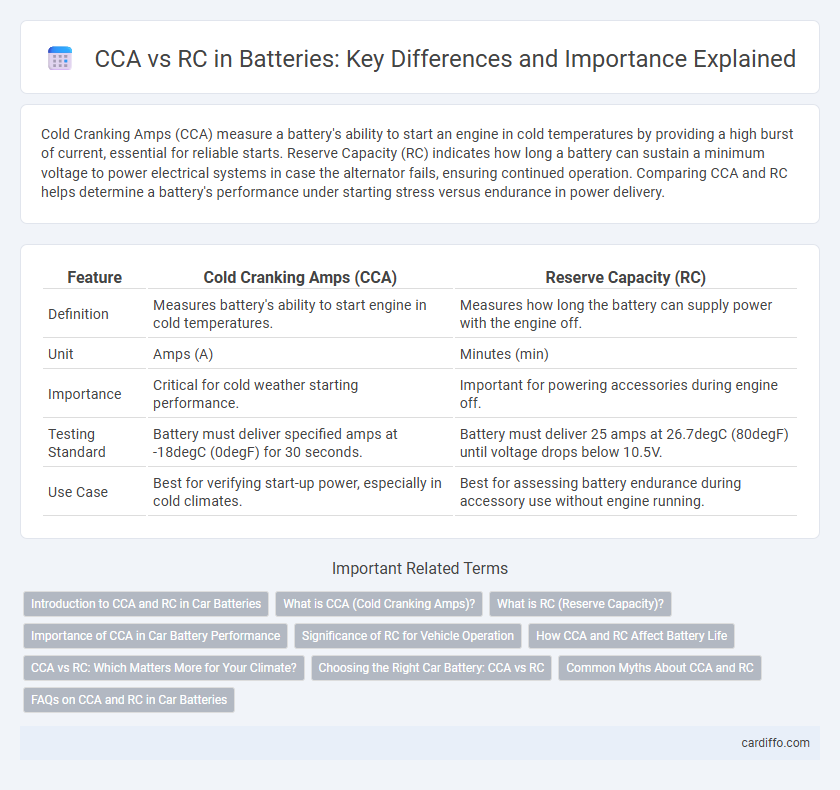
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by providing a high burst of current, essential for reliable starts. Reserve Capacity (RC) indicates how long a battery can sustain a minimum voltage to power electrical systems in case the alternator fails, ensuring continued operation. Comparing CCA and RC helps determine a battery's performance under starting stress versus endurance in power delivery.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) | Reserve Capacity (RC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures battery's ability to start engine in cold temperatures. | Measures how long the battery can supply power with the engine off. |
| Unit | Amps (A) | Minutes (min) |
| Importance | Critical for cold weather starting performance. | Important for powering accessories during engine off. |
| Testing Standard | Battery must deliver specified amps at -18degC (0degF) for 30 seconds. | Battery must deliver 25 amps at 26.7degC (80degF) until voltage drops below 10.5V. |
| Use Case | Best for verifying start-up power, especially in cold climates. | Best for assessing battery endurance during accessory use without engine running. |
Introduction to CCA and RC in Car Batteries
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measures a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by delivering a high burst of power for 30 seconds at 0degF. Reserve Capacity (RC) indicates how long a fully charged battery can supply a continuous 25-amp current before dropping below 10.5 volts, reflecting its endurance under non-starting conditions. Understanding CCA and RC helps in selecting car batteries tailored for cold climates and prolonged electrical use, ensuring reliable performance and longevity.
What is CCA (Cold Cranking Amps)?
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measures a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by indicating the number of amps a 12-volt battery can deliver at 0degF for 30 seconds while maintaining a voltage of at least 7.2 volts. CCA is a critical specification for automotive batteries, especially in cold climates, as it directly impacts the vehicle's starting performance during winter. Higher CCA ratings signify better starting power and reliability in freezing conditions, ensuring consistent engine ignition.
What is RC (Reserve Capacity)?
Reserve Capacity (RC) measures the number of minutes a fully charged battery can sustain a 25-amp draw before its voltage drops below 10.5 volts, indicating its ability to provide power during engine startup or electrical load failures. It is a critical metric for assessing battery endurance in vehicles, especially for maintaining essential systems when the alternator is not supplying power. Understanding RC helps consumers select batteries that ensure reliable performance over extended periods under high load conditions.
Importance of CCA in Car Battery Performance
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) is a critical measurement that indicates a car battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by delivering a high burst of current. A higher CCA rating ensures reliable engine starts during winter, preventing issues caused by thickened engine oil and reduced battery efficiency. While Reserve Capacity (RC) measures how long a battery can supply power without the engine running, CCA remains the paramount factor for immediate engine starting performance in cold weather conditions.
Significance of RC for Vehicle Operation
Reserve Capacity (RC) measures the time a battery can supply a vehicle with a continuous 25-amp discharge before voltage drops below 10.5 volts, reflecting how long the battery can power essential functions without engine power. A higher RC ensures reliable operation of critical systems such as lighting, infotainment, and safety electronics during engine off periods or unexpected alternator failure. Unlike Cold Cranking Amps (CCA), which focus on starting power, RC is crucial for maintaining vehicle operation and preventing power loss during extended engine-off conditions.
How CCA and RC Affect Battery Life
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) indicate a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, directly impacting short-term performance under extreme conditions. Reserve Capacity (RC) measures how long a battery can supply power if the alternator fails, affecting overall battery endurance and long-term reliability. Balancing high CCA with sufficient RC ensures optimal battery life by supporting both immediate starting power and extended energy supply.
CCA vs RC: Which Matters More for Your Climate?
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, making it crucial for harsh winter climates where engine starting power is vital. Reserve Capacity (RC) indicates how long a battery can run on its own power without the engine, which matters more in hot climates where electrical loads like cooling systems are high. Choosing between CCA and RC depends on your climate; prioritize CCA for cold environments and RC for warmer regions to ensure reliable battery performance.
Choosing the Right Car Battery: CCA vs RC
Choosing the right car battery involves understanding Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) and Reserve Capacity (RC), as CCA measures the battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures while RC indicates how long the battery can power the vehicle without the engine running. High CCA is essential for reliable starts in winter climates, whereas a high RC is crucial for running electrical components during engine off times or in emergencies. Evaluating vehicle needs and environmental conditions ensures optimal battery performance and longevity.
Common Myths About CCA and RC
Many believe Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) alone determine a battery's starting power, but Reserve Capacity (RC) is equally crucial for sustained energy delivery during engine off periods. Another misconception is that higher CCA means better overall battery performance, while a balanced rating with adequate RC ensures reliability under various conditions. Understanding the distinct roles of CCA and RC helps avoid purchasing a battery that excels in short bursts but lacks endurance for longer power demands.
FAQs on CCA and RC in Car Batteries
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measures a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by delivering a high burst of current, while Reserve Capacity (RC) indicates how long a battery can supply power if the alternator fails. Car batteries with higher CCA ratings ensure reliable starts in cold climates, and greater RC values provide extended power for electrical components during engine-off conditions. Common FAQs include understanding how CCA impacts starting performance and how RC affects battery life during power outages or heavy accessory use.
CCA vs RC Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com