Lease agreements typically include a mileage allowance, setting a maximum number of miles you can drive annually without extra fees. Exceeding this mileage results in mileage overage charges, which can significantly increase the total cost of the lease. Monitoring your mileage closely helps avoid unexpected expenses and keeps your lease budget predictable.
Table of Comparison
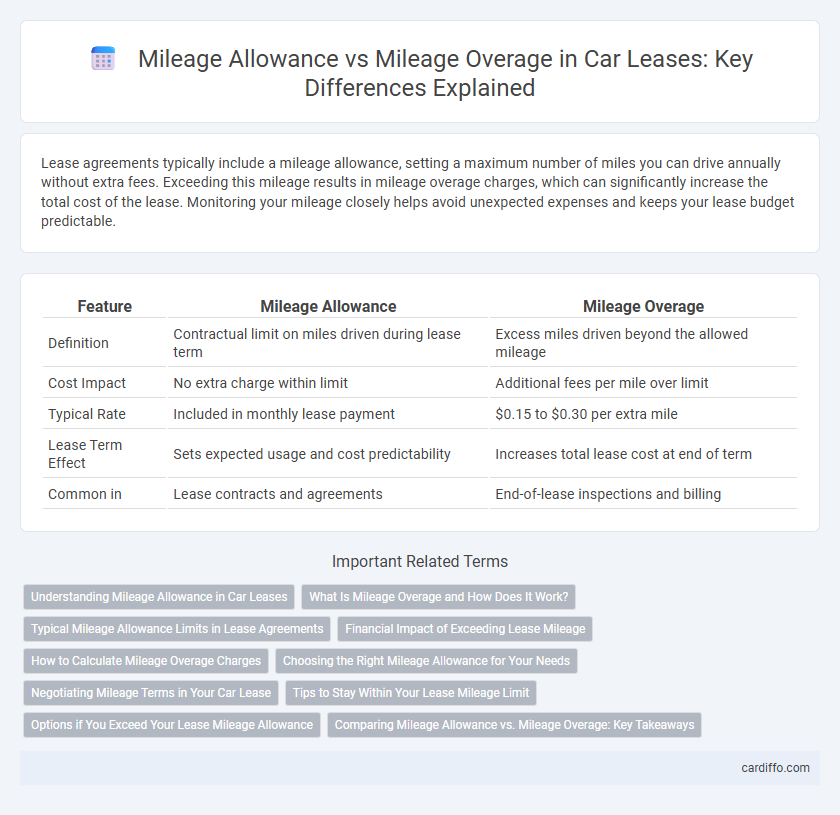
| Feature | Mileage Allowance | Mileage Overage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contractual limit on miles driven during lease term | Excess miles driven beyond the allowed mileage |
| Cost Impact | No extra charge within limit | Additional fees per mile over limit |
| Typical Rate | Included in monthly lease payment | $0.15 to $0.30 per extra mile |
| Lease Term Effect | Sets expected usage and cost predictability | Increases total lease cost at end of term |
| Common in | Lease contracts and agreements | End-of-lease inspections and billing |
Understanding Mileage Allowance in Car Leases
Mileage allowance in car leases specifies the maximum number of miles a lessee can drive annually without incurring extra fees, typically ranging from 10,000 to 15,000 miles per year. Exceeding this limit results in mileage overage charges, which can cost between 15 and 30 cents per additional mile, significantly increasing the total lease cost. Accurately estimating your annual mileage helps avoid unexpected expenses and ensures adherence to lease terms.
What Is Mileage Overage and How Does It Work?
Mileage overage occurs when a lessee drives more miles than the predetermined limit set in the lease agreement, resulting in additional charges. These excess miles are typically billed at a fixed per-mile rate detailed in the lease contract, often ranging from 15 to 25 cents per mile. Understanding mileage overage helps lessees avoid unexpected fees and better manage their lease expenses by estimating actual driving habits against allowed mileage.
Typical Mileage Allowance Limits in Lease Agreements
Typical mileage allowance limits in lease agreements range from 10,000 to 15,000 miles per year, designed to accommodate average driving habits without incurring additional costs. Exceeding the mileage allowance results in mileage overage charges, often set between 15 to 30 cents per mile, significantly increasing the total lease cost. Understanding mileage limits and potential overage fees is crucial to managing lease expenses and avoiding unexpected charges at lease-end.
Financial Impact of Exceeding Lease Mileage
Exceeding the mileage allowance specified in a lease agreement results in significant financial penalties, often calculated as a fixed rate per mile over the limit, typically ranging from $0.15 to $0.30 per mile. This overage can lead to unexpected costs that increase the total lease expense substantially, impacting the lessee's budget. Managing mileage within the agreed allowance is crucial to avoid these additional charges and maintain lease affordability.
How to Calculate Mileage Overage Charges
Mileage overage charges are calculated by subtracting the allowed mileage stipulated in the lease agreement from the actual miles driven. The resulting excess miles are then multiplied by the contract's specified per-mile overage rate, which typically ranges from $0.15 to $0.30 per mile. Accurate tracking of odometer readings at lease inception and termination ensures precise determination of mileage overage fees.
Choosing the Right Mileage Allowance for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate mileage allowance in a lease agreement is crucial to avoid costly mileage overage fees, which can significantly increase the total leasing cost. Assess your average annual driving habits accurately to match the mileage allowance with your usage patterns, ensuring you stay within limits and maintain the vehicle's residual value. Opting for a higher allowance may raise monthly payments but provides flexibility, while a lower allowance reduces costs but risks penalties for excess miles.
Negotiating Mileage Terms in Your Car Lease
Negotiating mileage terms in your car lease is crucial to balance mileage allowance and mileage overage costs. Standard allowances typically range from 10,000 to 15,000 miles per year, with overage charges averaging $0.15 to $0.25 per mile. Securing a higher mileage allowance upfront can prevent expensive penalties, especially if your driving habits exceed the lease agreement limits.
Tips to Stay Within Your Lease Mileage Limit
Tracking your mileage regularly helps avoid unexpected fees by staying within your lease mileage allowance. Use a reliable mileage log app or device to monitor daily driving and plan trips efficiently to minimize excess miles. Opt for alternative transportation methods like carpooling or public transit when possible to reduce total mileage and prevent costly mileage overage charges.
Options if You Exceed Your Lease Mileage Allowance
Exceeding your lease mileage allowance often triggers additional charges calculated per mile, typically ranging from $0.15 to $0.30. Leasing companies may offer options such as pre-purchasing extra miles at a discounted rate or negotiating a higher mileage cap upfront to avoid costly overage fees. Reviewing the lease agreement carefully and discussing mileage flexibility with the lessor can help manage and minimize unexpected expenses.
Comparing Mileage Allowance vs. Mileage Overage: Key Takeaways
Mileage allowance defines the maximum miles a lessee can drive without incurring extra charges, typically set between 10,000 to 15,000 miles annually depending on the lease agreement. Mileage overage occurs when the lessee exceeds this limit, resulting in fees that often range from $0.15 to $0.30 per additional mile driven. Understanding the cost implications of mileage overage compared to the benefits of a higher mileage allowance helps lessees avoid unexpected expenses and select lease terms that best match their driving habits.
Mileage allowance vs mileage overage Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com