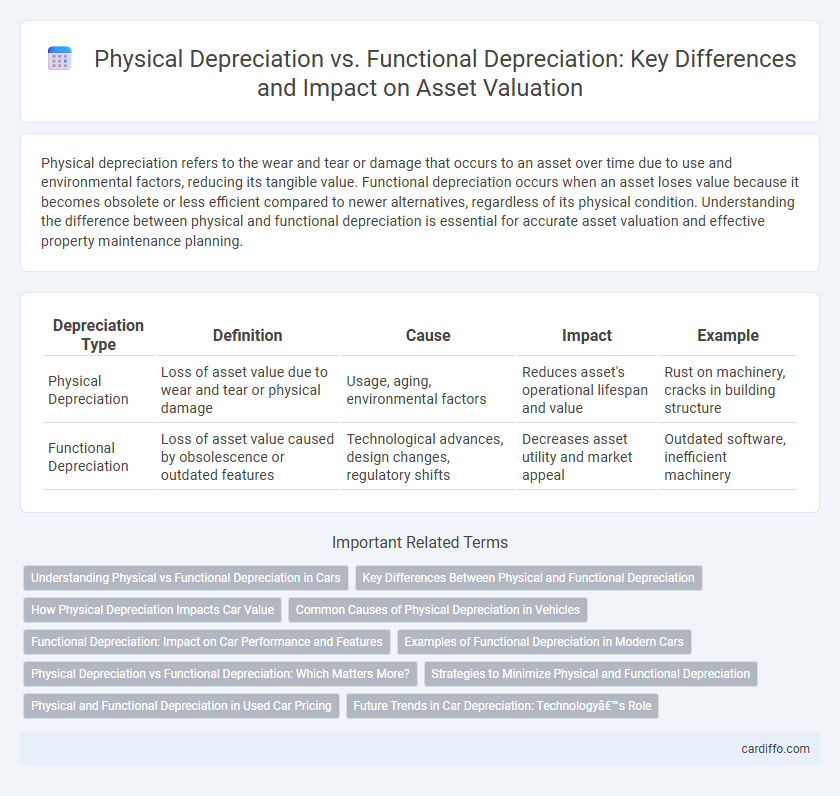
Physical depreciation refers to the wear and tear or damage that occurs to an asset over time due to use and environmental factors, reducing its tangible value. Functional depreciation occurs when an asset loses value because it becomes obsolete or less efficient compared to newer alternatives, regardless of its physical condition. Understanding the difference between physical and functional depreciation is essential for accurate asset valuation and effective property maintenance planning.
Table of Comparison
| Depreciation Type | Definition | Cause | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Depreciation | Loss of asset value due to wear and tear or physical damage | Usage, aging, environmental factors | Reduces asset's operational lifespan and value | Rust on machinery, cracks in building structure |
| Functional Depreciation | Loss of asset value caused by obsolescence or outdated features | Technological advances, design changes, regulatory shifts | Decreases asset utility and market appeal | Outdated software, inefficient machinery |
Understanding Physical vs Functional Depreciation in Cars
Physical depreciation in cars refers to the wear and tear caused by regular use, exposure to elements, and age, leading to visible damage like rust, scratches, and mechanical failures. Functional depreciation occurs when a vehicle loses value due to outdated features, technological obsolescence, or diminished performance relative to newer models. Understanding the distinction helps accurately assess a car's current market value and prioritize maintenance or upgrades.
Key Differences Between Physical and Functional Depreciation
Physical depreciation refers to the wear and tear or deterioration of an asset due to usage, aging, or environmental factors, impacting its tangible condition. Functional depreciation occurs when an asset loses value because it becomes obsolete or less efficient compared to newer alternatives, despite its physical condition. Key differences include physical depreciation affecting the asset's structure and usability, while functional depreciation affects its operational performance and market competitiveness.
How Physical Depreciation Impacts Car Value
Physical depreciation significantly reduces a car's market value by causing visible wear and tear, such as dents, scratches, and rust, which deteriorate its aesthetic appeal. This type of depreciation also negatively affects mechanical performance, leading to increased maintenance costs and lower reliability, which buyers factor into resale prices. As a result, physical depreciation directly lowers a car's worth by diminishing both its appearance and operational condition.
Common Causes of Physical Depreciation in Vehicles
Common causes of physical depreciation in vehicles include wear and tear from regular use, exposure to harsh weather conditions, and damage from accidents or improper maintenance. Rust, paint fading, tire wear, and engine component deterioration significantly reduce a vehicle's market value over time. Understanding these factors helps in accurate vehicle valuation and effective maintenance planning.
Functional Depreciation: Impact on Car Performance and Features
Functional depreciation refers to the loss in a car's value due to outdated features or reduced performance efficiency, independent of its physical condition. This type of depreciation impacts the vehicle's technological relevance, fuel efficiency, and overall driving experience as newer models introduce advanced safety systems, infotainment, and engine improvements. Functional depreciation drives a significant portion of value reduction, especially in rapidly evolving automotive markets where innovation accelerates feature obsolescence.
Examples of Functional Depreciation in Modern Cars
Examples of functional depreciation in modern cars include outdated infotainment systems that lack compatibility with current smartphone technologies, decreased fuel efficiency due to older engine designs, and limited advanced safety features compared to newer models. These functional obsolescences reduce a vehicle's market value even if its physical condition remains excellent. Manufacturers continually improve performance, technology integration, and emissions compliance, causing older models to depreciate faster based on functionality rather than physical wear.
Physical Depreciation vs Functional Depreciation: Which Matters More?
Physical depreciation refers to the tangible wear and tear of an asset over time, while functional depreciation involves the loss of value due to outdated design or reduced utility. In asset valuation, functional depreciation often matters more because it impacts an asset's efficiency and relevance in current operations, potentially causing greater financial loss than mere physical deterioration. Understanding the balance between these two depreciation types is crucial for accurate financial reporting and informed asset management decisions.
Strategies to Minimize Physical and Functional Depreciation
Regular maintenance and timely repairs are essential strategies to minimize physical depreciation by preserving the asset's structural integrity and preventing deterioration. To reduce functional depreciation, updating technology and adapting design layouts to current standards extend the asset's usability and relevance. Implementing these proactive measures helps sustain asset value and enhances long-term performance.
Physical and Functional Depreciation in Used Car Pricing
Physical depreciation in used car pricing refers to the reduction in value caused by tangible wear and tear, such as scratches, dents, and mechanical wear from mileage. Functional depreciation occurs when a car loses value due to outdated technology, diminished performance, or obsolescence in features compared to newer models. Both physical and functional depreciation critically impact resale value, with physical factors being more immediately visible and functional depreciation often driving longer-term market perception.
Future Trends in Car Depreciation: Technology’s Role
Physical depreciation in vehicles refers to the wear and tear from regular use, while functional depreciation occurs when a car becomes outdated due to advancing technologies. Future trends in car depreciation will heavily depend on the rate of innovation in electric and autonomous vehicles, which can accelerate functional obsolescence. As technology evolves rapidly, cars with outdated software or hardware may lose value faster than those affected primarily by physical deterioration.
Physical Depreciation vs Functional Depreciation Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com