A depreciation schedule tracks the gradual reduction in value of tangible assets like machinery or vehicles over their useful life, while an amortization schedule applies to intangible assets such as patents or loans, spreading their cost or repayment over time. Depreciation schedules calculate expense based on asset wear and tear, whereas amortization schedules outline periodic payments that include both principal and interest or cost allocation. Understanding the differences between these schedules is crucial for accurate financial reporting and tax compliance.
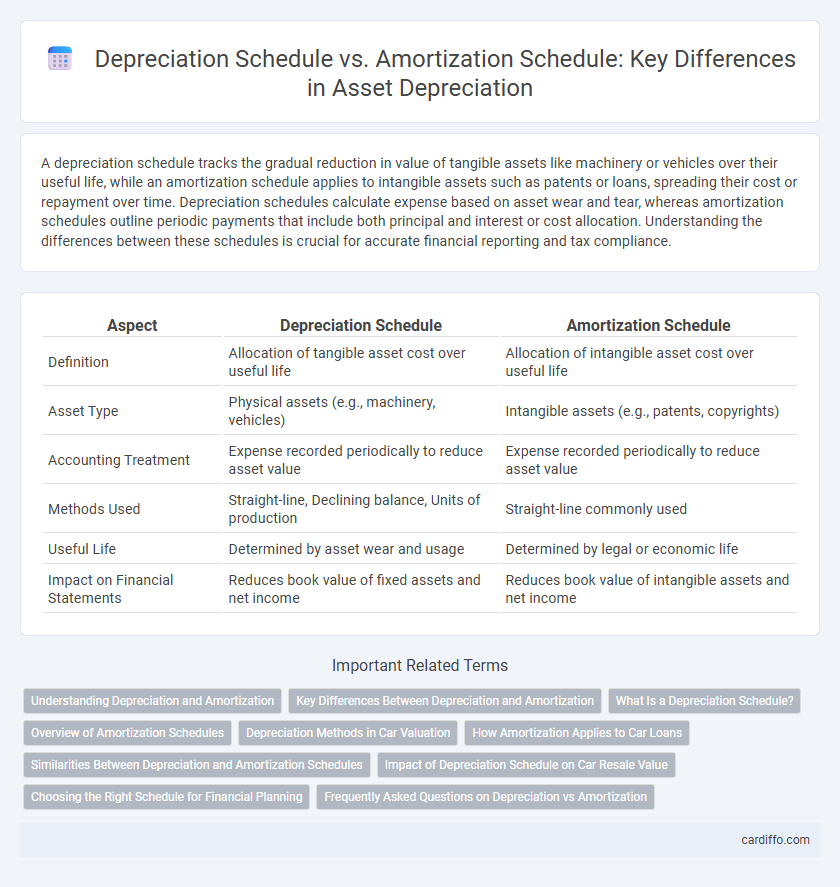
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Depreciation Schedule | Amortization Schedule |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allocation of tangible asset cost over useful life | Allocation of intangible asset cost over useful life |
| Asset Type | Physical assets (e.g., machinery, vehicles) | Intangible assets (e.g., patents, copyrights) |
| Accounting Treatment | Expense recorded periodically to reduce asset value | Expense recorded periodically to reduce asset value |
| Methods Used | Straight-line, Declining balance, Units of production | Straight-line commonly used |
| Useful Life | Determined by asset wear and usage | Determined by legal or economic life |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Reduces book value of fixed assets and net income | Reduces book value of intangible assets and net income |
Understanding Depreciation and Amortization
A depreciation schedule outlines the systematic allocation of the cost of tangible fixed assets over their useful life, reflecting asset wear and tear and reducing taxable income. An amortization schedule, on the other hand, pertains to intangible assets or loan repayments, detailing the gradual expense recognition or principal and interest payments over time. Understanding both schedules is essential for accurate financial reporting and effective asset management in accounting practices.
Key Differences Between Depreciation and Amortization
A depreciation schedule tracks the allocation of tangible asset costs over their useful lives, while an amortization schedule applies to intangible assets, spreading their expenses systematically. Depreciation impacts physical assets like machinery and vehicles, whereas amortization relates to non-physical assets such as patents and copyrights. Both schedules provide structured expense recognition for accurate financial reporting and tax purposes, but differ in the types of assets and applicable accounting methods.
What Is a Depreciation Schedule?
A depreciation schedule is a detailed table that outlines the systematic allocation of an asset's cost over its useful life, tracking annual depreciation expenses for accounting and tax purposes. It records key data such as the asset's original cost, accumulated depreciation, and book value at each period, ensuring compliance with accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS. This schedule plays a critical role in financial reporting by providing transparency and accuracy in reflecting asset value reduction over time.
Overview of Amortization Schedules
Amortization schedules outline the gradual repayment of intangible assets or loans over a fixed period, detailing principal and interest components for each payment. Unlike depreciation schedules, which allocate the cost of tangible assets over their useful lives, amortization schedules focus on reducing debt or intangible asset value systematically. These schedules provide clear timelines, payment amounts, and interest calculations, essential for accurate financial planning and reporting.
Depreciation Methods in Car Valuation
Depreciation methods in car valuation include straight-line, declining balance, and units of production, each affecting the depreciation schedule by determining how the vehicle's value decreases over time. The depreciation schedule outlines periodic expense allocation based on these methods, reflecting the car's wear and tear or usage. Unlike amortization schedules, which handle intangible assets, depreciation schedules specifically apply to tangible assets like vehicles to accurately track their decline in value.
How Amortization Applies to Car Loans
Amortization schedules for car loans outline the gradual repayment of principal and interest over time, providing a clear timeline for loan payoff. Unlike depreciation schedules that track a vehicle's loss in value, amortization emphasizes financial obligations and payment structure. Understanding amortization helps borrowers manage monthly payments and total interest costs effectively throughout the loan term.
Similarities Between Depreciation and Amortization Schedules
Depreciation schedules and amortization schedules both systematically allocate the cost of an asset over its useful life to match expenses with revenue generation periods. Each schedule uses a consistent method, such as straight-line or declining balance, to calculate periodic expense amounts, ensuring accurate financial reporting and tax compliance. Both schedules are essential for managing asset valuation, affecting balance sheet depreciation or amortization accounts and influencing cash flow planning.
Impact of Depreciation Schedule on Car Resale Value
A depreciation schedule systematically tracks the declining value of a vehicle over time, directly influencing its resale price by providing a clear historical record of its valuation. This schedule helps potential buyers assess the remaining useful life and market worth of the car, often resulting in more accurate pricing during resale. Unlike an amortization schedule, which pertains to loan repayment, the depreciation schedule specifically impacts car resale value by reflecting wear, usage, and age.
Choosing the Right Schedule for Financial Planning
A depreciation schedule tracks the allocation of tangible asset costs over their useful life, while an amortization schedule applies to intangible assets and loan repayments. Selecting the right schedule depends on the asset type and financial goals, ensuring accurate expense matching and cash flow management. Proper application of depreciation or amortization schedules enhances budgeting precision and tax compliance in financial planning.
Frequently Asked Questions on Depreciation vs Amortization
Depreciation schedules allocate the cost of tangible fixed assets over their useful life, reflecting wear and tear, while amortization schedules apply to intangible assets, spreading their purchase price across their estimated lifespan. Frequently asked questions often address the differences in asset types, tax implications, and calculation methods between depreciation and amortization. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses accurately report expenses and optimize tax deductions.
Depreciation Schedule vs Amortization Schedule Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com