Trickle charge provides a slow, steady current that maintains a battery's full capacity without overcharging, ideal for long-term battery care in pets' electronics. Fast charge delivers a high current quickly, enabling rapid power replenishment but can generate heat and reduce battery lifespan if used frequently. Choosing between trickle charge and fast charge depends on balancing the need for speed and battery health.
Table of Comparison
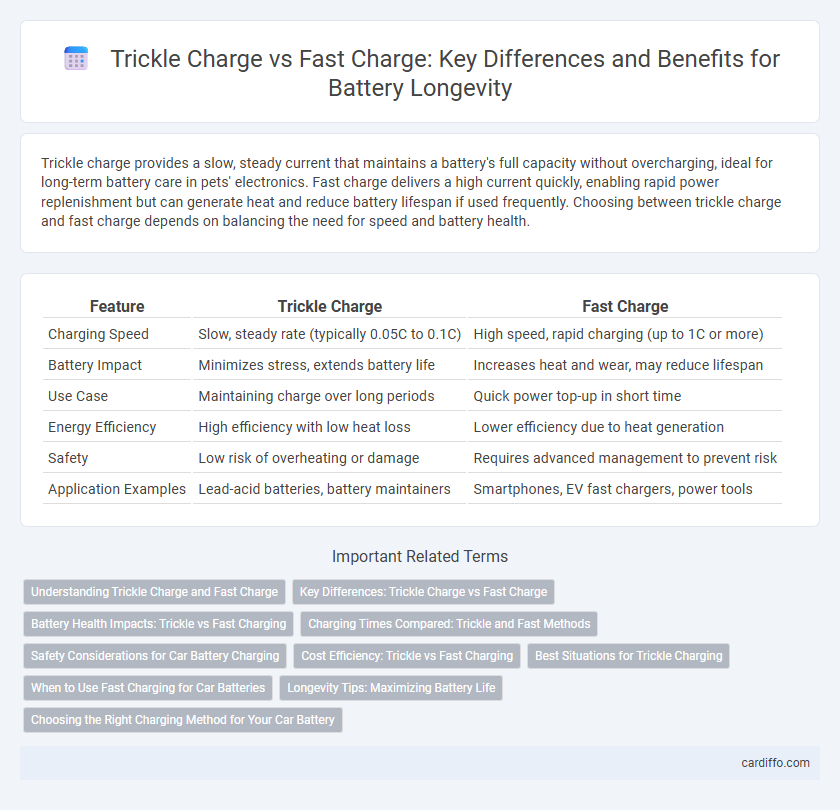
| Feature | Trickle Charge | Fast Charge |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | Slow, steady rate (typically 0.05C to 0.1C) | High speed, rapid charging (up to 1C or more) |
| Battery Impact | Minimizes stress, extends battery life | Increases heat and wear, may reduce lifespan |
| Use Case | Maintaining charge over long periods | Quick power top-up in short time |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency with low heat loss | Lower efficiency due to heat generation |
| Safety | Low risk of overheating or damage | Requires advanced management to prevent risk |
| Application Examples | Lead-acid batteries, battery maintainers | Smartphones, EV fast chargers, power tools |
Understanding Trickle Charge and Fast Charge
Trickle charge delivers a low, steady current to maintain a battery's full capacity without overcharging, primarily used for long-term battery maintenance in lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries. Fast charge provides a high current to quickly replenish battery capacity, significantly reducing charging time but potentially increasing heat and stress on battery cells. Understanding the differences is vital for optimizing battery lifespan, as trickle charging is suited for preservation while fast charging is ideal for rapid energy replenishment in devices like electric vehicles and portable electronics.
Key Differences: Trickle Charge vs Fast Charge
Trickle charge maintains a low, steady current to safely keep a battery fully charged without overcharging, ideal for long-term maintenance and preserving battery lifespan. Fast charge delivers a high current to quickly restore battery capacity, significantly reducing charging time but generating more heat and potentially shortening battery life if used frequently. Understanding these key differences helps optimize battery performance and longevity based on specific charging needs.
Battery Health Impacts: Trickle vs Fast Charging
Trickle charging maintains battery health by delivering a low, steady current, minimizing heat generation and reducing chemical stress, which extends battery lifespan. Fast charging increases battery temperature and accelerates wear due to rapid ion movement, potentially causing capacity loss and shorter cycle life. Optimizing charge rates according to battery chemistry and usage patterns can significantly mitigate degradation while balancing charging speed and longevity.
Charging Times Compared: Trickle and Fast Methods
Trickle charging typically requires several hours to fully recharge a battery by delivering a low, steady current that prevents overcharging and prolongs battery life. Fast charging significantly reduces charging times to under an hour by supplying a higher current, but this method can generate more heat and potentially shorten battery lifespan if used frequently. Comparing charge durations, trickle charge suits maintenance and long-term health, while fast charge optimizes quick energy replenishment for immediate use.
Safety Considerations for Car Battery Charging
Trickle charging delivers a low, steady current that minimizes the risk of overheating and extends car battery life by maintaining a safe voltage level. Fast charging supplies a higher current that can quickly restore battery capacity but increases the risk of thermal runaway and electrolyte evaporation if not properly monitored. Ensuring the use of compatible chargers with built-in safety features like temperature regulation and automatic shutoff is critical to prevent damage and maintain battery health.
Cost Efficiency: Trickle vs Fast Charging
Trickle charging offers greater cost efficiency by using lower power levels, reducing energy consumption and extending battery lifespan, which lowers replacement and maintenance costs over time. Fast charging consumes more electricity rapidly and can accelerate battery degradation, leading to higher long-term expenses despite shorter charging durations. Choosing trickle charging balances operational costs with battery longevity, making it ideal for devices with frequent, low-demand use.
Best Situations for Trickle Charging
Trickle charging is best suited for maintaining battery health in vehicles or devices that are not used frequently, as it supplies a low, steady current to keep the battery fully charged without overcharging. It is ideal for long-term storage of lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries, preventing sulfation and capacity loss. Trickle charging ensures optimal battery lifespan and performance in applications such as classic cars, emergency backup systems, and seasonal equipment.
When to Use Fast Charging for Car Batteries
Fast charging for car batteries is ideal when you need a rapid replenishment of energy, such as during long trips or unexpected power depletion. It delivers a high current that significantly reduces charging time while maintaining battery health through advanced charging technology. Fast charging is recommended when time efficiency is crucial and the battery's state of charge is low but not deeply discharged.
Longevity Tips: Maximizing Battery Life
Trickle charging maintains battery voltage at a low, steady rate, significantly reducing heat generation and extending battery lifespan by preventing overcharging. Fast charging delivers high current quickly, which can increase battery temperature and accelerate capacity degradation over time. To maximize battery longevity, use trickle charging when possible and reserve fast charging for urgent needs, ensuring proper cooling and avoiding prolonged high-voltage exposure.
Choosing the Right Charging Method for Your Car Battery
Selecting the appropriate charging method for your car battery depends on its condition and your time constraints. Trickle charging delivers a low, steady current ideal for maintaining battery health and preventing overcharging during long periods of inactivity. Fast charging supplies a higher current to quickly restore battery power but risks overheating and reducing battery lifespan if used frequently or improperly.
Trickle Charge vs Fast Charge Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com