A lease buyout allows the lessee to purchase the vehicle at the end of the lease term, often at a predetermined price, which can be beneficial if the vehicle's market value exceeds the buyout amount. A lease return involves simply handing the vehicle back to the leasing company, ending the obligation but potentially incurring fees for excess mileage or wear and tear. Evaluating the condition of the vehicle and comparing buyout costs to current market value helps determine the most cost-effective option.
Table of Comparison
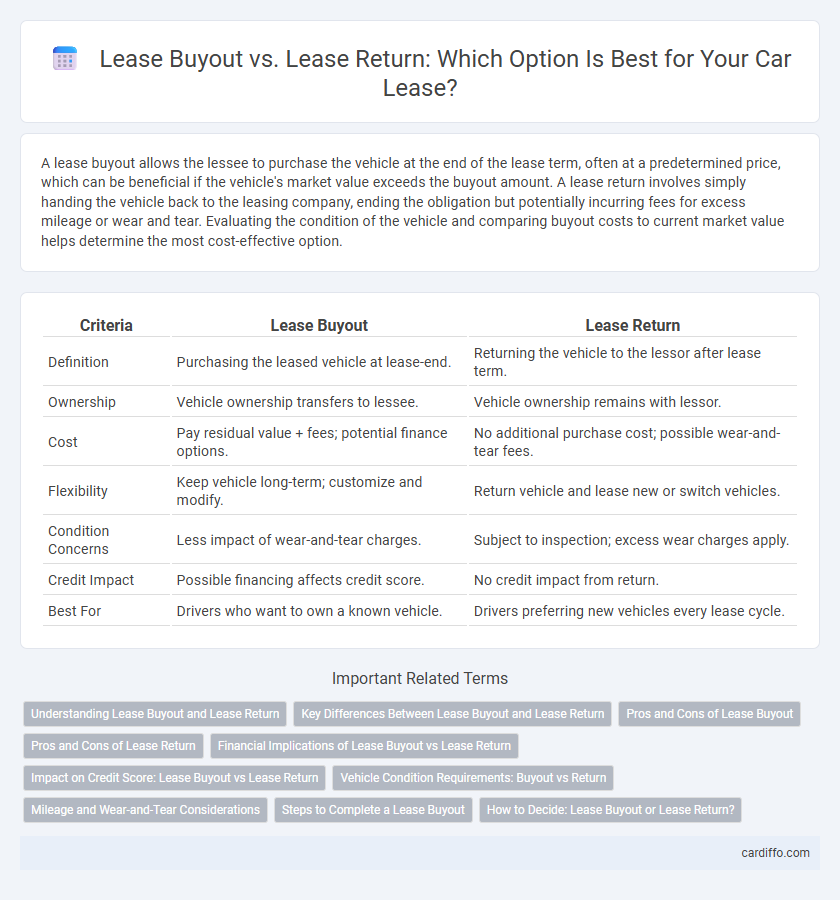
| Criteria | Lease Buyout | Lease Return |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Purchasing the leased vehicle at lease-end. | Returning the vehicle to the lessor after lease term. |
| Ownership | Vehicle ownership transfers to lessee. | Vehicle ownership remains with lessor. |
| Cost | Pay residual value + fees; potential finance options. | No additional purchase cost; possible wear-and-tear fees. |
| Flexibility | Keep vehicle long-term; customize and modify. | Return vehicle and lease new or switch vehicles. |
| Condition Concerns | Less impact of wear-and-tear charges. | Subject to inspection; excess wear charges apply. |
| Credit Impact | Possible financing affects credit score. | No credit impact from return. |
| Best For | Drivers who want to own a known vehicle. | Drivers preferring new vehicles every lease cycle. |
Understanding Lease Buyout and Lease Return
Understanding lease buyout involves purchasing the leased vehicle at the end or during the lease term, allowing the lessee to own the car outright and potentially avoid excess wear-and-tear fees. Lease return requires the lessee to return the vehicle to the dealership, where it undergoes inspection for damage or mileage overage, which may result in additional charges. Evaluating residual value, buyout price, and lease-end conditions is critical for deciding between lease buyout and lease return options.
Key Differences Between Lease Buyout and Lease Return
Lease buyout involves purchasing the leased vehicle outright, allowing ownership transfer and potential long-term cost savings, while lease return requires surrendering the vehicle at lease end without ownership rights. Key differences include financial obligations; lease buyout requires paying the residual value plus taxes and fees, whereas lease return may involve excess mileage or damage charges. Lease buyout offers flexibility for keeping or selling the vehicle, contrasting with lease return, which mandates returning the vehicle and possibly leasing or buying a new one.
Pros and Cons of Lease Buyout
Lease buyout allows vehicle owners to purchase their leased car at a predetermined price, offering the advantage of ownership without the hassle of searching for a new vehicle. This option provides potential equity if the buyout price is lower than the car's market value, but it may require a significant upfront cost or financing approval. However, the downside includes the risk of inheriting maintenance costs and depreciation beyond the lease term, unlike lease return, which avoids these long-term ownership expenses.
Pros and Cons of Lease Return
Lease returns offer the advantage of avoiding depreciation risk since the vehicle is simply returned at the end of the term, eliminating concerns about resale value. However, lease returns may incur additional fees for excess mileage, wear and tear, or damage, potentially increasing the overall cost. Choosing lease return provides simplicity but requires careful inspection to minimize unexpected charges.
Financial Implications of Lease Buyout vs Lease Return
Lease buyout typically requires an upfront payment or financing of the vehicle's residual value, which can lead to higher monthly costs but offers potential equity if the car's market value exceeds the buyout price. Lease return involves no additional payments beyond the lease-end fees, avoiding large immediate expenses but may incur charges for excess mileage or wear and tear. Choosing between buyout and return depends on comparing total cost implications, including residual value, market conditions, and potential penalties.
Impact on Credit Score: Lease Buyout vs Lease Return
Lease buyout typically has a neutral or slightly positive impact on credit score, as it involves paying off the lease balance and potentially financing a new loan, which can improve credit history if managed well. Lease return may temporarily lower credit utilization by ending monthly payments, but missed payments or lease-end fees can negatively affect credit standing. Timely payments and clear account closure during either process play crucial roles in maintaining or improving credit scores.
Vehicle Condition Requirements: Buyout vs Return
Vehicle condition requirements differ significantly between lease buyout and lease return. Lease buyout allows the lessee to keep the vehicle regardless of wear and tear, while lease return requires the vehicle to meet specific condition standards to avoid excessive wear charges. Proper documentation of the vehicle's current condition is essential in both processes to ensure fair assessment.
Mileage and Wear-and-Tear Considerations
Lease buyout allows lessees to purchase the vehicle, often avoiding excess mileage and wear-and-tear fees that typically apply at lease return. Lease return requires careful inspection, as exceeding mileage limits or damaging the vehicle can result in significant penalties. Evaluating current mileage against lease terms and assessing the vehicle's condition helps determine whether buying out the lease or returning the car minimizes additional costs.
Steps to Complete a Lease Buyout
Completing a lease buyout involves several key steps: first, review your lease agreement to determine the buyout price and any associated fees, which often includes the vehicle's residual value plus any remaining payments. Next, secure financing if necessary, as lease buyouts can be paid in cash or financed through a loan. Finally, contact the leasing company to negotiate the buyout terms, complete the required paperwork, and arrange for payment to transfer ownership and title of the vehicle.
How to Decide: Lease Buyout or Lease Return?
Evaluating lease buyout versus lease return hinges on factors such as the vehicle's current market value, lease-end conditions, and your long-term vehicle needs. If the buyout price is below or close to the market value and you desire to keep the car, purchasing can be cost-effective; however, returning the lease might be preferable to avoid maintenance costs or if you want a new model. Thoroughly reviewing lease agreements and assessing financial implications will help determine the best option for your situation.
Lease Buyout vs Lease Return Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com