A single-payment lease requires one lump sum payment upfront, offering simplicity and often lower total costs compared to multiple-payment leases. Multiple-payment leases spread payments over time, improving cash flow management and making the lease more affordable monthly. Choosing between the two depends on budget flexibility and financial planning preferences.
Table of Comparison
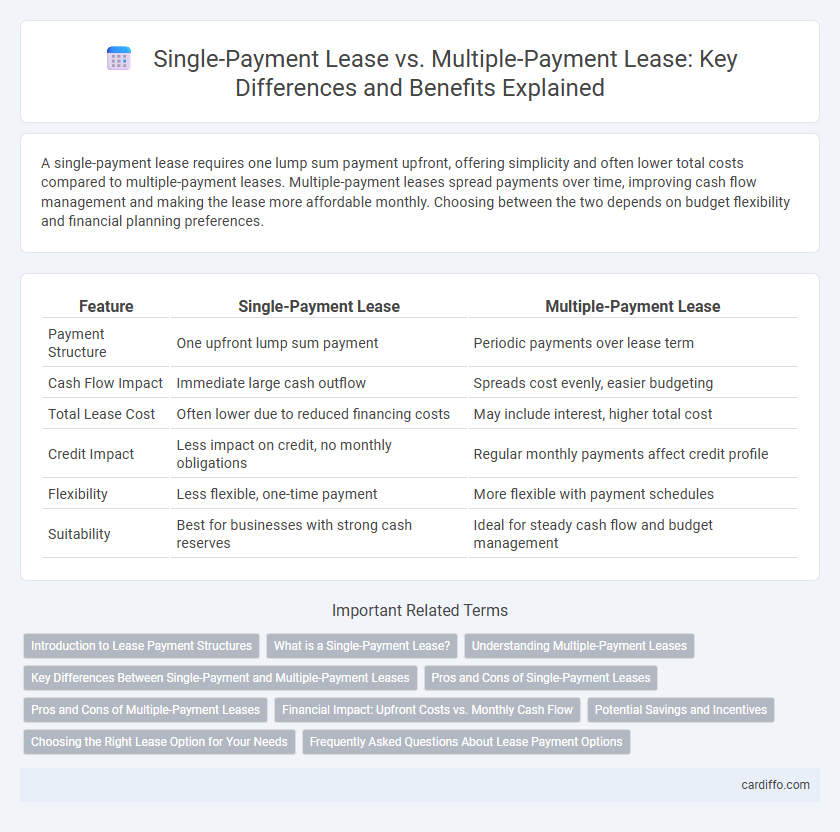
| Feature | Single-Payment Lease | Multiple-Payment Lease |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Structure | One upfront lump sum payment | Periodic payments over lease term |
| Cash Flow Impact | Immediate large cash outflow | Spreads cost evenly, easier budgeting |
| Total Lease Cost | Often lower due to reduced financing costs | May include interest, higher total cost |
| Credit Impact | Less impact on credit, no monthly obligations | Regular monthly payments affect credit profile |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, one-time payment | More flexible with payment schedules |
| Suitability | Best for businesses with strong cash reserves | Ideal for steady cash flow and budget management |
Introduction to Lease Payment Structures
Single-payment leases require the lessee to pay the entire lease amount upfront, often resulting in lower overall costs due to reduced interest charges. Multiple-payment leases distribute payments over the lease term, providing flexibility and easier cash flow management by breaking down the total cost into monthly or periodic installments. Understanding these payment structures is crucial for businesses and individuals to select the lease agreement that aligns with their financial strategy and cash flow requirements.
What is a Single-Payment Lease?
A Single-Payment Lease is a leasing option where the lessee makes one upfront payment covering the entire lease term instead of multiple installments. This type of lease often results in lower overall costs due to reduced interest and administrative fees compared to a Multiple-Payment Lease. It provides financial simplicity by eliminating monthly payments and consolidating lease expenses into a single transaction.
Understanding Multiple-Payment Leases
Multiple-payment leases involve spreading lease payments over a series of scheduled installments, typically monthly or quarterly, allowing lessees to manage cash flow more effectively throughout the lease term. Each payment often includes a portion of the asset's depreciation, interest charges, and sometimes taxes or fees, making budgeting predictable and flexible for individuals or businesses. Understanding the total cost, payment schedule, and terms of a multiple-payment lease is essential to compare it accurately against a single-payment lease and select the best financing option.
Key Differences Between Single-Payment and Multiple-Payment Leases
Single-payment leases require a lump sum payment upfront, covering the entire lease term's cost, which minimizes monthly financial obligations and often results in overall cost savings. Multiple-payment leases spread the total lease amount into regular monthly installments, offering improved cash flow management but potentially higher total expenses due to financing charges. Key differences include payment structure, financial impact, and potential benefits related to budgeting and cost efficiency.
Pros and Cons of Single-Payment Leases
Single-payment leases require a one-time upfront payment covering the entire lease term, offering lower monthly obligations and reduced administrative hassle compared to multiple-payment leases. They often result in cost savings through discounted lease rates and lower financing charges, but tie up a substantial amount of capital initially, reducing liquidity. Single-payment leases risk losing money if the vehicle is totaled early, as refunds are generally not proportional to remaining lease time.
Pros and Cons of Multiple-Payment Leases
Multiple-payment leases offer the advantage of spreading out expenses over time, enhancing affordability and preserving cash flow for lessees. These leases provide flexibility in budgeting but often come with higher total costs due to interest or finance charges embedded in monthly payments. However, the ongoing payment obligation can increase financial strain and complicate budgeting compared to a single-payment lease.
Financial Impact: Upfront Costs vs. Monthly Cash Flow
A Single-Payment Lease requires a large upfront payment, significantly reducing monthly cash outflows and improving monthly cash flow management. In contrast, a Multiple-Payment Lease spreads costs across regular monthly payments, resulting in manageable ongoing expenses but higher total interest over time. Businesses must weigh the immediate financial liquidity impact against long-term cash flow predictability when choosing between these lease structures.
Potential Savings and Incentives
Single-payment leases often provide significant cost savings by reducing or eliminating money factor interest and lease fees, resulting in a lower overall lease cost compared to multiple-payment leases. Leasing companies may offer exclusive incentives such as rebates or discounts for single-payment options that are not available with monthly payment plans. These financial benefits, combined with less administrative hassle, make single-payment leases an attractive choice for lessees seeking to minimize total lease expenses.
Choosing the Right Lease Option for Your Needs
Choosing between a single-payment lease and a multiple-payment lease depends on your cash flow, tax strategy, and budget flexibility. Single-payment leases offer the advantage of one upfront payment, which can reduce interest costs and simplify accounting, while multiple-payment leases spread costs over time, preserving liquidity and easing monthly budgeting. Evaluating your financial goals, vehicle usage, and potential tax benefits helps determine the best lease structure for maximizing both cost efficiency and cash management.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lease Payment Options
Single-payment leases require one upfront payment covering the entire lease term, often resulting in lower overall costs and simplified budgeting compared to multiple-payment leases, which involve periodic payments throughout the lease duration. Frequently asked questions include inquiries about the benefits of single-payment leases for cash flow management and whether interest rates differ between the two payment structures. Leasing experts emphasize evaluating total cost, tax implications, and personal financial preferences to determine the optimal lease payment option.
Single-Payment Lease vs Multiple-Payment Lease Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com