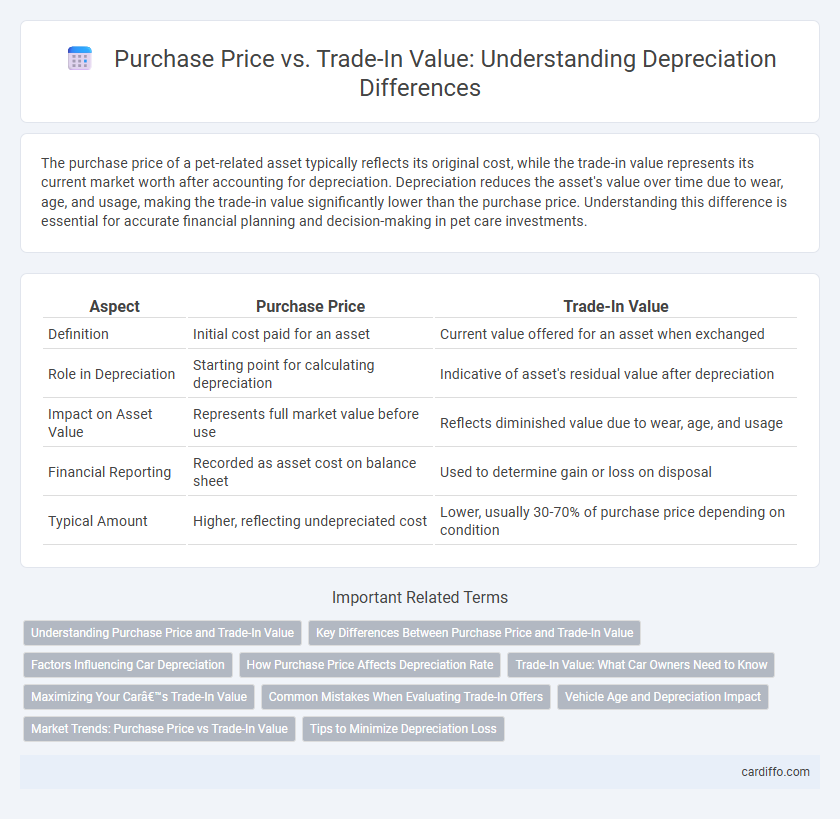
The purchase price of a pet-related asset typically reflects its original cost, while the trade-in value represents its current market worth after accounting for depreciation. Depreciation reduces the asset's value over time due to wear, age, and usage, making the trade-in value significantly lower than the purchase price. Understanding this difference is essential for accurate financial planning and decision-making in pet care investments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Purchase Price | Trade-In Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Initial cost paid for an asset | Current value offered for an asset when exchanged |
| Role in Depreciation | Starting point for calculating depreciation | Indicative of asset's residual value after depreciation |
| Impact on Asset Value | Represents full market value before use | Reflects diminished value due to wear, age, and usage |
| Financial Reporting | Recorded as asset cost on balance sheet | Used to determine gain or loss on disposal |
| Typical Amount | Higher, reflecting undepreciated cost | Lower, usually 30-70% of purchase price depending on condition |
Understanding Purchase Price and Trade-In Value
Understanding purchase price involves recognizing it as the initial amount paid to acquire an asset, which sets the baseline for calculating depreciation. Trade-in value represents the assessed worth of the asset when exchanging it for another, often lower than the original purchase price due to accumulated depreciation. Accurate comparison between purchase price and trade-in value is essential for evaluating the asset's current financial position and making informed decisions on replacement or sale.
Key Differences Between Purchase Price and Trade-In Value
Purchase price reflects the original cost paid to acquire an asset, often higher due to including taxes, fees, and dealer margins, while trade-in value represents the depreciated worth of the asset when exchanged, influenced by age, condition, and market demand. Depreciation significantly lowers trade-in value compared to purchase price, accounting for wear and usage over time. Understanding this difference is crucial for accurate financial planning and asset valuation in both personal and business contexts.
Factors Influencing Car Depreciation
Purchase price significantly impacts car depreciation, with higher initial costs often leading to greater absolute value loss over time. Trade-in value reflects current market demand, vehicle condition, and mileage, all crucial factors influencing depreciation rates. Other elements such as brand reputation, maintenance history, and technological advancements also shape the trade-in value and depreciation trajectory.
How Purchase Price Affects Depreciation Rate
The purchase price of a vehicle directly influences its depreciation rate, as higher-priced automobiles typically experience steeper initial depreciation percentages. Luxury cars or vehicles with premium features often lose value more quickly relative to their purchase price compared to economy models. Understanding the relationship between purchase cost and expected trade-in value helps consumers make informed decisions about long-term ownership expenses.
Trade-In Value: What Car Owners Need to Know
Trade-in value represents the amount a dealer offers for a vehicle when exchanging it for another car, significantly impacted by depreciation since the purchase price. Car owners should understand that trade-in value is typically lower than the original purchase price due to age, mileage, and condition factors that accelerate depreciation. Evaluating trade-in offers against private sale prices and current market trends can help owners maximize their vehicle's residual value.
Maximizing Your Car’s Trade-In Value
Maximizing your car's trade-in value involves understanding the impact of depreciation on both the purchase price and current market conditions. Maintaining regular service records and addressing minor repairs can help preserve the vehicle's value, ensuring better offers compared to heavily depreciated models. Researching trade-in offers from multiple dealerships enables you to leverage the difference between the original purchase price and current trade-in value for optimal financial returns.
Common Mistakes When Evaluating Trade-In Offers
Many consumers misjudge the value gap between purchase price and trade-in value, often expecting trade-in offers to reflect the original purchase cost rather than the vehicle's current market depreciation. Overlooking factors such as vehicle condition, mileage, and market demand leads to unrealistic trade-in expectations. Ignoring these key variables results in missed opportunities for better trade-in negotiations or selling alternatives.
Vehicle Age and Depreciation Impact
Vehicle age significantly influences depreciation, causing the trade-in value to decline sharply compared to the original purchase price. Newer vehicles retain a higher percentage of their purchase price due to slower depreciation rates, while older vehicles experience accelerated value loss. Understanding the correlation between vehicle age and depreciation impact is essential for accurately assessing trade-in value and making informed financial decisions.
Market Trends: Purchase Price vs Trade-In Value
Purchase price and trade-in value are influenced significantly by current market trends, which dictate vehicle demand and supply dynamics. Trade-in values often depreciate faster than purchase prices due to factors like mileage, model year, and overall market saturation of similar vehicles. Understanding these trends allows consumers to anticipate depreciation rates and make informed decisions about timing their vehicle purchases or trade-ins.
Tips to Minimize Depreciation Loss
Maximize resale value by maintaining your vehicle's condition through regular servicing and prompt repairs, as well-kept cars retain higher trade-in values. Opt for popular models and colors that have strong market demand to reduce rapid depreciation compared to niche or less sought-after vehicles. Document all maintenance and upgrades transparently to build buyer confidence and justify a trade-in value closer to the original purchase price.
Purchase Price vs Trade-In Value Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com