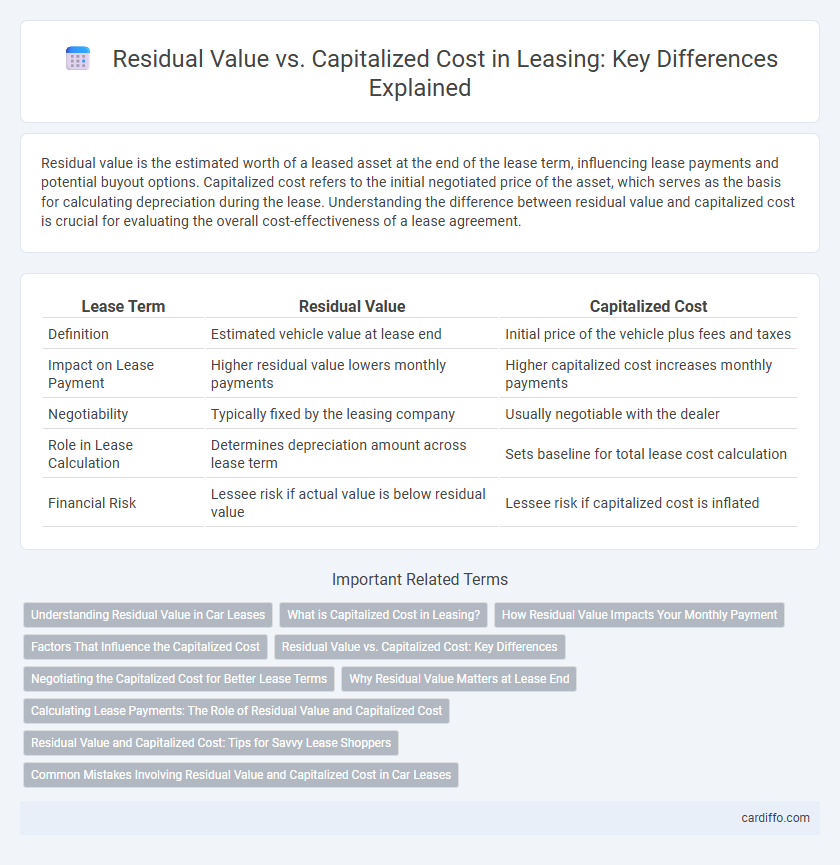
Residual value is the estimated worth of a leased asset at the end of the lease term, influencing lease payments and potential buyout options. Capitalized cost refers to the initial negotiated price of the asset, which serves as the basis for calculating depreciation during the lease. Understanding the difference between residual value and capitalized cost is crucial for evaluating the overall cost-effectiveness of a lease agreement.
Table of Comparison
| Lease Term | Residual Value | Capitalized Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Estimated vehicle value at lease end | Initial price of the vehicle plus fees and taxes |
| Impact on Lease Payment | Higher residual value lowers monthly payments | Higher capitalized cost increases monthly payments |
| Negotiability | Typically fixed by the leasing company | Usually negotiable with the dealer |
| Role in Lease Calculation | Determines depreciation amount across lease term | Sets baseline for total lease cost calculation |
| Financial Risk | Lessee risk if actual value is below residual value | Lessee risk if capitalized cost is inflated |
Understanding Residual Value in Car Leases
Residual value in car leases represents the estimated worth of the vehicle at the end of the lease term, significantly impacting monthly payments and overall lease cost. A higher residual value leads to lower depreciation charges, reducing monthly lease payments by minimizing the difference between the capitalized cost and the residual value. Understanding residual value helps lessees evaluate lease offers, as this figure directly influences the financial advantage of leasing versus buying a vehicle.
What is Capitalized Cost in Leasing?
Capitalized cost in leasing refers to the agreed-upon value of the vehicle or asset at the start of the lease agreement, including the negotiated price plus any additional fees or taxes. This amount serves as the basis for calculating lease payments, directly impacting monthly costs and total lease expense. Understanding capitalized cost helps lessees negotiate better terms and minimize overall leasing expenses.
How Residual Value Impacts Your Monthly Payment
Residual value directly impacts your monthly lease payment by determining the vehicle's estimated worth at the end of the lease term; a higher residual value results in lower depreciation costs spread over the lease period, reducing monthly payments. Capitalized cost, which represents the negotiated price of the vehicle, combined with residual value, forms the basis for calculating lease payments. Understanding the balance between residual value and capitalized cost enables lessees to optimize their monthly payments and overall lease affordability.
Factors That Influence the Capitalized Cost
The capitalized cost in a lease is primarily influenced by the vehicle's negotiated sale price, trade-in value, and any down payment applied. Incentives and rebates offered by manufacturers or dealers also significantly reduce the capitalized cost. Lease terms such as fees, taxes, and add-ons like extended warranties further affect the final amount used to calculate monthly payments.
Residual Value vs. Capitalized Cost: Key Differences
Residual value represents the estimated worth of a leased asset at the end of the lease term, influencing monthly payment calculations by offsetting depreciation costs. Capitalized cost, also known as the lease's negotiated price, is the starting value of the asset on which lease payments are based and can be reduced through discounts or trade-ins. Understanding the distinction between residual value and capitalized cost is essential for evaluating lease affordability and potential savings.
Negotiating the Capitalized Cost for Better Lease Terms
Negotiating the capitalized cost is essential for securing favorable lease terms, as it directly affects monthly lease payments and overall lease affordability. Lowering the capitalized cost reduces the depreciation portion included in the lease, decreasing the total lease expense compared to the residual value. Understanding the interplay between the residual value and capitalized cost empowers lessees to negotiate effectively for better financial outcomes in vehicle leases.
Why Residual Value Matters at Lease End
Residual value directly impacts the financial outcome at lease-end by determining the asset's expected market worth, influencing purchase options or disposition costs. A higher residual value reduces depreciation expense embedded in monthly payments, making leases more affordable and preserving equity for the lessee. Understanding residual value helps in negotiating lease terms and planning for potential buyout or turnover costs accurately.
Calculating Lease Payments: The Role of Residual Value and Capitalized Cost
Residual value and capitalized cost are essential factors in calculating lease payments, directly impacting the monthly amount a lessee pays. The capitalized cost represents the negotiated price of the vehicle or asset, while the residual value estimates its worth at the end of the lease term. Lease payments are derived by subtracting the residual value from the capitalized cost, then dividing the result over the lease period, incorporating interest and fees.
Residual Value and Capitalized Cost: Tips for Savvy Lease Shoppers
Residual value represents the estimated worth of a leased asset at the end of the lease term, directly impacting monthly lease payments by lowering depreciation costs. Capitalized cost is the agreed-upon value of the vehicle or equipment at lease inception, serving as the base for calculating lease fees and negotiable to reduce overall payments. Savvy lease shoppers prioritize negotiating both residual value and capitalized cost to optimize lease terms and minimize total leasing expenses.
Common Mistakes Involving Residual Value and Capitalized Cost in Car Leases
Common mistakes in car leases often involve misunderstanding the residual value and capitalized cost, leading to higher monthly payments and unexpected fees. Many lessees overlook that an inflated capitalized cost increases depreciation charges, while underestimating the residual value reduces equity at lease-end. It is crucial to verify both figures during lease negotiations to avoid financial pitfalls and ensure transparent lease terms.
Residual value vs capitalized cost Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com