Residual value refers to the estimated amount an asset is expected to be worth at the end of its useful life, considering normal wear and tear, while scrap value is the tangible worth of the asset's components when sold for recycling or disposal. Understanding the difference between residual and scrap value is crucial for accurate depreciation calculations and financial reporting. Residual value influences the depreciation expense over the asset's life, whereas scrap value represents the asset's salvage price when it is no longer functional.
Table of Comparison
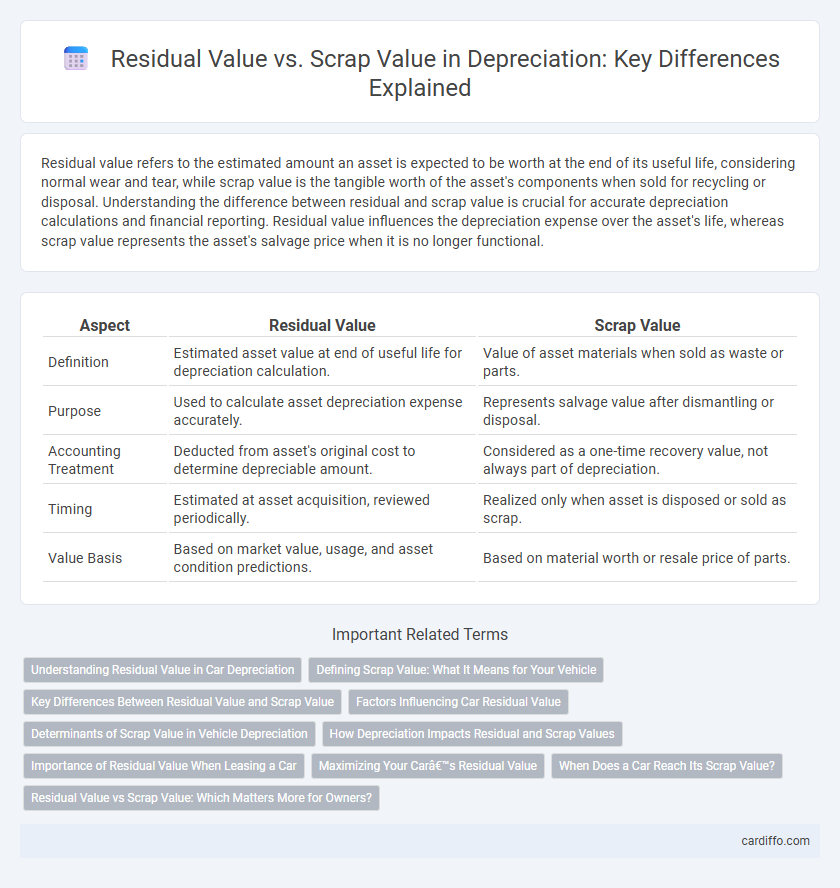
| Aspect | Residual Value | Scrap Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Estimated asset value at end of useful life for depreciation calculation. | Value of asset materials when sold as waste or parts. |
| Purpose | Used to calculate asset depreciation expense accurately. | Represents salvage value after dismantling or disposal. |
| Accounting Treatment | Deducted from asset's original cost to determine depreciable amount. | Considered as a one-time recovery value, not always part of depreciation. |
| Timing | Estimated at asset acquisition, reviewed periodically. | Realized only when asset is disposed or sold as scrap. |
| Value Basis | Based on market value, usage, and asset condition predictions. | Based on material worth or resale price of parts. |
Understanding Residual Value in Car Depreciation
Residual value in car depreciation represents the estimated amount a vehicle is worth at the end of its useful life or lease term, reflecting factors like market demand, condition, and mileage. Accurate residual value assessment is crucial for calculating depreciation expense and determining lease payments or resale price. Unlike scrap value, which is the minimal worth of a car sold for parts or recycling, residual value considers the vehicle's overall remaining usefulness and marketability.
Defining Scrap Value: What It Means for Your Vehicle
Scrap value refers to the estimated amount a vehicle can be sold for at the end of its useful life, typically based on the weight and material worth rather than its operational condition. It represents the salvageable worth after depreciation has fully accounted for wear and tear, often influencing decisions in asset disposal and accounting. Understanding scrap value helps vehicle owners and businesses accurately assess total cost recovery and residual asset worth during depreciation calculations.
Key Differences Between Residual Value and Scrap Value
Residual value represents the estimated amount an asset will be worth at the end of its useful life, often used for calculating depreciation, while scrap value refers to the value of the asset when it is no longer usable and is sold for parts or recycling. Residual value impacts the depreciation expense in financial reporting, whereas scrap value is primarily concerned with the asset's disposal phase. Understanding the distinction ensures accurate asset valuation and correct depreciation calculations in accounting practices.
Factors Influencing Car Residual Value
Car residual value is influenced by factors such as brand reputation, vehicle condition, mileage, market demand, and economic trends. Maintenance history, accident records, and technological advancements in newer models also significantly impact the estimated residual value. Understanding these elements helps in accurately forecasting depreciation and determining the true worth of a car at the end of its useful life.
Determinants of Scrap Value in Vehicle Depreciation
Scrap value in vehicle depreciation is primarily determined by factors such as the metal content, market demand for recyclable materials, and the condition of the vehicle at the end of its useful life. Economic conditions and environmental regulations also influence scrap value by affecting recycling costs and processes. Estimating accurate scrap value helps in calculating more precise depreciation expenses and residual value forecasts.
How Depreciation Impacts Residual and Scrap Values
Depreciation reduces the book value of an asset over time, directly influencing its residual value, which represents the estimated worth after useful life. Scrap value, often considered a minimal salvage amount, may remain relatively fixed but contributes to calculating total depreciation expense. Accurate assessment of both residual and scrap values is essential for precise depreciation schedules and financial reporting.
Importance of Residual Value When Leasing a Car
Residual value is crucial in leasing a car because it determines the vehicle's estimated worth at the end of the lease term, directly impacting monthly lease payments. A higher residual value reduces depreciation expense, lowering lease costs and making leasing more affordable. Understanding residual value helps lessees make informed financial decisions and negotiate better lease agreements.
Maximizing Your Car’s Residual Value
Maximizing your car's residual value involves regular maintenance, keeping mileage low, and preserving the vehicle's condition to ensure it retains higher worth at the end of a lease or ownership period. Residual value represents the estimated market value after depreciation, while scrap value refers to the minimal worth if the car is sold for parts or recycling. Focusing on enhancing residual value can significantly reduce overall depreciation costs and improve resale or trade-in price.
When Does a Car Reach Its Scrap Value?
A car reaches its scrap value when its market worth declines to a point where it is only valuable for parts or materials, often due to extensive wear, mechanical failure, or outdated technology. This typically occurs after several years of use, depending on factors like mileage, maintenance, and accident history. At this stage, the residual value approaches the scrap value, signaling minimal economic benefit in continued operation or sale as a functional vehicle.
Residual Value vs Scrap Value: Which Matters More for Owners?
Residual value represents the estimated worth of an asset at the end of its useful life, directly impacting depreciation expense and tax calculations, while scrap value refers to the minimal amount recoverable from selling the asset for parts or recycling. For owners, residual value matters more because it influences financial planning, asset replacement strategies, and overall return on investment. Understanding residual value aids in accurate asset valuation and depreciation schedules, ensuring better decision-making compared to focusing solely on scrap value.
Residual Value vs Scrap Value Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com