The EGR valve functionality is crucial for recirculating exhaust gases to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions and improve engine efficiency, whereas an EGR valve bypass disables this recirculation, often leading to increased emissions and potential legal issues. Maintaining a properly working EGR valve ensures optimal exhaust gas management and compliance with emission standards. Bypassing the EGR valve can result in engine performance issues, higher pollutant output, and accelerated engine wear.
Table of Comparison
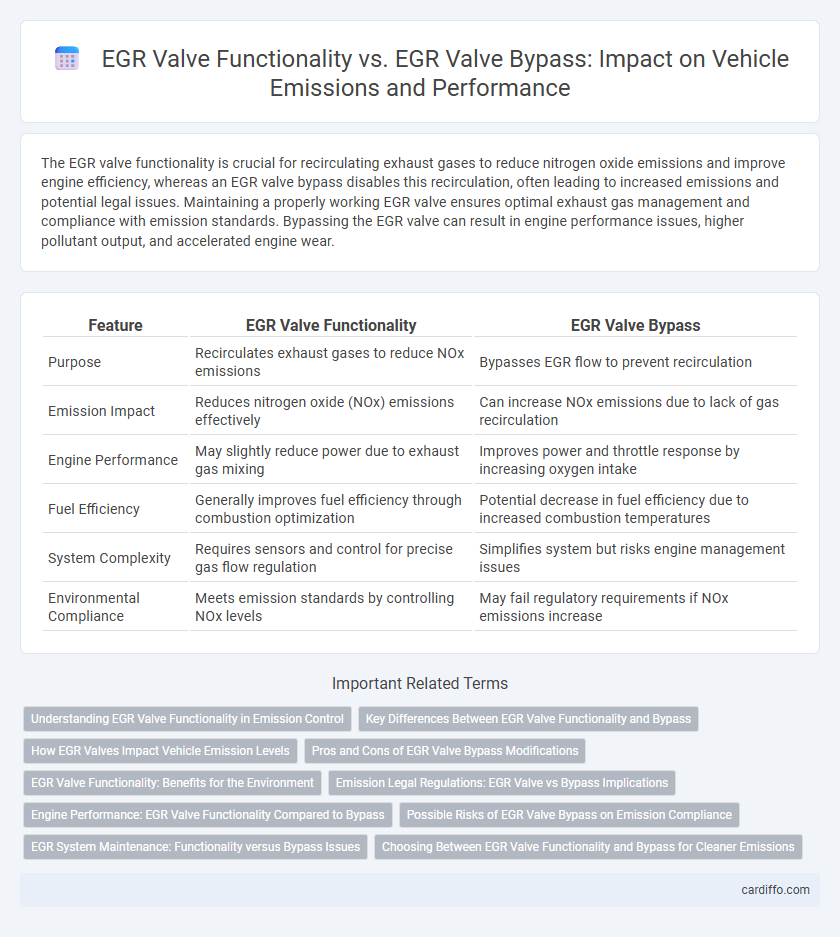
| Feature | EGR Valve Functionality | EGR Valve Bypass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Recirculates exhaust gases to reduce NOx emissions | Bypasses EGR flow to prevent recirculation |
| Emission Impact | Reduces nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions effectively | Can increase NOx emissions due to lack of gas recirculation |
| Engine Performance | May slightly reduce power due to exhaust gas mixing | Improves power and throttle response by increasing oxygen intake |
| Fuel Efficiency | Generally improves fuel efficiency through combustion optimization | Potential decrease in fuel efficiency due to increased combustion temperatures |
| System Complexity | Requires sensors and control for precise gas flow regulation | Simplifies system but risks engine management issues |
| Environmental Compliance | Meets emission standards by controlling NOx levels | May fail regulatory requirements if NOx emissions increase |
Understanding EGR Valve Functionality in Emission Control
EGR valve functionality plays a crucial role in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by recirculating a portion of exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber, lowering combustion temperatures and limiting pollutant formation. In contrast, bypassing the EGR valve disrupts this controlled recirculation, often resulting in increased NOx emissions and potential non-compliance with emission regulations. Understanding how the EGR valve modulates exhaust flow enables precise emission control and optimizes engine performance while minimizing environmental impact.
Key Differences Between EGR Valve Functionality and Bypass
EGR valve functionality regulates exhaust gas recirculation to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating a controlled amount of exhaust gases into the intake manifold, which lowers combustion temperatures. In contrast, EGR valve bypass allows exhaust gases to bypass the valve, often leading to higher emissions and potential engine performance issues. Key differences include emission control effectiveness, engine temperature management, and impact on fuel efficiency, with proper EGR valve operation ensuring optimal emission reduction and engine performance.
How EGR Valves Impact Vehicle Emission Levels
EGR valves recirculate a portion of exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber, reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by lowering combustion temperatures. In contrast, an EGR valve bypass disables this recirculation, leading to increased NOx emissions and reduced emission control efficiency. Proper EGR valve functionality is critical for compliance with emission standards and improving air quality by minimizing harmful pollutants.
Pros and Cons of EGR Valve Bypass Modifications
EGR valve bypass modifications enhance engine performance by allowing increased airflow and reducing exhaust gas recirculation, leading to higher power output and improved throttle response. However, bypassing the EGR valve compromises emission control by increasing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and potentially causing the vehicle to fail regulatory inspections. While these modifications benefit performance enthusiasts, they pose environmental drawbacks and legal challenges due to non-compliance with emissions standards.
EGR Valve Functionality: Benefits for the Environment
EGR valve functionality reduces nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by recirculating exhaust gases back into the engine intake, lowering combustion temperatures and minimizing pollutant formation. This process improves air quality and helps vehicles comply with stringent emissions standards such as Euro 6 and EPA Tier 3 regulations. Maintaining a properly functioning EGR valve supports sustainable transportation and reduces environmental impact by decreasing harmful emissions that contribute to smog and acid rain.
Emission Legal Regulations: EGR Valve vs Bypass Implications
EGR valve functionality plays a critical role in reducing NOx emissions by recirculating exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber, ensuring compliance with stringent emission legal regulations such as Euro 6 and EPA Tier 3 standards. Bypassing the EGR valve disrupts this process, leading to increased nitrogen oxide emissions and potential violations of environmental laws, resulting in fines and vehicle non-compliance. Maintaining a properly functioning EGR valve is essential for meeting legal emission limits and avoiding regulatory penalties.
Engine Performance: EGR Valve Functionality Compared to Bypass
Proper EGR valve functionality reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating exhaust gases, enhancing combustion efficiency and maintaining engine performance. Bypassing the EGR valve may improve short-term horsepower and throttle response, but it often leads to increased engine temperatures and potential long-term damage. Maintaining an operational EGR valve ensures optimal air-fuel mixture and prevents excessive engine wear while supporting emission standards compliance.
Possible Risks of EGR Valve Bypass on Emission Compliance
EGR valve bypass compromises the recirculation of exhaust gases, leading to increased nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and potential non-compliance with emission regulations such as Euro 6 and EPA standards. This modification disrupts the engine's emission control system, risking legal penalties and vehicle inspection failures. Maintaining functional EGR valves ensures proper exhaust gas recirculation, optimal combustion, and adherence to stringent emission limits.
EGR System Maintenance: Functionality versus Bypass Issues
The EGR valve plays a critical role in reducing nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber, improving emission control and engine efficiency. Bypassing the EGR valve may temporarily resolve clogging or malfunction but often leads to increased emissions, engine knocking, and potential long-term damage to the emission control system. Regular maintenance of the EGR system, including cleaning and functionality checks, ensures optimal performance and compliance with emission standards, avoiding the negative consequences associated with EGR valve bypass.
Choosing Between EGR Valve Functionality and Bypass for Cleaner Emissions
EGR valve functionality plays a critical role in reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by recirculating exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber, lowering combustion temperatures. Bypassing the EGR valve may increase engine performance but leads to higher NOx emissions and non-compliance with emissions regulations. Selecting functional EGR valves ensures adherence to environmental standards and promotes cleaner air by effectively minimizing harmful pollutants.
EGR Valve Functionality vs EGR Valve Bypass Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com