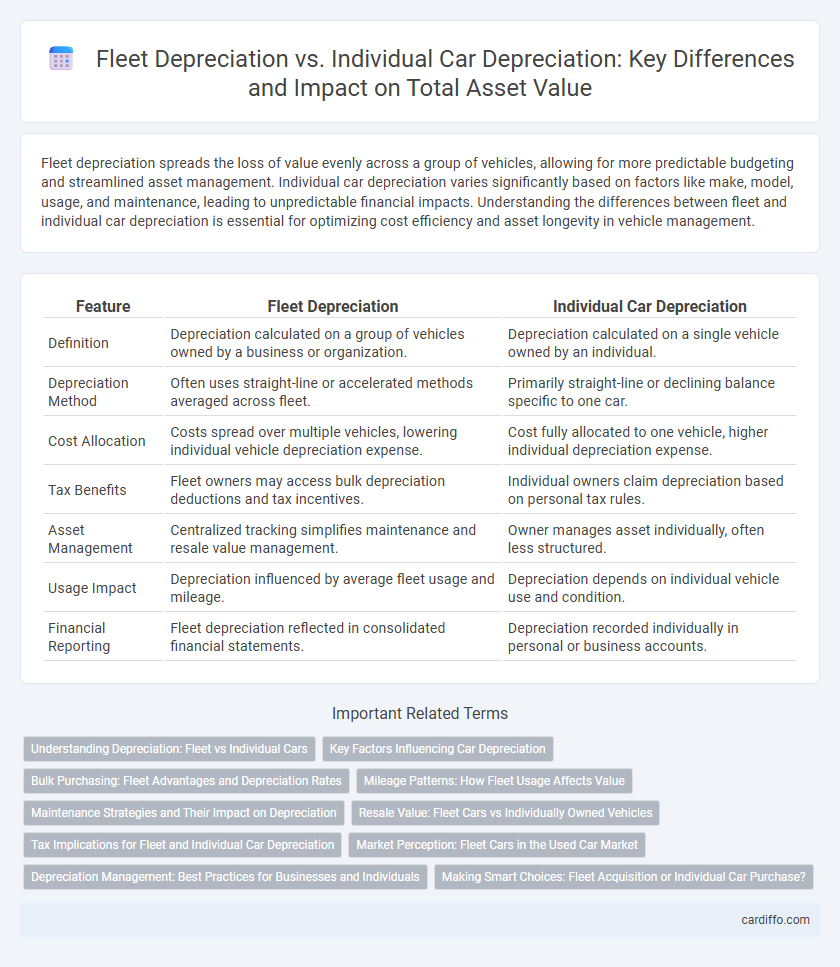
| Feature | Fleet Depreciation | Individual Car Depreciation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Depreciation calculated on a group of vehicles owned by a business or organization. | Depreciation calculated on a single vehicle owned by an individual. |
| Depreciation Method | Often uses straight-line or accelerated methods averaged across fleet. | Primarily straight-line or declining balance specific to one car. |
| Cost Allocation | Costs spread over multiple vehicles, lowering individual vehicle depreciation expense. | Cost fully allocated to one vehicle, higher individual depreciation expense. |
| Tax Benefits | Fleet owners may access bulk depreciation deductions and tax incentives. | Individual owners claim depreciation based on personal tax rules. |
| Asset Management | Centralized tracking simplifies maintenance and resale value management. | Owner manages asset individually, often less structured. |
| Usage Impact | Depreciation influenced by average fleet usage and mileage. | Depreciation depends on individual vehicle use and condition. |
| Financial Reporting | Fleet depreciation reflected in consolidated financial statements. | Depreciation recorded individually in personal or business accounts. |
Understanding Depreciation: Fleet vs Individual Cars
Fleet depreciation typically reflects aggregated data from multiple vehicles, offering a broader perspective on overall asset value decline and operational costs for businesses managing large fleets. Individual car depreciation centers on specific factors like make, model, mileage, and condition, providing precise valuation for single vehicle ownership. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize financial planning, tax deductions, and resale strategies tailored to fleet management or individual car ownership.
Key Factors Influencing Car Depreciation
Fleet depreciation typically experiences a more accelerated rate compared to individual car depreciation due to higher mileage, consistent usage, and uniform maintenance schedules. Key factors influencing car depreciation include vehicle age, mileage, maintenance history, brand reputation, and market demand. Individual cars may retain value better with personalized care, lower usage intensity, and selective resale timing, impacting overall depreciation differently than fleet vehicles.
Bulk Purchasing: Fleet Advantages and Depreciation Rates
Fleet depreciation benefits from bulk purchasing, which often secures vehicles at lower initial costs compared to individual car purchases. This cost advantage reduces the overall depreciation expense per vehicle, enhancing fleet value retention over time. Moreover, standardized maintenance schedules for fleets help maintain consistent depreciation rates, optimizing long-term asset management.
Mileage Patterns: How Fleet Usage Affects Value
Fleet depreciation typically accelerates due to higher average mileage and more intensive usage patterns compared to individual cars, which often have more variable and lower mileage. Vehicles in fleets experience consistent wear and tear, leading to a faster decline in market value, especially when usage involves long-distance driving or frequent stops. In contrast, individual car depreciation is influenced more by personal driving habits and mileage, resulting in potentially slower value reduction.
Maintenance Strategies and Their Impact on Depreciation
Fleet depreciation benefits from standardized maintenance strategies that optimize service schedules and reduce overall wear, thereby slowing asset value decline across multiple vehicles. In contrast, individual car depreciation often hinges on personalized maintenance, where inconsistent service can accelerate value loss due to uneven upkeep and potential mechanical issues. Effective maintenance strategies directly influence depreciation rates by ensuring vehicle reliability and preserving market value.
Resale Value: Fleet Cars vs Individually Owned Vehicles
Fleet depreciation typically results in lower resale values compared to individually owned vehicles due to standardized usage patterns and bulk selling practices. Individually owned cars often retain higher resale value because of personalized maintenance, varied mileage, and selective sale timing, which appeal more to private buyers. Resale pricing algorithms and market demand for individual cars further enhance their value compared to fleet vehicles sold at auction.
Tax Implications for Fleet and Individual Car Depreciation
Fleet depreciation offers more streamlined tax benefits by allowing businesses to aggregate vehicle expenses, potentially maximizing deductions under Section 179 and bonus depreciation rules. Individual car depreciation requires separate tracking of each vehicle, complicating tax filings but allowing precise allocation of costs based on usage and depreciation schedules. Tax implications differ as fleet depreciation can simplify compliance and optimize overall deductions, while individual depreciation may benefit taxpayers with varying vehicle usage and resale strategies.
Market Perception: Fleet Cars in the Used Car Market
Fleet depreciation typically results in a lower resale value compared to individual car depreciation due to market perception associating fleet cars with higher mileage and less personalized maintenance. Buyers often view fleet vehicles as less desirable because they are presumed to have undergone more rigorous use and quicker wear, negatively impacting their market demand. This perception causes fleet cars to depreciate faster in the used car market versus individually owned vehicles.
Depreciation Management: Best Practices for Businesses and Individuals
Effective depreciation management requires tailored strategies for fleet and individual car assets, emphasizing accurate tracking and consistent valuation methods. Businesses benefit from leveraging fleet depreciation schedules that consider bulk purchase dates, usage patterns, and maintenance costs to optimize tax benefits and asset replacement timing. Individuals managing depreciation on single vehicles should focus on mileage, condition, and market trends to accurately estimate value loss and plan resale or trade-in decisions.
Making Smart Choices: Fleet Acquisition or Individual Car Purchase?
Evaluating fleet depreciation versus individual car depreciation reveals key cost-efficiency differences critical for smart vehicle investments. Fleet vehicles often experience accelerated depreciation due to higher utilization and standardized maintenance schedules, leading to predictable but potentially steeper value loss compared to individual cars. Strategic decisions hinge on balancing fleet acquisition benefits, such as bulk pricing and streamlined management, against the typically slower, more variable depreciation rates of individual car purchases.
Fleet Depreciation vs Individual Car Depreciation Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com